Abstract
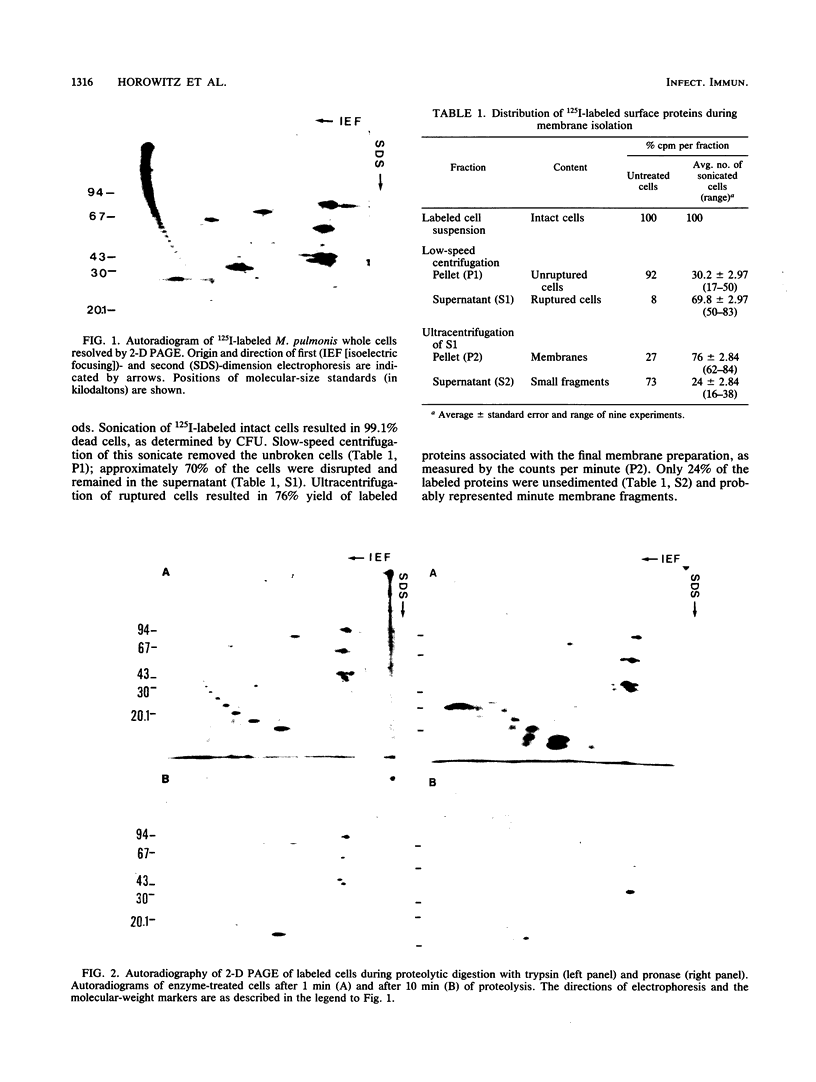
Labeling of Mycoplasma pulmonis cells by iodination with the Bolton-Hunter reagent was shown to efficiently label membrane-associated proteins without significant loss of viability. Labeled proteins proven to be surface exposed by differential proteolytic digestion were analyzed by autoradiography of two-dimensional polyacrylamide gel electrophoresis (PAGE), and seven labeled major polypeptides were identified. To identify all the membrane-associated antigens, pure membranes were isolated by using the surface-labeled proteins as markers. Analysis of the isolated membranes by autoradiography of both sodium dodecyl sulfate-PAGE and the two-dimensional PAGE indicated that the labeled surface proteins were retained in the pure membranes; by immunoblotting with sera from naturally infected animals, these surface proteins were shown to be the predominant antigens recognized by the host during natural infection.
