Abstract
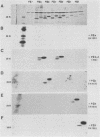
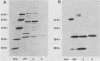
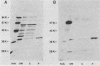
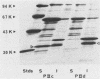
Gonococci express a family of related outer membrane proteins designated protein II (P.II), which undergo both phase and antigenic variation. Six P.II proteins have been identified in strain FA1090. We developed monoclonal antibodies specific for each P.II protein. Using these antibodies as probes, we purified the six different P.II proteins of this strain. Despite the relatedness of the proteins, we could not purify all of them by a single purification scheme. Four P.II proteins were purified by chromatofocusing, and the remaining two proteins were purified by hydrophobic interaction chromatography on phenyl-Sepharose. The N-terminal amino acid sequence of the proteins showed a high degree of sequence conservation. However, there was variability at specific amino acid residues, giving each P.II protein a unique N-terminal amino acid sequence. Thus P.II proteins of one strain differ among themselves not only in antigenic determinants and primary structure, but also in other characteristics affecting their properties in different chromatographic systems.
Full text
PDF




Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Black W. J., Schwalbe R. S., Nachamkin I., Cannon J. G. Characterization of Neisseria gonorrhoeae protein II phase variation by use of monoclonal antibodies. Infect Immun. 1984 Aug;45(2):453–457. doi: 10.1128/iai.45.2.453-457.1984. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Blake M. S., Gotschlich E. C. Purification and partial characterization of the opacity-associated proteins of Neisseria gonorrhoeae. J Exp Med. 1984 Feb 1;159(2):452–462. doi: 10.1084/jem.159.2.452. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bradford M. M. A rapid and sensitive method for the quantitation of microgram quantities of protein utilizing the principle of protein-dye binding. Anal Biochem. 1976 May 7;72:248–254. doi: 10.1006/abio.1976.9999. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Cannon J. G., Black W. J., Nachamkin I., Stewart P. W. Monoclonal antibody that recognizes an outer membrane antigen common to the pathogenic Neisseria species but not to most nonpathogenic Neisseria species. Infect Immun. 1984 Mar;43(3):994–999. doi: 10.1128/iai.43.3.994-999.1984. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Diaz J. L., Heckels J. E. Antigenic variation of outer membrane protein II in colonial variants of Neisseria gonorrhoeae P9. J Gen Microbiol. 1982 Mar;128(3):585–591. doi: 10.1099/00221287-128-3-585. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Draper D. L., James J. F., Brooks G. F., Sweet R. L. Comparison of virulence markers of peritoneal and fallopian tube isolates with endocervical Neisseria gonorrhoeae isolates from women with acute salpingitis. Infect Immun. 1980 Mar;27(3):882–888. doi: 10.1128/iai.27.3.882-888.1980. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Heckels J. E. Structural comparison of Neisseria gonorrhoeae outer membrane proteins. J Bacteriol. 1981 Feb;145(2):736–742. doi: 10.1128/jb.145.2.736-742.1981. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Heckels J. E. The surface of Neisseria gonorrhoeae: isolation of the major components of the outer membrane. J Gen Microbiol. 1977 Apr;99(2):333–341. doi: 10.1099/00221287-99-2-333. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- James J. F., Swanson J. Studies on gonococcus infection. XIII. Occurrence of color/opacity colonial variants in clinical cultures. Infect Immun. 1978 Jan;19(1):332–340. doi: 10.1128/iai.19.1.332-340.1978. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Johnston K. H., Holmes K. K., Gotschlich E. C. The serological classification of Neisseria gonorrhoeae. I. Isolation of the outer membrane complex responsible for serotypic specificity. J Exp Med. 1976 Apr 1;143(4):741–758. doi: 10.1084/jem.143.4.741. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Judd R. C. Structure and surface exposure of protein IIs of Neisseria gonorrhoeae JS3. Infect Immun. 1985 May;48(2):452–457. doi: 10.1128/iai.48.2.452-457.1985. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- KELLOGG D. S., Jr, PEACOCK W. L., Jr, DEACON W. E., BROWN L., PIRKLE D. I. NEISSERIA GONORRHOEAE. I. VIRULENCE GENETICALLY LINKED TO CLONAL VARIATION. J Bacteriol. 1963 Jun;85:1274–1279. doi: 10.1128/jb.85.6.1274-1279.1963. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kolodkin A. B., Clark V. L., Tenover F. C., Young F. E. High correlation of the presence of methyladenine in Neisseria gonorrhoeae DNA with the AHU auxotype. Infect Immun. 