Abstract
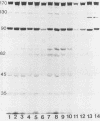
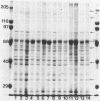
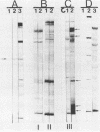
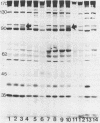
To determine whether antigenic variation in protein antigens of Mycoplasma pneumoniae occurred over time, 12 isolates obtained from pneumonia patients over a 10-year period (1964 to 1974) were compared by immunoblotting (Western blotting) against acute and convalescent human serum samples obtained from the same patients. The strains selected were isolated from patients who had low anti-lipid complement-fixing antibody titers in their acute-phase serum samples and high titers in their convalescent-phase serum samples. The polypeptide composition of the strains was closely similar by protein staining even when compared with prototype FH-Liu. On immunoblotting, all strains showed five bands (170, 130, 90, 45, and 35 kilodaltons [kDa]) which were stained more intensely by convalescent-phase than by acute-phase specimens. A sixth band (62 kDa) was detected by the conjugate alone. In FH-Liu, one band (110 kDa) was prominently stained by convalescent-phase specimens; this band was much less apparent in all of the clinical isolates. Two isolates possessed an additional band (92 kDa) which was stained more prominently by some but not all convalescent-phase specimens. Because of its known antigenic relationships and culture similarities, Mycoplasma genitalium was used for comparison. More polypeptides of M. genitalium than of M. pneumoniae were recognized by acute-phase serum samples, and 4 of 12 convalescent-phase serum samples showed increases in antibodies to certain M. genitalium polypeptides. However, these reactive polypeptides did not correspond in molecular mass to polypeptides recognized in M. pneumoniae; thus the signature profile of human convalescent-phase specimens with M. pneumoniae was distinct. These five polypeptides, individually or in combination, are especially promising for use in detection of human serum antibodies by enzyme-linked immunosorbent assay because they were found in all M. pneumoniae isolates tested.
Full text
PDF
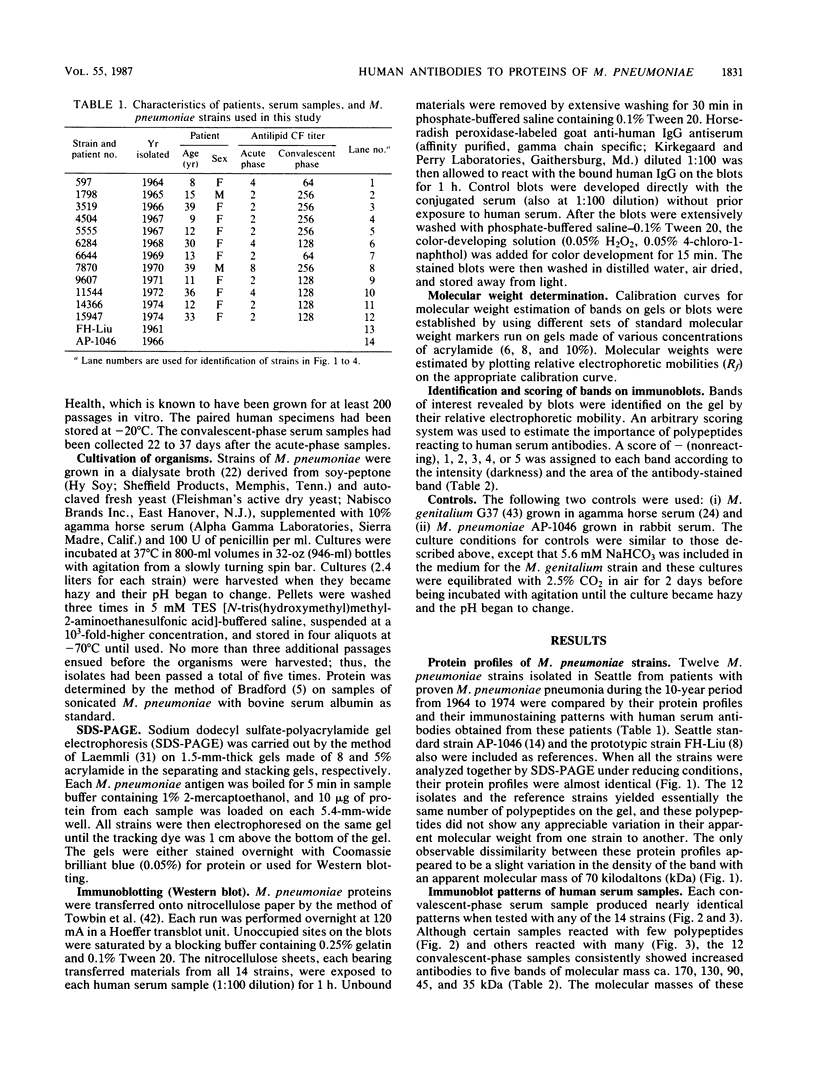
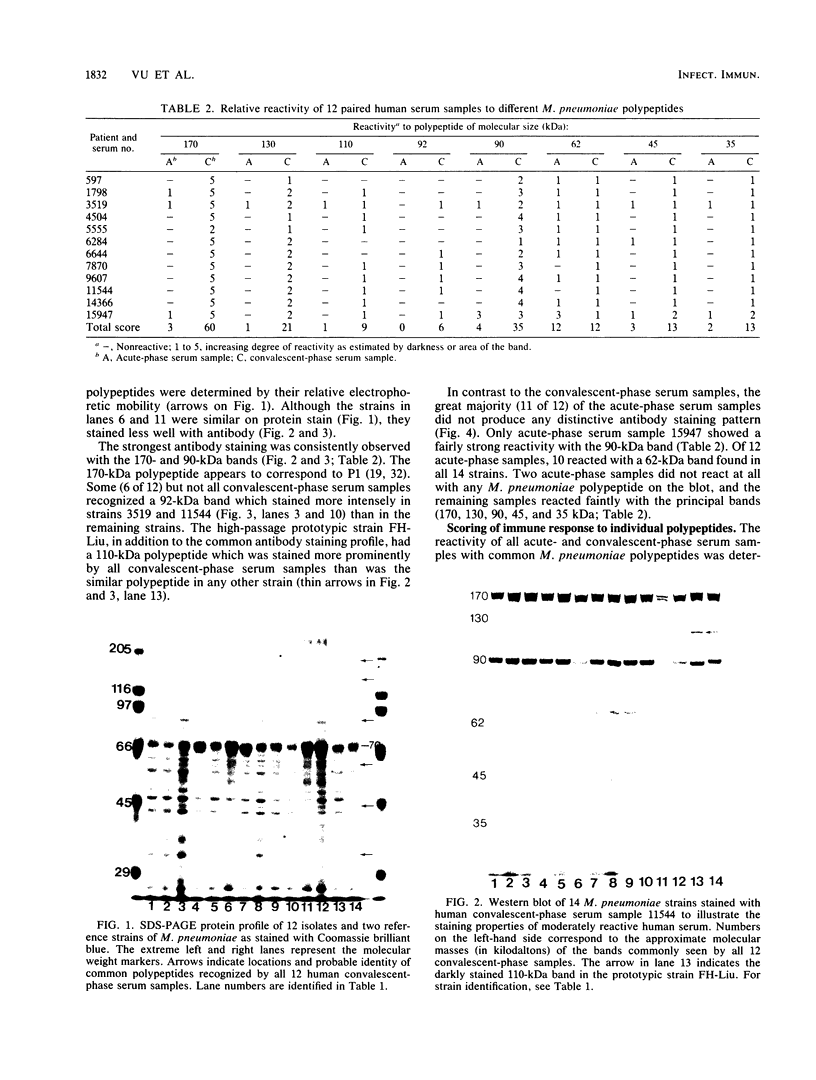
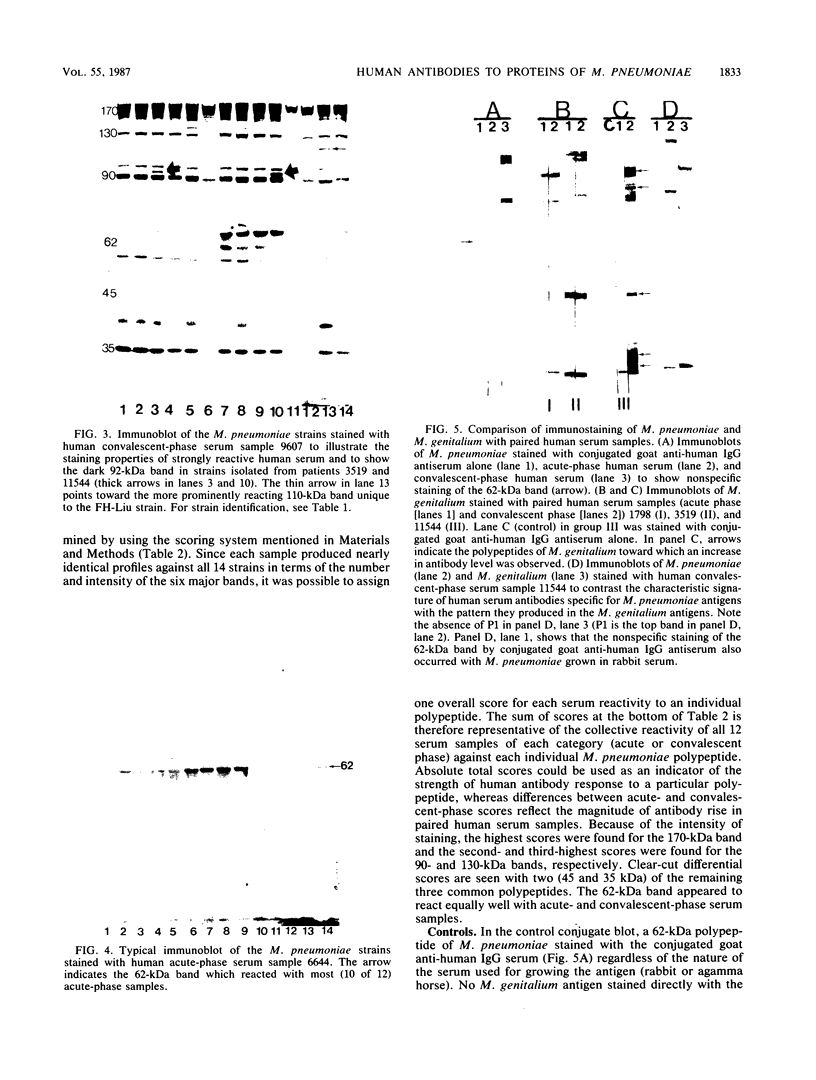



Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Alexander E. R., Foy H. M., Kenny G. E., Kronmal R. A., McMahan R., Clarke E. R., MacColl W. A., Grayston J. T. Pneumonia due to Mycoplasma pneumoniae. Its incidence in the membership of a co-operative medical group. N Engl J Med. 1966 Jul 21;275(3):131–136. doi: 10.1056/NEJM196607212750303. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Assaad F., Gispen R., Kleemola M., Syrůcek L., Esteves K. Neurological diseases associated with viral and Mycoplasma pneumoniae infections. Bull World Health Organ. 1980;58(2):297–311. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Baseman J. B., Cole R. M., Krause D. C., Leith D. K. Molecular basis for cytadsorption of Mycoplasma pneumoniae. J Bacteriol. 1982 Sep;151(3):1514–1522. doi: 10.1128/jb.151.3.1514-1522.1982. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Baseman J. B., Drouillard D. L., Leith D. K., Tully J. G. Absence of Mycoplasma pneumoniae cytadsorption protein P1 in Mycoplasma genitalium and Mycoplasma gallisepticum. Infect Immun. 1984 Mar;43(3):1103–1105. doi: 10.1128/iai.43.3.1103-1105.1984. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bradford M. M. A rapid and sensitive method for the quantitation of microgram quantities of protein utilizing the principle of protein-dye binding. Anal Biochem. 1976 May 7;72:248–254. doi: 10.1006/abio.1976.9999. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- CHANOCK R. M., HAYFLICK L., BARILE M. F. Growth on artificial medium of an agent associated with atypical pneumonia and its identification as a PPLO. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1962 Jan 15;48:41–49. doi: 10.1073/pnas.48.1.41. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Cassell G. H., Cole B. C. Mycoplasmas as agents of human disease. N Engl J Med. 1981 Jan 8;304(2):80–89. doi: 10.1056/NEJM198101083040204. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Chandler D. K., Razin S., Stephens E. B., Harasawa R., Barile M. F. Genomic and phenotypic analyses of Mycoplasma pneumoniae strains. Infect Immun. 1982 Nov;38(2):604–609. doi: 10.1128/iai.38.2.604-609.1982. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Clyde W. A., Jr, Hu P. C. Antigenic determinants of the attachment protein of Mycoplasma pneumoniae shared by other pathogenic Mycoplasma species. Infect Immun. 1986 Feb;51(2):690–692. doi: 10.1128/iai.51.2.690-692.1986. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Clyde W. A., Jr Mycoplasma pneumoniae respiratory disease symposium: summation and significance. Yale J Biol Med. 1983 Sep-Dec;56(5-6):523–527. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Clyde W. A., Jr Neurological syndromes and mycoplasmal infections. Arch Neurol. 1980 Feb;37(2):65–66. doi: 10.1001/archneur.1980.00500510023001. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- ENNY G. E., GRAYSTON J. T. EATON PLEUROPNEUMONIA-LIKE ORGANISM (MYCOPLASMA PNEUMONIAE) COMPLEMENT-FIXING ANTIGEN: EXTRACTION WITH ORGANIC SOLVENTS. J Immunol. 1965 Jul;95:19–25. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Foy H. M., Kenny G. E., Cooney M. K., Allan I. D. Long-term epidemiology of infections with Mycoplasma pneumoniae. J Infect Dis. 1979 Jun;139(6):681–687. doi: 10.1093/infdis/139.6.681. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Foy H. M., Kenny G. E., McMahan R., Mansy A. M., Grayston J. T. Mycoplasma pneumoniae pneumonia in an urban area. Five years of surveillance. JAMA. 1970 Nov 30;214(9):1666–1672. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gale J. L., Kenny G. E. Complement dependent killing of Mycoplasma pneumoniae by antibody: kinetics of the reaction. J Immunol. 1970 May;104(5):1175–1183. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hu P. C., Cole R. M., Huang Y. S., Graham J. A., Gardner D. E., Collier A. M., Clyde W. A., Jr Mycoplasma pneumoniae infection: role of a surface protein in the attachment organelle. Science. 1982 Apr 16;216(4543):313–315. doi: 10.1126/science.6801766. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hu P. C., Huang C. H., Collier A. M., Clyde W. A., Jr Demonstration of antibodies to Mycoplasma pneumoniae attachment protein in human sera and respiratory secretions. Infect Immun. 1983 Jul;41(1):437–439. doi: 10.1128/iai.41.1.437-439.1983. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hu P. C., Huang C. H., Huang Y. S., Collier A. M., Clyde W. A., Jr Demonstration of multiple antigenic determinants on Mycoplasma pneumoniae attachment protein by monoclonal antibodies. Infect Immun. 1985 Oct;50(1):292–296. doi: 10.1128/iai.50.1.292-296.1985. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hu P. C., Huang Y. S., Graham J. A., Gardner D. E. Identification of immunogens of Mycoplasma pneumoniae by protein blotting. Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 1981 Dec 31;103(4):1363–1370. doi: 10.1016/0006-291x(81)90273-4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Jacobs E., Bennewitz A., Bredt W. Reaction pattern of human anti-Mycoplasma pneumoniae antibodies in enzyme-linked immunosorbent assays and immunoblotting. J Clin Microbiol. 1986 Mar;23(3):517–522. doi: 10.1128/jcm.23.3.517-522.1986. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kahane I., Tucker S., Baseman J. B. Detection of Mycoplasma pneumoniae adhesin (P1) in the nonhemadsorbing population of virulent Mycoplasma pneumoniae. Infect Immun. 