Abstract
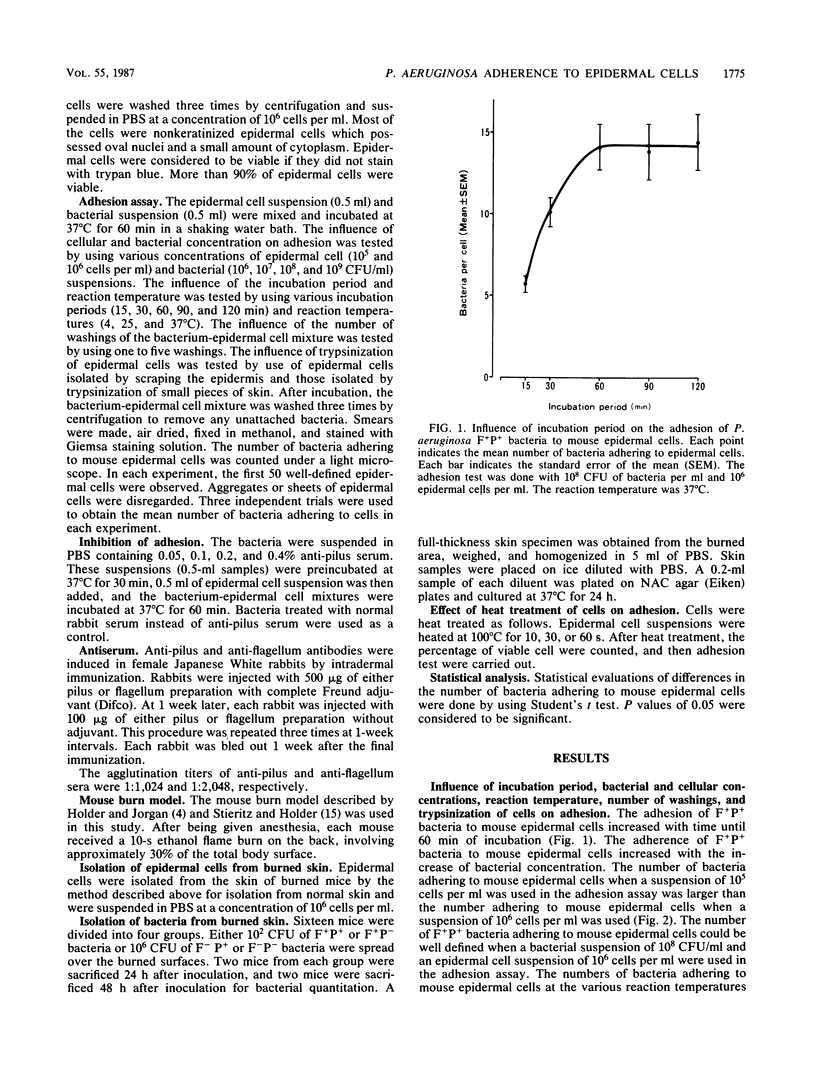
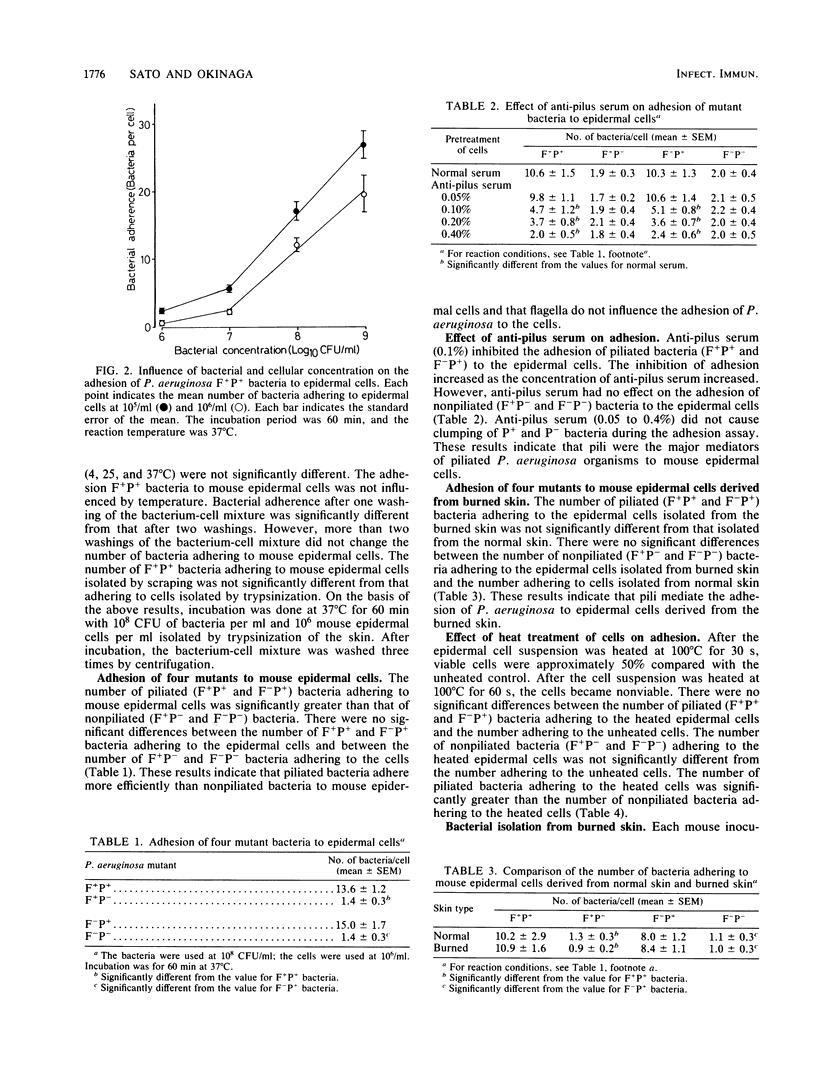
Pili have been demonstrated to be the adhesins of Pseudomonas aeruginosa for mouse epidermal cells. The mechanisms of adhesion of P. aeruginosa to mouse epidermal cells was studied by using four mutants derived from a single strain: flagellated and piliated (F+P+), flagellated and nonpiliated (F+P-), nonflagellated and piliated (F-P+), and nonflagellated and nonpiliated (F-P-) mutants. F+P+ and F-P+ bacteria efficiently adhered to mouse epidermal cells, while F+P- and F-P- bacteria hardly adhered to mouse epidermal cells. The number of F+P+ bacteria that adhered to mouse epidermal cells was almost the same as that of F-P+ bacteria. The number of F+P- bacteria that adhered to mouse epidermal cells was almost the same as that of F-P- bacteria. The adhesion of P+ (F+P+ and F-P+) bacteria was inhibited by antipilus serum, while that of P- (F+P- and F-P-) bacteria was not inhibited by antipilus serum. There were no significant differences between the number of bacteria adhering to mouse epidermal cells isolated from normal skin and those adhering to cells isolated from burned skin. Heating of the mouse epidermal cell suspension had no effect on the adhesion of P. aeruginosa. These results suggest that pili mediate the adhesion of P. aeruginosa to mouse epidermal cells and that P. aeruginosa adheres efficiently to mouse epidermal cells despite the loss of cell viability caused by burning.