1982 May;36(2):586–590. doi: 10.1128/iai.36.2.586-590.1982. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Laemmli U. K. Cleavage of structural proteins during the assembly of the head of bacteriophage T4. Nature. 1970 Aug 15;227(5259):680–685. doi: 10.1038/227680a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lambden P. R., Heckels J. E., James L. T., Watt P. J. Variations in surface protein composition associated with virulence properties in opacity types of Neisseria gonorrhoeae. J Gen Microbiol. 1979 Oct;114(2):305–312. doi: 10.1099/00221287-114-2-305. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mayer L. W. Rates in vitro changes of gonococcal colony opacity phenotypes. Infect Immun. 1982 Aug;37(2):481–485. doi: 10.1128/iai.37.2.481-485.1982. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Nachamkin I., Cannon J. G., Mittler R. S. Monoclonal antibodies against Neisseria gonorrhoeae: production of antibodies directed against a strain-specific cell surface antigen. Infect Immun. 1981 May;32(2):641–648. doi: 10.1128/iai.32.2.641-648.1981. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Newhall WJ5th, Mail L. B., Wilde C. E., 3rd, Jones R. B. Purification and antigenic relatedness of proteins II of Neisseria gonorrhoeae. Infect Immun. 1985 Sep;49(3):576–580. doi: 10.1128/iai.49.3.576-580.1985. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Raschke W. C. Expression of murine IgM, IgD and Ia molecules on hybrids of murine LPS blasts with a Syrian hamster B lymphoma. Curr Top Microbiol Immunol. 1978;81:70–76. doi: 10.1007/978-3-642-67448-8_12. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Schwalbe R. S., Sparling P. F., Cannon J. G. Variation of Neisseria gonorrhoeae protein II among isolates from an outbreak caused by a single gonococcal strain. Infect Immun. 1985 Jul;49(1):250–252. doi: 10.1128/iai.49.1.250-252.1985. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sparling P. F., Cannon J. G., So M. Phase and antigenic variation of pili and outer membrane protein II of Neisseria gonorrhoeae. J Infect Dis. 1986 Feb;153(2):196–201. doi: 10.1093/infdis/153.2.196. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Stern A., Brown M., Nickel P., Meyer T. F. Opacity genes in Neisseria gonorrhoeae: control of phase and antigenic variation. Cell. 1986 Oct 10;47(1):61–71. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(86)90366-1. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Stern A., Nickel P., Meyer T. F., So M. Opacity determinants of Neisseria gonorrhoeae: gene expression and chromosomal linkage to the gonococcal pilus gene. Cell. 1984 Jun;37(2):447–456. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(84)90375-1. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sugasawara R. J., Cannon J. G., Black W. J., Nachamkin I., Sweet R. L., Brooks G. F. Inhibition of Neisseria gonorrhoeae attachment to HeLa cells with monoclonal antibody directed against a protein II. Infect Immun. 1983 Dec;42(3):980–985. doi: 10.1128/iai.42.3.980-985.1983. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Swanson J. 125I-labeled peptide mapping of some heat-modifiable proteins of the gonococcal outer membrane. Infect Immun. 1980 Apr;28(1):54–64. doi: 10.1128/iai.28.1.54-64.1980. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Swanson J., Barrera O. Immunological characteristics of gonococcal outer membrane protein II assessed by immunoprecipitation, immunoblotting, and coagglutination. J Exp Med. 1983 May 1;157(5):1405–1420. doi: 10.1084/jem.157.5.1405. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Swanson J. Colony opacity and protein II compositions of gonococci. Infect Immun. 1982 Jul;37(1):359–368. doi: 10.1128/iai.37.1.359-368.1982. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Swanson J. Studies on gonococcus infection. XII. Colony color and opacity varienats of gonococci. Infect Immun. 1978 Jan;19(1):320–331. doi: 10.1128/iai.19.1.320-331.1978. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Swanson J. Studies on gonococcus infection. XIV. Cell wall protein differences among color/opacity colony variants of Neisseria gonorrhoeae. Infect Immun. 1978 Jul;21(1):292–302. doi: 10.1128/iai.21.1.292-302.1978. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Walstad D. L., Guymon L. F., Sparling P. F. Altered outer membrane protein in different colonial types of Neisseria gonorrhoeae. J Bacteriol. 1977 Mar;129(3):1623–1627. doi: 10.1128/jb.129.3.1623-1627.1977. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]