1985 Aug;49(2):457–458. doi: 10.1128/iai.49.2.457-458.1985. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kahane I., Tucker S., Leith D. K., Morrison-Plummer J., Baseman J. B. Detection of the major adhesin P1 in triton shells of virulent Mycoplasma pneumoniae. Infect Immun. 1985 Dec;50(3):944–946. doi: 10.1128/iai.50.3.944-946.1985. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kenny G. E., Cartwright F. D. Immunoblotting for determination of the antigenic specificities of antibodies to the Mycoplasmatales. Isr J Med Sci. 1984 Oct;20(10):908–911. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kenny G. E., Dunsmoor C. L. Principles, problems, and strategies in the use of antigenic mixtures for the enzyme-linked immunosorbent assay. J Clin Microbiol. 1983 Apr;17(4):655–665. doi: 10.1128/jcm.17.4.655-665.1983. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kenny G. E. Heat-lability and organic solvent-solubility of mycoplasma antigens. Ann N Y Acad Sci. 1967 Jul 28;143(1):676–681. doi: 10.1111/j.1749-6632.1967.tb27713.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kleemola M., Käyhty H. Increase in titers of antibodies to Mycoplasma pneumoniae in patients with purulent meningitis. J Infect Dis. 1982 Aug;146(2):284–288. doi: 10.1093/infdis/146.2.284. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Krause D. C., Baseman J. B. Inhibition of mycoplasma pneumoniae hemadsorption and adherence to respiratory epithelium by antibodies to a membrane protein. Infect Immun. 1983 Mar;39(3):1180–1186. doi: 10.1128/iai.39.3.1180-1186.1983. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Laemmli U. K. Cleavage of structural proteins during the assembly of the head of bacteriophage T4. Nature. 1970 Aug 15;227(5259):680–685. doi: 10.1038/227680a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lederman M. M., Ellner J. J. Presence of antibodies to Mycoplasma pneumoniae in patients with bacterial meningitis. J Infect Dis. 1983 Aug;148(2):363–365. doi: 10.1093/infdis/148.2.363. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Leith D. K., Trevino L. B., Tully J. G., Senterfit L. B., Baseman J. B. Host discrimination of Mycoplasma pneumoniae proteinaceous immunogens. J Exp Med. 1983 Feb 1;157(2):502–514. doi: 10.1084/jem.157.2.502. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lind K., Lindhardt B. O., Schütten H. J., Blom J., Christiansen C. Serological cross-reactions between Mycoplasma genitalium and Mycoplasma pneumoniae. J Clin Microbiol. 