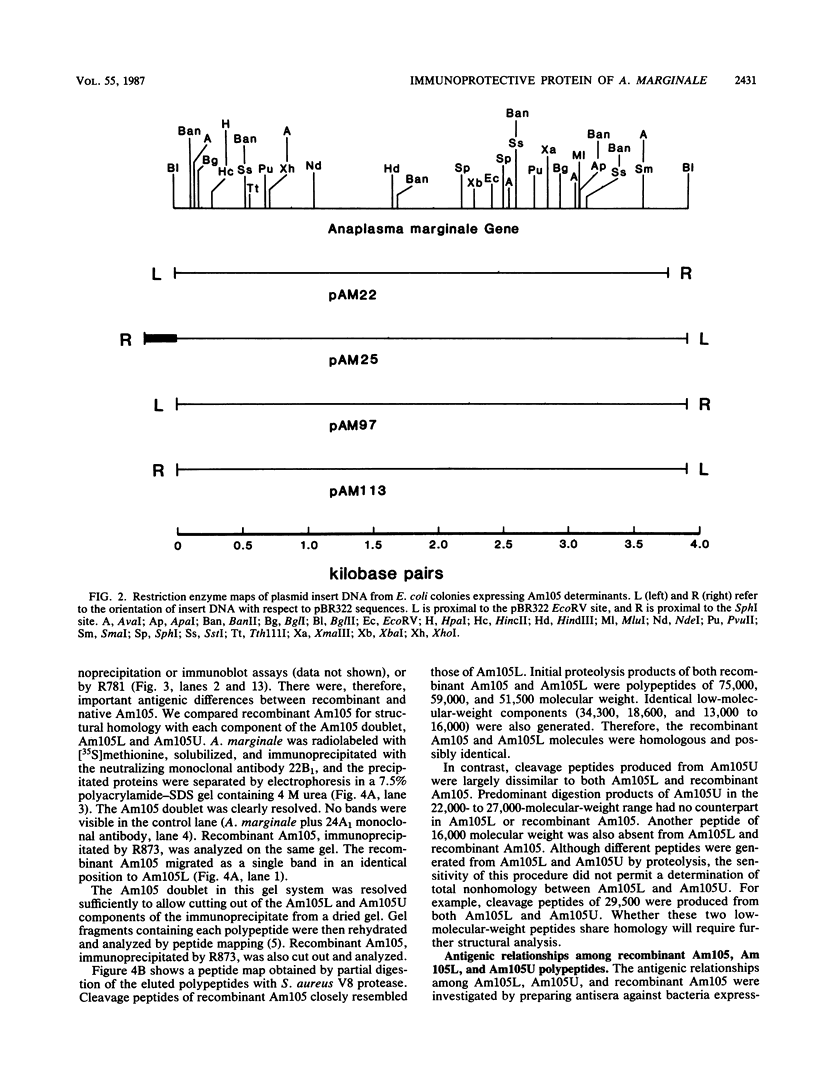
Abstract
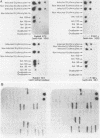
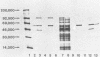
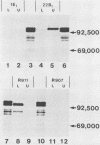
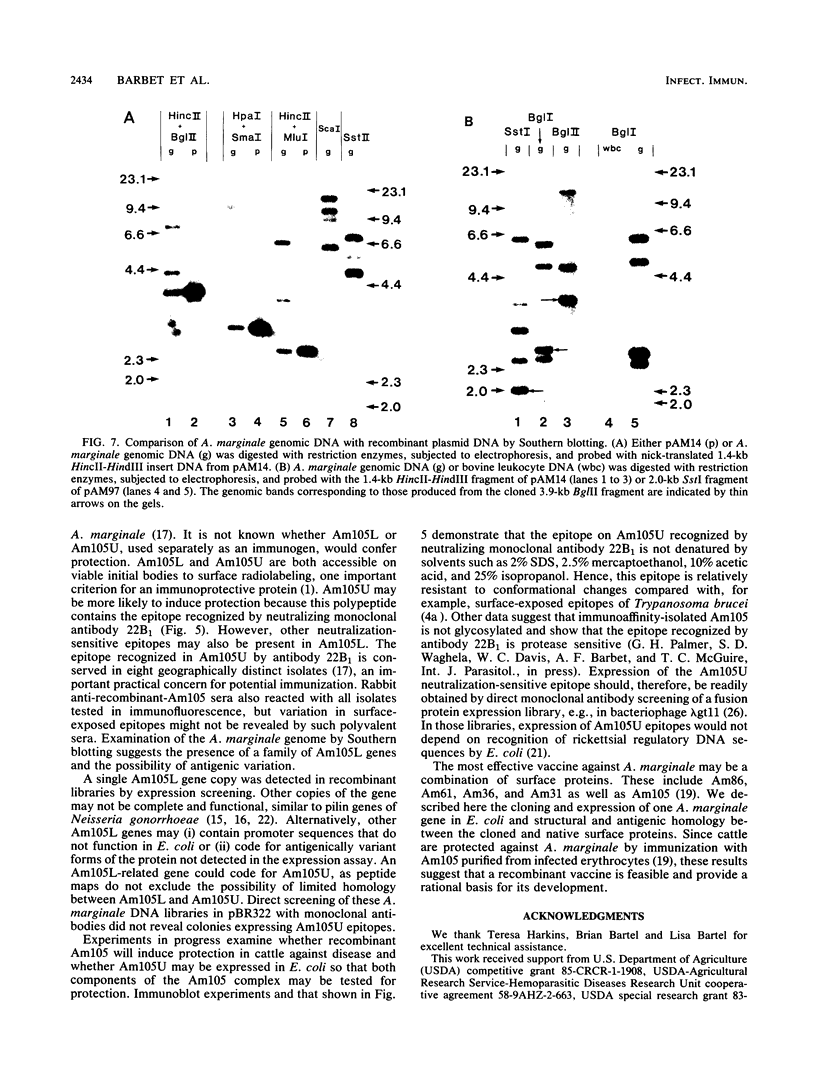
Immunization with an Anaplasma marginale surface protein complex containing two polypeptides (Am105U and Am105L), each having a molecular weight of 105,000, protected cattle against challenge with virulent organisms. These polypeptides were immunoprecipitated together from detergent extracts of A. marginale by a neutralizing monoclonal antibody. After surface radioiodination of intact parasites, both Am105U and Am105L contained the radiolabel. To define the structural and antigenic relationships between Am105U and Am105L and to determine individual efficacies as protective immunogens, we cloned and expressed A. marginale DNA in Escherichia coli. We identified recombinant bacteria which expressed a novel protein of 105,000 molecular weight as a major cellular component. The recombinant protein was structurally and antigenically homologous to Am105L. There were multiple, partially homologous copies of the cloned DNA sequence in the rickettsial genome.
Full text
PDF




Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Barbet A. F., Anderson L. W., Palmer G. H., McGuire T. C. Comparison of proteins synthesized by two different isolates of Anaplasma marginale. Infect Immun. 1983 Jun;40(3):1068–1074. doi: 10.1128/iai.40.3.1068-1074.1983. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Barbet A. F. Identification and analysis of parasite surface antigens and parasite-induced antigens on host cells. Vet Parasitol. 1982 Jun;10(2-3):181–189. doi: 10.1016/0304-4017(82)90023-1. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Barbet A. F., McGuire T. C. Crossreacting determinants in variant-specific surface antigens of African trypanosomes. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1978 Apr;75(4):1989–1993. doi: 10.1073/pnas.75.4.1989. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bonner W. M., Laskey R. A. A film detection method for tritium-labelled proteins and nucleic acids in polyacrylamide gels. Eur J Biochem. 1974 Jul 1;46(1):83–88. doi: 10.1111/j.1432-1033.1974.tb03599.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Clarke M. W., Barbet A. F., Pearson T. W. Structural features of antigenic determinants on variant surface glycoproteins from Trypanosoma brucei. Mol Immunol. 