Abstract
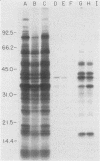
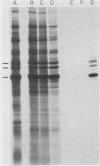
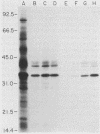
We previously reported that a number of Treponema pallidum membrane proteins appear to reside on the cell surface, since intact treponemes radiolabeled by overnight incubation in medium containing [35S]methionine bind immunoglobulin G (IgG) antibodies directed against these proteins. In the present study, it was found that freshly extracted organisms radiolabeled in vitro for only 2 h inefficiently bound IgG antibodies directed against just two proteins of molecular weights 40,000 and 34,000. An in vitro incubation period of greater than 8 h was required before IgG antibodies present in rabbit syphilitic serum could recognize additional protein antigens on the cell surface. Treatment of aged treponemes, but not freshly extracted organisms, with 0.04% sodium dodecyl sulfate selectively removed a membranous layer from the treponemal surface. Only three treponemal proteins were found associated with this structure, including the same 40,000- and 34,000-molecular-weight proteins mentioned above. These two proteins most likely represent endoflagellar subunits, since they were precipitated with rabbit antisera prepared against purified endoflagellar subunits of the cultivable treponemal strain Treponema phagedenis. Further evidence also was obtained that cells of T. pallidum actively secrete into their extracellular environment a unique class of low-molecular-weight proteins.
Full text
PDF





Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Alderete J. F., Baseman J. B. Surface characterization of virulent Treponema pallidum. Infect Immun. 1980 Dec;30(3):814–823. doi: 10.1128/iai.30.3.814-823.1980. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Alderete J. F., Baseman J. B. Surface-associated host proteins on virulent Treponema pallidum. Infect Immun. 1979 Dec;26(3):1048–1056. doi: 10.1128/iai.26.3.1048-1056.1979. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Baker-Zander S. A., Lukehart S. A. Molecular basis of immunological cross-reactivity between Treponema pallidum and Treponema pertenue. Infect Immun. 1983 Nov;42(2):634–638. doi: 10.1128/iai.42.2.634-638.1983. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bishop N. H., Miller J. N. Humoral immunity in experimental syphilis. II. The relationship of neutralizing factors in immune serum to acquired resistance. J Immunol. 1976 Jul;117(1):197–207. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Blanco D. R., Radolf J. D., Lovett M. A., Miller J. N. Correlation of treponemicidal activity in normal human serum with the presence of IgG antibody directed against polypeptides of Treponema phagedenis biotype Reiter and Treponema pallidum, Nichols strain. J Immunol. 1986 Sep 15;137(6):2031–2036. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Blanco D. R., Radolf J. D., Lovett M. A., Miller J. N. The antigenic interrelationship between the endoflagella of Treponema phagedenis biotype Reiter and Treponema pallidum Nichols strain. I. Treponemicidal activity of cross-reactive endoflagellar antibodies against T. pallidum. J Immunol. 1986 Nov 1;137(9):2973–2979. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Fehniger T. E., Radolf J. D., Walfield A. M., Cunningham T. M., Miller J. N., Lovett M. A. Native surface association of a recombinant 38-kilodalton Treponema pallidum antigen isolated from the Escherichia coli outer membrane. Infect Immun. 1986 May;52(2):586–593. doi: 10.1128/iai.52.2.586-593.1986. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Fitzgerald T. J., Johnson R. C. Surface mucopolysaccharides of Treponema pallidum. Infect Immun. 1979 Apr;24(1):244–251. doi: 10.1128/iai.24.1.244-251.1979. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- HARDY P. H., Jr, NELL E. E. Study of the antigenic structure of Treponema pallidum by specific agglutination. Am J Hyg. 1957 Sep;66(2):160–172. doi: 10.1093/oxfordjournals.aje.a119893. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hanff P. A., Bishop N. H., Miller J. N., Lovett M. A. Humoral immune response in experimental syphilis to polypeptides of Treponema pallidum. J Immunol. 1983 Oct;131(4):1973–1977. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hanff P. A., Norris S. J., Lovett M. A., Miller J. N. Purification of Treponema pallidum, Nichols strain, by Percoll density gradient centrifugation. Sex Transm Dis. 1984 Oct-Dec;11(4):275–286. doi: 10.1097/00007435-198410000-00003. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hansen E. J., Frisch C. F., Johnston K. H. Detection of antibody-accessible proteins on the cell surface of Haemophilus influenzae type b. Infect Immun. 1981 Sep;33(3):950–953. doi: 10.1128/iai.33.3.950-953.1981. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Johnson R. C., Wachter M. S., Ritzi D. M. Treponeme outer cell envelope: solubilization and reaggregation. Infect Immun. 1973 Feb;7(2):249–258. doi: 10.1128/iai.7.2.249-258.1973. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Jones S. A., Marchitto K. S., Miller J. N., Norgard M. V. Monoclonal antibody with hemagglutination, immobilization, and neutralization activities defines an immunodominant, 47,000 mol wt, surface-exposed immunogen of Treponema pallidum (Nichols). J Exp Med. 1984 Nov 1;160(5):1404–1420. doi: 10.1084/jem.160.5.1404. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Konishi H., Yoshii Z., Cox D. L. Electron microscopy of Treponema pallidum (Nichols) cultivated in tissue cultures of Sf1Ep cells. Infect Immun. 1986 Jul;53(1):32–37. doi: 10.1128/iai.53.1.32-37.1986. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Limberger R. J., Charon N. W. Antiserum to the 33,000-dalton periplasmic-flagellum protein of "Treponema phagedenis" reacts with other treponemes and Spirochaeta aurantia. J Bacteriol. 1986 Nov;168(2):1030–1032. doi: 10.1128/jb.168.2.1030-1032.1986. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Limberger R. J., Charon N. W. Treponema phagedenis has at least two proteins residing together on its periplasmic flagella. J Bacteriol. 1986 Apr;166(1):105–112. doi: 10.1128/jb.166.1.105-112.1986. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- METZGER M., HARDY P. H., Jr, NELL E. E. Influence of lysozyme upon the treponeme immobilization reaction. Am J Hyg. 1961 Mar;73:236–244. doi: 10.1093/oxfordjournals.aje.a120182. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- METZGER M., RUCZKOWSKA J. INFLUENCE OF LYSOZYME UPON THE REACTIVITY OF TREPONEMA PALLIDUM IN THE FLUORESCENT ANTIBODY REACTION. Arch Immunol Ther Exp (Warsz) 1964;12:702–708. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Marchitto K. S., Selland-Grossling C. K., Norgard M. V. Molecular specificities of monoclonal antibodies directed against virulent Treponema pallidum. Infect Immun. 1986 Jan;51(1):168–176. doi: 10.1128/iai.51.1.168-176.1986. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Metzger M., Podwińska J. Studies of the mechanism of development of agglutinability of pathogenic Treponema pallidum. 3. Changes in the activity of different antigenic components to agglutinating antibodies. Arch Immunol Ther Exp (Warsz) 1967;15(1):34–41. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Miao R., Fieldsteel A. H. Genetics of Treponema: relationship between Treponema pallidum and five cultivable treponemes. J Bacteriol. 1978 Jan;133(1):101–107. doi: 10.1128/jb.133.1.101-107.1978. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Moskophidis M., Müller F. Molecular characterization of glycoprotein antigens on surface of Treponema pallidum: comparison with nonpathogenic Treponema phagedenis biotype Reiter. Infect Immun. 1984 Dec;46(3):867–869. doi: 10.1128/iai.46.3.867-869.1984. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Norris S. J., Sell S. Antigenic complexity of Treponema pallidum: antigenicity and surface localization of major polypeptides. J Immunol. 