1984 Dec;20(6):1036–1043. doi: 10.1128/jcm.20.6.1036-1043.1984. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lind K., Zoffmann H., Larsen S. O., Jessen O. Mycoplasma pneumoniae infection associated with affection of the central nervous system. Acta Med Scand. 1979;205(4):325–332. doi: 10.1111/j.0954-6820.1979.tb06057.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Michel D., Laurent B., Granouillet R., Gaudin-Terrasse O. D. Infections aiguës, récentes, et parfois persistantes à Mycoplasma pneumoniae, associées à des manifestations neurologiques. Discussion des liens de causalité. Rev Neurol (Paris) 1981;137(6-7):393–413. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Pönkä A., Pönkä T., Sarna S., Penttinen K. Questionable specificity of lipid antigen in the Mycoplasma pneumoniae complement fixation test in patients with extrapulmonary manifestations. J Infect. 1981 Dec;3(4):332–338. doi: 10.1016/s0163-4453(81)91901-0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Pönkä A. The occurrence and clinical picture of serologically verified Mycoplasma pneumoniae infections with emphasis on central nervous system, cardiac and joint manifestations. Ann Clin Res. 1979;11 (Suppl 24):1–60. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Senterfit L. B., Jensen K. E. Antimetabolic antibodies to Mycoplasma pneumoniae measured by tetrazolium reduction inhibition. Proc Soc Exp Biol Med. 1966 Jul;122(3):786–790. doi: 10.3181/00379727-122-31252. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Senterfit L. B., Pollack J. D., Somerson N. L. Antibodies to Mycoplasma pneumoniae: correlation of complement fixation and tetrazolium reduction inhibition tests. Proc Soc Exp Biol Med. 1972 Sep;140(4):1294–1297. doi: 10.3181/00379727-140-36661. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Taylor-Robinson D., Purcell R. H., Wong D. C., Chanock R. M. A colour test for the measurement of antibody to certain mycoplasma species based upon the inhibition of acid production. J Hyg (Lond) 1966 Mar;64(1):91–104. doi: 10.1017/s0022172400040377. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Towbin H., Staehelin T., Gordon J. Electrophoretic transfer of proteins from polyacrylamide gels to nitrocellulose sheets: procedure and some applications. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1979 Sep;76(9):4350–4354. doi: 10.1073/pnas.76.9.4350. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]