Full text
PDF




Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Alexander A. G., Kenny G. E. Characterization of membrane and cytoplasmic antigens of Mycoplasma arginini by two-dimensional (crossed) immunoelectrophoresis. Infect Immun. 1977 Jan;15(1):313–321. doi: 10.1128/iai.15.1.313-321.1977. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Amar A., Rottem S., Razin S. Characterization of the mycoplasma membrane proteins. IV. Disposition of proteins in the membrane. Biochim Biophys Acta. 1974 Jun 13;352(2):228–244. doi: 10.1016/0005-2736(74)90214-4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bender W. W., Garan H., Berg H. C. Proteins of the human erythrocyte membrane as modified by pronase. J Mol Biol. 1971 Jun 28;58(3):783–797. doi: 10.1016/0022-2836(71)90040-4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bolton A. E., Hunter W. M. The labelling of proteins to high specific radioactivities by conjugation to a 125I-containing acylating agent. Biochem J. 1973 Jul;133(3):529–539. doi: 10.1042/bj1330529. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Habeeb A. F. Comparative studies on radiolabeling of lysozyme by iodination and reductive methylation. J Immunol Methods. 1983 Dec 16;65(1-2):27–39. doi: 10.1016/0022-1759(83)90301-0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Howard C. J., Taylor G. Variation in the virulence of strains of Mycoplasma pulmonis related to susceptibility to killing by macrophages in vivo. J Gen Microbiol. 1979 Oct;114(2):289–294. doi: 10.1099/00221287-114-2-289. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kahane I., Razin S. pH-dependent changes in density of plasma membranes of growing Mycoplasma laidlawii cells. FEBS Lett. 1970 Oct 16;10(4):261–264. doi: 10.1016/0014-5793(70)80643-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- LOWRY O. H., ROSEBROUGH N. J., FARR A. L., RANDALL R. J. Protein measurement with the Folin phenol reagent. J Biol Chem. 1951 Nov;193(1):265–275. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Laemmli U. K. Cleavage of structural proteins during the assembly of the head of bacteriophage T4. Nature. 1970 Aug 15;227(5259):680–685. doi: 10.1038/227680a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Langone J. J. Radioiodination by use of the Bolton-Hunter and related reagents. Methods Enzymol. 1980;70(A):221–247. doi: 10.1016/s0076-6879(80)70052-6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lindsey J. R., Baker H. J., Overcash R. G., Cassell G. H., Hunt C. E. Murine chronic respiratory disease. Significance as a research complication and experimental production with Mycoplasma pulmonis. Am J Pathol. 1971 Sep;64(3):675–708. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Loeb M. R., Smith D. H. Lactoperoxidase and Iodo-Gen-catalyzed iodination labels inner and outer membrane proteins of Haemophilus influenzae. J Bacteriol. 1983 Jul;155(1):443–446. doi: 10.1128/jb.155.1.443-446.1983. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Marchalonis J. J., Cone R. E., Santer V. Enzymic iodination. A probe for accessible surface proteins of normal and neoplastic lymphocytes. Biochem J. 1971 Oct;124(5):921–927. doi: 10.1042/bj1240921. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Markwell M. A., Fox C. F. Surface-specific iodination of membrane proteins of viruses and eucaryotic cells using 1,3,4,6-tetrachloro-3alpha,6alpha-diphenylglycoluril. Biochemistry. 1978 Oct 31;17(22):4807–4817. doi: 10.1021/bi00615a031. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Minion F. C., Brown M. B., Cassell G. H. Identification of cross-reactive antigens between Mycoplasma pulmonis and Mycoplasma arthritidis. Infect Immun. 1984 Jan;43(1):115–121. doi: 10.1128/iai.43.1.115-121.1984. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Minion F. C., Cassell G. H., Pnini S., Kahane I. Multiphasic interactions of Mycoplasma pulmonis with erythrocytes defined by adherence and hemagglutination. Infect Immun. 1984 May;44(2):394–400. doi: 10.1128/iai.44.2.394-400.1984. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Morowitz H. J., Terry T. M. Characterization of the plasma membrane of Mycoplasma laidlawii. V. Effects of selective removal of protein and lipid. Biochim Biophys Acta. 1969 Jul 15;183(2):276–294. doi: 10.1016/0005-2736(69)90084-4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Naot Y., Merchav S., Ben-David E., Ginsburg H. Mitogenic activity of Mycoplasma pulmonis. I. Stimulation of rat B and T lymphocytes. Immunology. 1979 Mar;36(3):399–406. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- O'Farrell P. H. High resolution two-dimensional electrophoresis of proteins. J Biol Chem. 1975 May 25;250(10):4007–4021. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Phillips D. R., Morrison M. Exposed protein on the intact human erythrocyte. Biochemistry. 1971 May 11;10(10):1766–1771. doi: 10.1021/bi00786a006. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Pollock M. E., Bonner S. V. Comparison of undefined medium and its dialyzable fraction for growth of Mycoplasma. J Bacteriol. 1969 Feb;97(2):522–525. doi: 10.1128/jb.97.2.522-525.1969. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sullivan K. H., Williams R. P. Use of iodo-gen and iodine-125 to label the outer membrane proteins of whole cells of Neisseria gonorrhoeae. Anal Biochem. 1982 Mar 1;120(2):254–258. doi: 10.1016/0003-2697(82)90344-x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Towbin H., Staehelin T., Gordon J. Electrophoretic transfer of proteins from polyacrylamide gels to nitrocellulose sheets: procedure and some applications. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1979 Sep;76(9):4350–4354. doi: 10.1073/pnas.76.9.4350. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wallach D. F. The dispositions of proteins in the plasma membranes of animal cells: analytical approaches using controlled peptidolysis and protein labels. Biochim Biophys Acta. 1972 Feb 14;265(1):61–83. doi: 10.1016/0304-4157(72)90019-6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wise G. E., Shienvold F. L., Rubin R. W. Effects of pronase and concanavalin A upon the freeze-etch morphology of cell membranes of intact human erythrocytes. J Cell Sci. 1978 Apr;30:63–76. doi: 10.1242/jcs.30.1.63. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]