1984 Nov;133(5):2686–2692. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Pedersen N. S., Petersen C. S., Vejtorp M., Axelsen N. H. Serodiagnosis of syphilis by an enzyme-linked immunosorbent assay for IgG antibodies against the Reiter treponeme flagellum. Scand J Immunol. 1982 Apr;15(4):341–348. doi: 10.1111/j.1365-3083.1982.tb00657.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Penn C. W. Avoidance of host defences by Treponema pallidum in situ and on extraction from infected rabbit testes. J Gen Microbiol. 1981 Sep;126(1):69–75. doi: 10.1099/00221287-126-1-69. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Penn C. W., Bailey M. J., Cockayne A. The axial filament antigen of Treponema pallidum. Immunology. 1985 Apr;54(4):635–641. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Penn C. W., Cockayne A., Bailey M. J. The outer membrane of Treponema pallidum: biological significance and biochemical properties. J Gen Microbiol. 1985 Sep;131(9):2349–2357. doi: 10.1099/00221287-131-9-2349. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
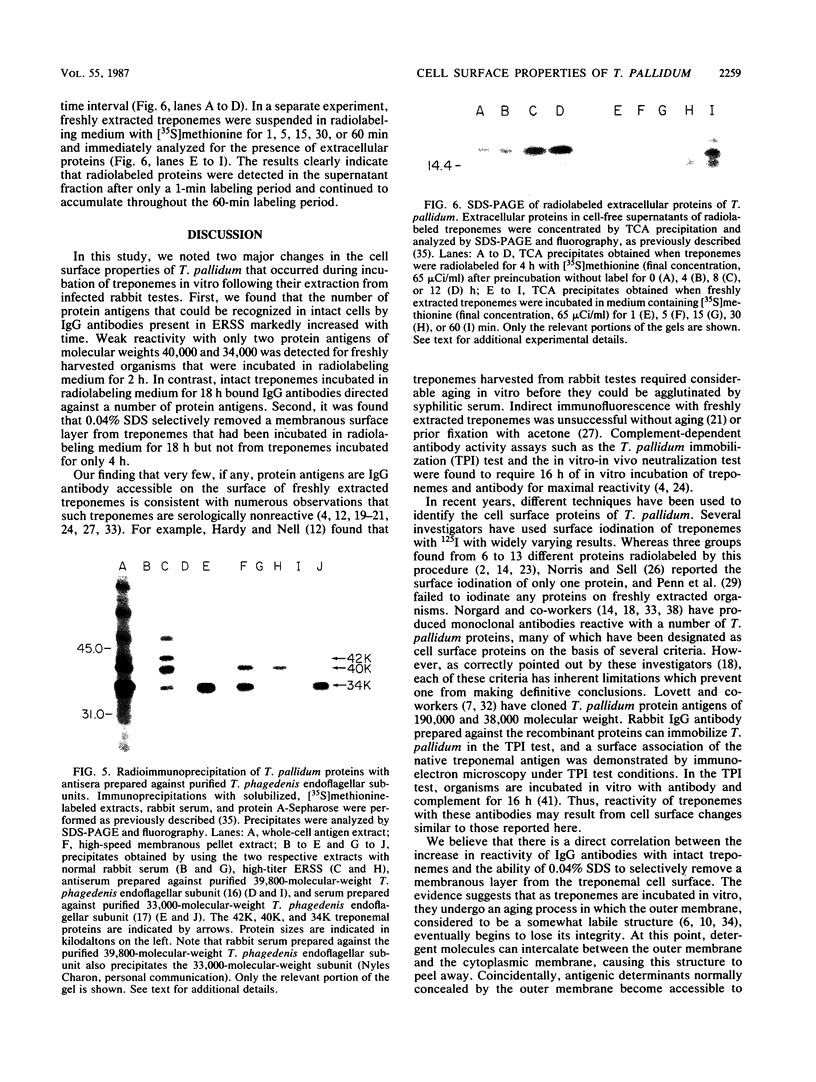
- Penn C. W., Rhodes J. G. Surface-associated antigens of Treponema pallidum concealed by an inert outer layer. Immunology. 1982 May;46(1):9–16. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Radolf J. D., Blanco D. R., Miller J. N., Lovett M. A. Antigenic interrelationship between endoflagella of Treponema phagedenis biotype Reiter and Treponema pallidum (Nichols): molecular characterization of endoflagellar proteins. Infect Immun. 1986 Dec;54(3):626–634. doi: 10.1128/iai.54.3.626-634.1986. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Radolf J. D., Fehniger T. E., Silverblatt F. J., Miller J. N., Lovett M. A. The surface of virulent Treponema pallidum: resistance to antibody binding in the absence of complement and surface association of recombinant antigen 4D. Infect Immun. 1986 May;52(2):579–585. doi: 10.1128/iai.52.2.579-585.1986. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Robertson S. M., Kettman J. R., Miller J. N., Norgard M. V. Murine monoclonal antibodies specific for virulent Treponema pallidum (Nichols). Infect Immun. 1982 Jun;36(3):1076–1085. doi: 10.1128/iai.36.3.1076-1085.1982. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sell S., Norris S. J. The biology, pathology, and immunology of syphilis. Int Rev Exp Pathol. 1983;24:203–276. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Stamm L. V., Bassford P. J., Jr Cellular and extracellular protein antigens of Treponema pallidum synthesized during in vitro incubation of freshly extracted organisms. Infect Immun. 1985 Mar;47(3):799–807. doi: 10.1128/iai.47.3.799-807.1985. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Stamm L. V., Kerner T. C., Jr, Bankaitis V. A., Bassford P. J., Jr Identification and preliminary characterization of Treponema pallidum protein antigens expressed in Escherichia coli. Infect Immun. 1983 Aug;41(2):709–721. doi: 10.1128/iai.41.2.709-721.1983. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Swancutt M. A., Twehous D. A., Norgard M. V. Monoclonal antibody selection and analysis of a recombinant DNA-derived surface immunogen of Treponema pallidum expressed in Escherichia coli. Infect Immun. 1986 Apr;52(1):110–119. doi: 10.1128/iai.52.1.110-119.1986. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sykes J. A., Miller J. N. Ultrastructural studies of treponemes: location of axial filaments and some dimensions of Treponema pallidum (Nichols strain), Treponema denticola, and Treponema reiteri. Infect Immun. 1973 Jan;7(1):100–110. doi: 10.1128/iai.7.1.100-110.1973. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Thornburg R. W., Baseman J. B. Comparison of major protein antigens and protein profiles of Treponema pallidum and Treponema pertenue. Infect Immun. 1983 Nov;42(2):623–627. doi: 10.1128/iai.42.2.623-627.1983. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]