1987 Jul;24(7):707–713. doi: 10.1016/0161-5890(87)90052-6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Cleveland D. W., Fischer S. G., Kirschner M. W., Laemmli U. K. Peptide mapping by limited proteolysis in sodium dodecyl sulfate and analysis by gel electrophoresis. J Biol Chem. 1977 Feb 10;252(3):1102–1106. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ellens D. J., Gielkens A. L. A simple method for the purification of 5-aminosalicylic acid. Application of the product as substrate in enzyme-linked immunosorbent assay (ELISA). J Immunol Methods. 1980;37(3-4):325–332. doi: 10.1016/0022-1759(80)90318-x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Goodger W. J., Carpenter T., Riemann H. Estimation of economic loss associated with anaplasmosis in California beef cattle. J Am Vet Med Assoc. 1979 Jun 15;174(12):1333–1336. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hanahan D. Studies on transformation of Escherichia coli with plasmids. J Mol Biol. 1983 Jun 5;166(4):557–580. doi: 10.1016/s0022-2836(83)80284-8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kessler S. W. Use of protein A-bearing staphylococci for the immunoprecipitation and isolation of antigens from cells. Methods Enzymol. 1981;73(Pt B):442–459. doi: 10.1016/0076-6879(81)73084-2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Krause D. C., Winkler H. H., Wood D. O. Cosmid cloning of Rickettsia prowazekii antigens in Escherichia coli K-12. Infect Immun. 1985 Jan;47(1):157–165. doi: 10.1128/iai.47.1.157-165.1985. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- McDonald G. A., Anacker R. L., Garjian K. Cloned gene of Rickettsia rickettsii surface antigen: candidate vaccine for Rocky Mountain spotted fever. Science. 1987 Jan 2;235(4784):83–85. doi: 10.1126/science.3099387. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- McGuire T. C., Palmer G. H., Goff W. L., Johnson M. I., Davis W. C. Common and isolate-restricted antigens of Anaplasma marginale detected with monoclonal antibodies. Infect Immun. 1984 Sep;45(3):697–700. doi: 10.1128/iai.45.3.697-700.1984. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Meyer T. F., Billyard E., Haas R., Storzbach S., So M. Pilus genes of Neisseria gonorrheae: chromosomal organization and DNA sequence. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1984 Oct;81(19):6110–6114. doi: 10.1073/pnas.81.19.6110. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Meyer T. F., Mlawer N., So M. Pilus expression in Neisseria gonorrhoeae involves chromosomal rearrangement. Cell. 1982 Aug;30(1):45–52. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(82)90010-1. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Palmer G. H., Barbet A. F., Davis W. C., McGuire T. C. Immunization with an isolate-common surface protein protects cattle against anaplasmosis. Science. 1986 Mar 14;231(4743):1299–1302. doi: 10.1126/science.3945825. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Palmer G. H., Kocan K. M., Barron S. J., Hair J. A., Barbet A. F., Davis W. C., McGuire T. C. Presence of common antigens, including major surface protein epitopes, between the cattle (intraerythrocytic) and tick stages of Anaplasma marginale. Infect Immun. 1985 Dec;50(3):881–886. doi: 10.1128/iai.50.3.881-886.1985. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Palmer G. H., McGuire T. C. Immune serum against Anaplasma marginale initial bodies neutralizes infectivity for cattle. J Immunol. 1984 Aug;133(2):1010–1015. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rosenberg M., Court D. Regulatory sequences involved in the promotion and termination of RNA transcription. Annu Rev Genet. 1979;13:319–353. doi: 10.1146/annurev.ge.13.120179.001535. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Segal E., Billyard E., So M., Storzbach S., Meyer T. F. Role of chromosomal rearrangement in N. gonorrhoeae pilus phase variation. Cell. 1985 Feb;40(2):293–300. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(85)90143-6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Shapiro S. Z., August T. The use of immunoprecipitation to study the synthesis and cleavage processing of viral proteins. J Immunol Methods. 1976;13(2):153–159. doi: 10.1016/0022-1759(76)90153-8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wahl G. M., Stern M., Stark G. R. Efficient transfer of large DNA fragments from agarose gels to diazobenzyloxymethyl-paper and rapid hybridization by using dextran sulfate. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1979 Aug;76(8):3683–3687. doi: 10.1073/pnas.76.8.3683. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wood D. O., Atkinson W. H., Sikorski R. S., Winkler H. H. Expression of the Rickettsia prowazekii citrate synthase gene in Escherichia coli. J Bacteriol. 1983 Jul;155(1):412–416. doi: 10.1128/jb.155.1.412-416.1983. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Young R. A., Davis R. W. Efficient isolation of genes by using antibody probes. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1983 Mar;80(5):1194–1198. doi: 10.1073/pnas.80.5.1194. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]