Full text
PDF


Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Fischer S. M., Viaje A., Mills G. D., Slaga T. J. Explant methods for epidermal cell culture. Methods Cell Biol. 1980;21A:207–227. doi: 10.1016/s0091-679x(08)60768-2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Fujita H., Yamaguchi S., Taira T., Iino T. A simple method for the isolation of flagellar shape mutants in Salmonella. J Gen Microbiol. 1981 Jul;125(1):213–216. doi: 10.1099/00221287-125-1-213. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Higuchi J. H., Johanson W. G., Jr The relationship between adherence of Pseudomonas aeruginosa to upper respiratory cells in vitro and susceptibility to colonization in vivo. J Lab Clin Med. 1980 May;95(5):698–705. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Holder I. A., Jogan M. Enhanced survival in burned mice treated with antiserum prepared against normal and burned skin. J Trauma. 1971 Dec;11(12):1041–1046. doi: 10.1097/00005373-197112000-00008. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- MacMillan B. G. Infections following burn injury. Surg Clin North Am. 1980 Feb;60(1):185–196. doi: 10.1016/s0039-6109(16)42043-8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Okamoto R., Takai S., Yanagawa R., Sato H. Isolation of non-piliated clone of Corynebacterium renale strain 115. Jpn J Vet Res. 1981 Oct;29(3-4):79–82. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ramphal R., Pier G. B. Role of Pseudomonas aeruginosa mucoid exopolysaccharide in adherence to tracheal cells. Infect Immun. 1985 Jan;47(1):1–4. doi: 10.1128/iai.47.1.1-4.1985. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ramphal R., Pyle M. Adherence of mucoid and nonmucoid Pseudomonas aeruginosa to acid-injured tracheal epithelium. Infect Immun. 1983 Jul;41(1):345–351. doi: 10.1128/iai.41.1.345-351.1983. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ramphal R., Pyle M. Evidence for mucins and sialic acid as receptors for Pseudomonas aeruginosa in the lower respiratory tract. Infect Immun. 1983 Jul;41(1):339–344. doi: 10.1128/iai.41.1.339-344.1983. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ramphal R., Sadoff J. C., Pyle M., Silipigni J. D. Role of pili in the adherence of Pseudomonas aeruginosa to injured tracheal epithelium. Infect Immun. 1984 Apr;44(1):38–40. doi: 10.1128/iai.44.1.38-40.1984. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rheinwald J. G. Serial cultivation of normal human epidermal keratinocytes. Methods Cell Biol. 1980;21A:229–254. doi: 10.1016/s0091-679x(08)60769-4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sato H., Yanagawa R., Fukuyama H. Adhesion of Corynebacterium renale, Corynebacterium pilosum, and Corynebacterium cystitidis to bovine urinary bladder epithelial cells of various ages and levels of differentiation. Infect Immun. 1982 Jun;36(3):1242–1245. doi: 10.1128/iai.36.3.1242-1245.1982. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Stephens D. S., McGee Z. A. Attachment of Neisseria meningitidis to human mucosal surfaces: influence of pili and type of receptor cell. J Infect Dis. 1981 Apr;143(4):525–532. doi: 10.1093/infdis/143.4.525. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Stieritz D. D., Holder I. A. Experimental studies of the pathogenesis of infections due to Pseudomonas aeruginosa: description of a burned mouse model. J Infect Dis. 1975 Jun;131(6):688–691. doi: 10.1093/infdis/131.6.688. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Takai S., Yanagawa R., Kitamura Y. pH-dependent adhesion of piliated Corynebacterium renale to bovine bladder epithelial cells. Infect Immun. 1980 Jun;28(3):669–674. doi: 10.1128/iai.28.3.669-674.1980. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wevers P., Picken R., Schmidt G., Jann B., Jann K., Golecki J. R., Kist M. Characterization of pili associated with Escherichia coli O18ac. Infect Immun. 1980 Aug;29(2):685–691. doi: 10.1128/iai.29.2.685-691.1980. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Woods D. E., Bass J. A., Johanson W. G., Jr, Straus D. C. Role of adherence in the pathogenesis of Pseudomonas aeruginosa lung infection in cystic fibrosis patients. Infect Immun. 1980 Dec;30(3):694–699. doi: 10.1128/iai.30.3.694-699.1980. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Woods D. E., Straus D. C., Johanson W. G., Jr, Berry V. K., Bass J. A. Role of pili in adherence of Pseudomonas aeruginosa to mammalian buccal epithelial cells. Infect Immun. 1980 Sep;29(3):1146–1151. doi: 10.1128/iai.29.3.1146-1151.1980. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]


