Abstract
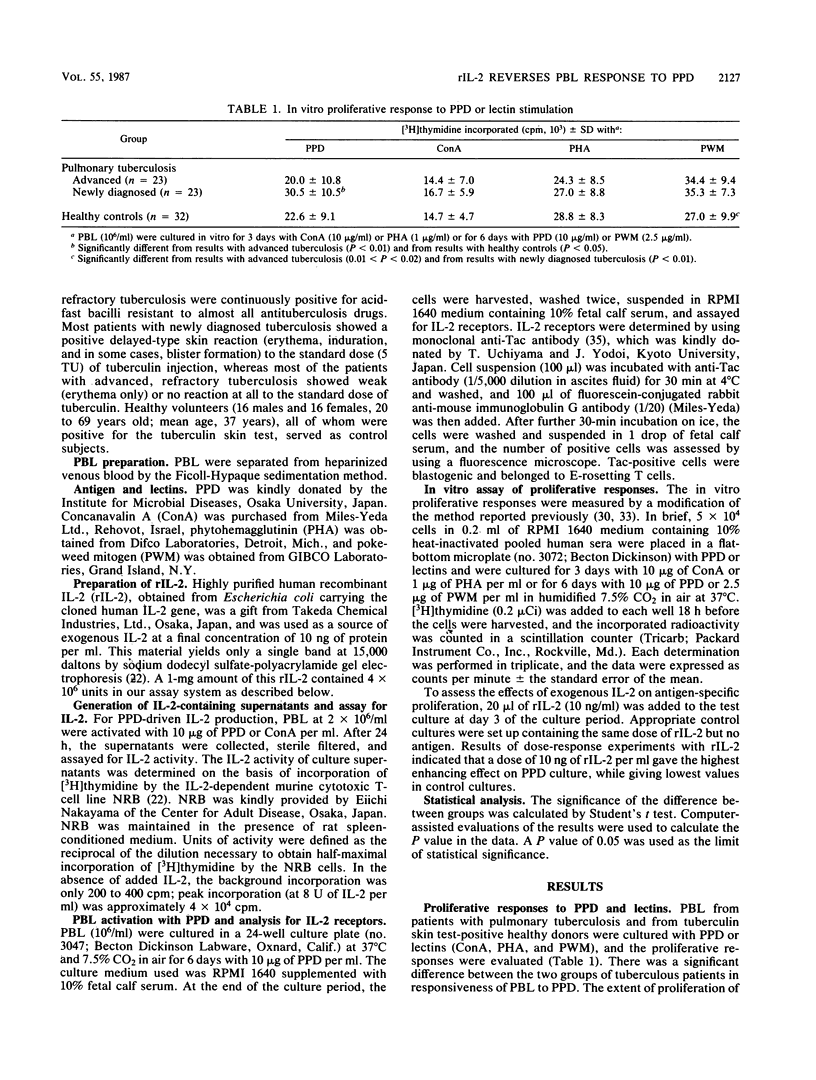
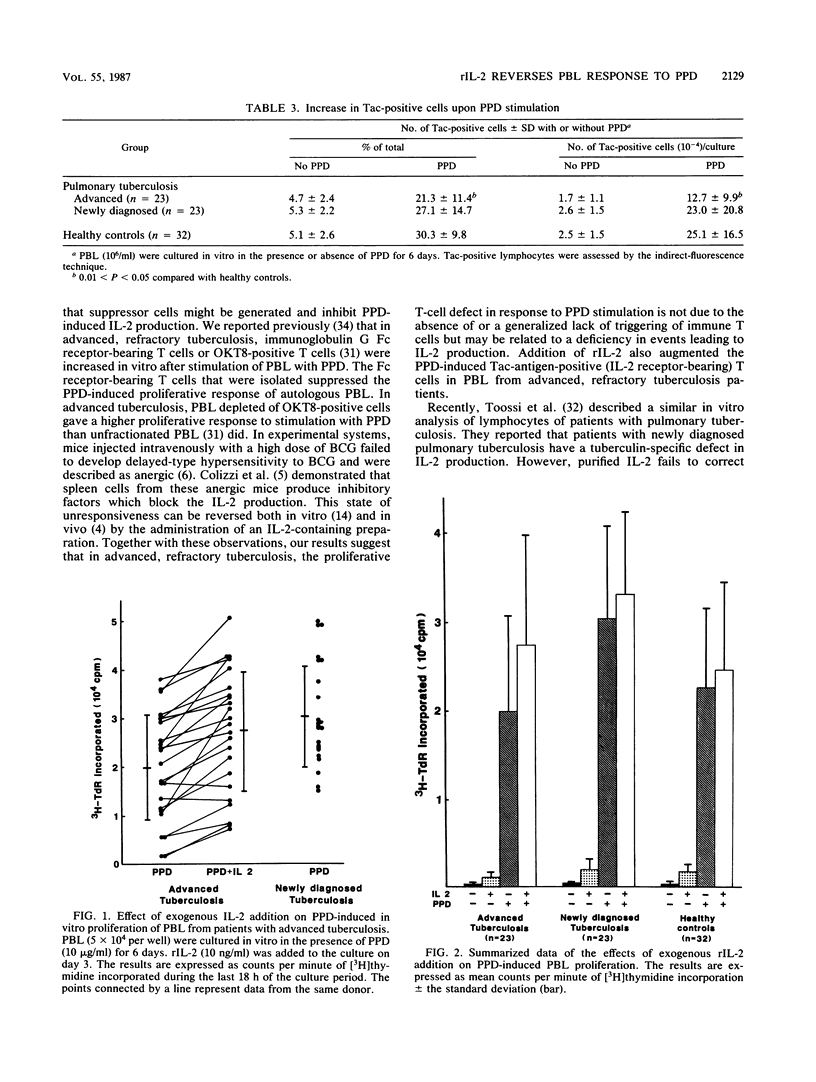
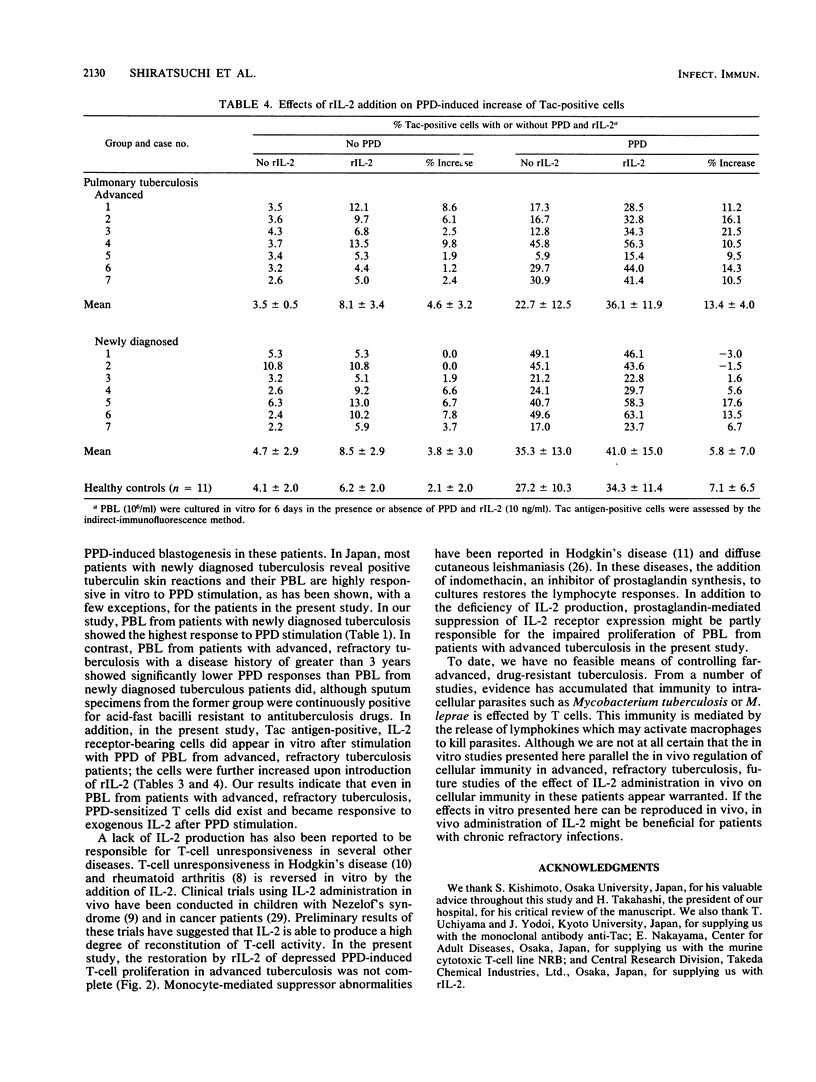
In vitro lymphocyte proliferative response to purified protein derivative of tuberculin (PPD) was investigated in patients with tuberculosis. Peripheral blood lymphocytes (PBL) from patients with advanced, refractory tuberculosis showed a significantly depressed response compared with the response of PBL from patients with newly diagnosed tuberculosis (P less than 0.01). A further characterization of this low responsiveness to PPD revealed that PBL from these advanced tuberculous patients failed to generate interleukin-2 (IL-2) in response to PPD stimulation. IL-2 receptor (Tac antigen) expression on the surface of T cells after PPD stimulation was also impaired, although to a lesser extent, in the patients with advanced, refractory tuberculosis. We attempted to overcome the depressed in vitro response observed in PBL from patients with advanced, refractory tuberculosis and found that the addition of exogenous, recombinant IL-2 returned the depressed PPD-induced PBL proliferation in these patients to the level of response observed in PBL from patients with newly diagnosed tuberculosis. The addition of recombinant IL-2 also had a restorative effect (up regulation) in vitro on the partly impaired PPD-induced IL-2 receptor expression by PBL from the patients with advanced, refractory tuberculosis. Our results suggest that recombinant IL-2 may offer a novel approach to the therapy of advanced, drug-resistant tuberculosis.
Full text
PDF


Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Bhatnagar R., Malaviya A. N., Narayanan S., Rajgopalan P., Kumar R., Bharadwaj O. P. Spectrum of immune response abnormalities in different clinical forms of tuberculosis. Am Rev Respir Dis. 1977 Feb;115(2):207–212. doi: 10.1164/arrd.1977.115.2.207. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Cantrell D. A., Smith K. A. The interleukin-2 T-cell system: a new cell growth model. Science. 1984 Jun 22;224(4655):1312–1316. doi: 10.1126/science.6427923. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Cantrell D. A., Smith K. A. Transient expression of interleukin 2 receptors. Consequences for T cell growth. J Exp Med. 1983 Dec 1;158(6):1895–1911. doi: 10.1084/jem.158.6.1895. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Colizzi V., Ferluga J., Garreau F., Malkovsky M., Asherson G. L. Suppressor cells induced by BCG release non-specific factors in vitro which inhibit DNA synthesis and interleukin-2 production. Immunology. 1984 Jan;51(1):65–71. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Colizzi V. In vivo and in vitro administration of interleukin 2-containing preparation reverses T-cell unresponsiveness in Mycobacterium bovis BCG-infected mice. Infect Immun. 1984 Jul;45(1):25–28. doi: 10.1128/iai.45.1.25-28.1984. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Collins F. M., Watson S. R. Suppressor T-cells in BCG-infected mice. Infect Immun. 1979 Aug;25(2):491–496. doi: 10.1128/iai.25.2.491-496.1979. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Cotner T., Williams J. M., Christenson L., Shapiro H. M., Strom T. B., Strominger J. Simultaneous flow cytometric analysis of human T cell activation antigen expression and DNA content. J Exp Med. 1983 Feb 1;157(2):461–472. doi: 10.1084/jem.157.2.461. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Emery P., Panayi G. S., Nouri A. M. Interleukin-2 reverses deficient cell-mediated immune responses in rheumatoid arthritis. Clin Exp Immunol. 1984 Jul;57(1):123–129. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Flomenberg N., Welte K., Mertelsmann R., Kernan N., Ciobanu N., Venuta S., Feldman S., Kruger G., Kirkpatrick D., Dupont B. Immunologic effects of interleukin 2 in primary immunodeficiency diseases. J Immunol. 1983 Jun;130(6):2644–2650. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ford R. J., Tsao J., Kouttab N. M., Sahasrabuddhe C. G., Mehta S. R. Association of an interleukin abnormality with the T cell defect in Hodgkin's disease. Blood. 1984 Aug;64(2):386–392. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Goodwin J. S., Messner R. P., Bankhurst A. D., Peake G. T., Saiki J. H., Williams R. C., Jr Prostaglandin-producing suppressor cells in Hodgkin's disease. N Engl J Med. 1977 Nov 3;297(18):963–968. doi: 10.1056/NEJM197711032971802. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gullberg M., Larsson E. L. Studies on induction and effector functions of concanavalin A-induced suppressor cells that limit TCGF production. J Immunol. 1982 Feb;128(2):746–750. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Haregewoin A., Godal T., Mustafa A. S., Belehu A., Yemaneberhan T. T-cell conditioned media reverse T-cell unresponsiveness in lepromatous leprosy. Nature. 1983 May 26;303(5915):342–344. doi: 10.1038/303342a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hoffenbach A., Lagrange P. H., Bach M. A. Deficit of interleukin 2 production associated with impaired T-cell proliferative responses in Mycobacterium lepraemurium infection. Infect Immun. 1983 Jan;39(1):109–116. doi: 10.1128/iai.39.1.109-116.1983. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Horwitz M. A., Levis W. R., Cohn Z. A. Defective production of monocyte-activating cytokines in lepromatous leprosy. J Exp Med. 1984 Mar 1;159(3):666–678. doi: 10.1084/jem.159.3.666. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kaplan G., Weinstein D. E., Steinman R. M., Levis W. R., Elvers U., Patarroyo M. E., Cohn Z. A. An analysis of in vitro T cell responsiveness in lepromatous leprosy. J Exp Med. 1985 Sep 1;162(3):917–929. doi: 10.1084/jem.162.3.917. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kramer M., Koszinowski U. T cell-specific suppressor factor(s) with regulatory influence on interleukin 2 production and function. J Immunol. 1982 Feb;128(2):784–790. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- McMurray D. N., Echeverri A. Cell-mediated immunity in anergic patients with pulmonary tuberculosis. Am Rev Respir Dis. 1978 Nov;118(5):827–834. doi: 10.1164/arrd.1978.118.5.827. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mehra V., Convit J., Rubinstein A., Bloom B. R. Activated suppressor T cells in leprosy. J Immunol. 1982 Nov;129(5):1946–1951. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mohagheghpour N., Gelber R. H., Larrick J. W., Sasaki D. T., Brennan P. J., Engleman E. G. Defective cell-mediated immunity in leprosy: failure of T cells from lepromatous leprosy patients to respond to Mycobacterium leprae is associated with defective expression of interleukin 2 receptors and is not reconstituted by interleukin 2. J Immunol. 1985 Aug;135(2):1443–1449. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mustafa A. S., Godal T. BCG-induced suppressor T cells optimal conditions for in vitro induction and mode of action. Clin Exp Immunol. 1985 Dec;62(3):474–481. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Naruo K., Hinuma S., Kato K., Koyama M., Tada H., Shiho O., Tsukamoto K. Comparison of the biological properties of purified natural and recombinant human interleukin-2. Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 1985 Apr 16;128(1):257–264. doi: 10.1016/0006-291x(85)91672-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Nash D. R., Douglass J. E. Anergy in active pulmonary tuberculosis. A comparison between positive and negative reactors and an evaluation of 5 TU and 250 TU skin test doses. Chest. 1980 Jan;77(1):32–37. doi: 10.1378/chest.77.1.32. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Nath I., Sathish M., Jayaraman T., Bhutani L. K., Sharma A. K. Evidence for the presence of M. leprae reactive T lymphocytes in patients with lepromatous leprosy. Clin Exp Immunol. 1984 Dec;58(3):522–530. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ohta N., Minai M., Sasazuki T. Antigen-specific suppressor T lymphocytes (Leu-2a+3a-) in human schistosomiasis japonica. J Immunol. 1983 Nov;131(5):2524–2528. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Petersen E. A., Neva F. A., Oster C. N., Bogaert Diaz H. Specific inhibition of lymphocyte-proliferation responses by adherent suppressor cells in diffuse cutaneous leishmaniasis. N Engl J Med. 1982 Feb 18;306(7):387–392. doi: 10.1056/NEJM198202183060702. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Reem G. H., Yeh N. H. Interleukin 2 regulates expression of its receptor and synthesis of gamma interferon by human T lymphocytes. Science. 1984 Jul 27;225(4660):429–430. doi: 10.1126/science.6429853. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ridley D. S., Jopling W. H. Classification of leprosy according to immunity. A five-group system. Int J Lepr Other Mycobact Dis. 1966 Jul-Sep;34(3):255–273. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rosenberg S. A., Lotze M. T., Muul L. M., Leitman S., Chang A. E., Ettinghausen S. E., Matory Y. L., Skibber J. M., Shiloni E., Vetto J. T. Observations on the systemic administration of autologous lymphokine-activated killer cells and recombinant interleukin-2 to patients with metastatic cancer. N Engl J Med. 1985 Dec 5;313(23):1485–1492. doi: 10.1056/NEJM198512053132327. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Shiratsuchi H., Tsuyuguchi I. Analysis of T cell subsets by monoclonal antibodies in patients with tuberculosis after in vitro stimulation with purified protein derivative of tuberculin. Clin Exp Immunol. 1984 Aug;57(2):271–278. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Shiratsuchi H., Tsuyuguchi I. Tuberculin purified protein derivative-reactive T cells in cord blood lymphocytes. Infect Immun. 1981 Sep;33(3):651–657. doi: 10.1128/iai.33.3.651-657.1981. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Toossi Z., Kleinhenz M. E., Ellner J. J. Defective interleukin 2 production and responsiveness in human pulmonary tuberculosis. J Exp Med. 1986 May 1;163(5):1162–1172. doi: 10.1084/jem.163.5.1162. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Tsuyuguchi I., Shiratsuchi H., Fujiwara H., Teraoka O. Nonspecific recruitment of lymphocytes in purified protein derivative-induced lymphocyte proliferative response of patients with tuberculosis. Infect Immun. 1982 Aug;37(2):702–709. doi: 10.1128/iai.37.2.702-709.1982. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Tsuyuguchi I., Shiratsuchi H., Teraoka O., Hirano T. Increase in T cells bearing IgG Fc receptors in peripheral blood of patients with tuberculosis by in vitro stimulation with purified protein derivative. Am Rev Respir Dis. 1980 Jun;121(6):951–957. doi: 10.1164/arrd.1980.121.6.951. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Uchiyama T., Broder S., Waldmann T. A. A monoclonal antibody (anti-Tac) reactive with activated and functionally mature human T cells. I. Production of anti-Tac monoclonal antibody and distribution of Tac (+) cells. J Immunol. 1981 Apr;126(4):1393–1397. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Vismara D., Lombardi G., Piccolella E., Colizzi V. Dissociation between interleukin-1 and interleukin-2 production in proliferative response to microbial antigens: restorative effect of exogenous interleukin-2. Infect Immun. 1985 Aug;49(2):298–304. doi: 10.1128/iai.49.2.298-304.1985. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Welte K., Andreeff M., Platzer E., Holloway K., Rubin B. Y., Moore M. A., Mertelsmann R. Interleukin 2 regulates the expression of Tac antigen on peripheral blood T lymphocytes. J Exp Med. 1984 Nov 1;160(5):1390–1403. doi: 10.1084/jem.160.5.1390. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]


