Abstract
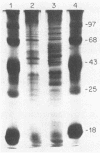
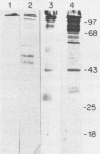
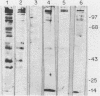
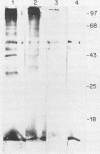
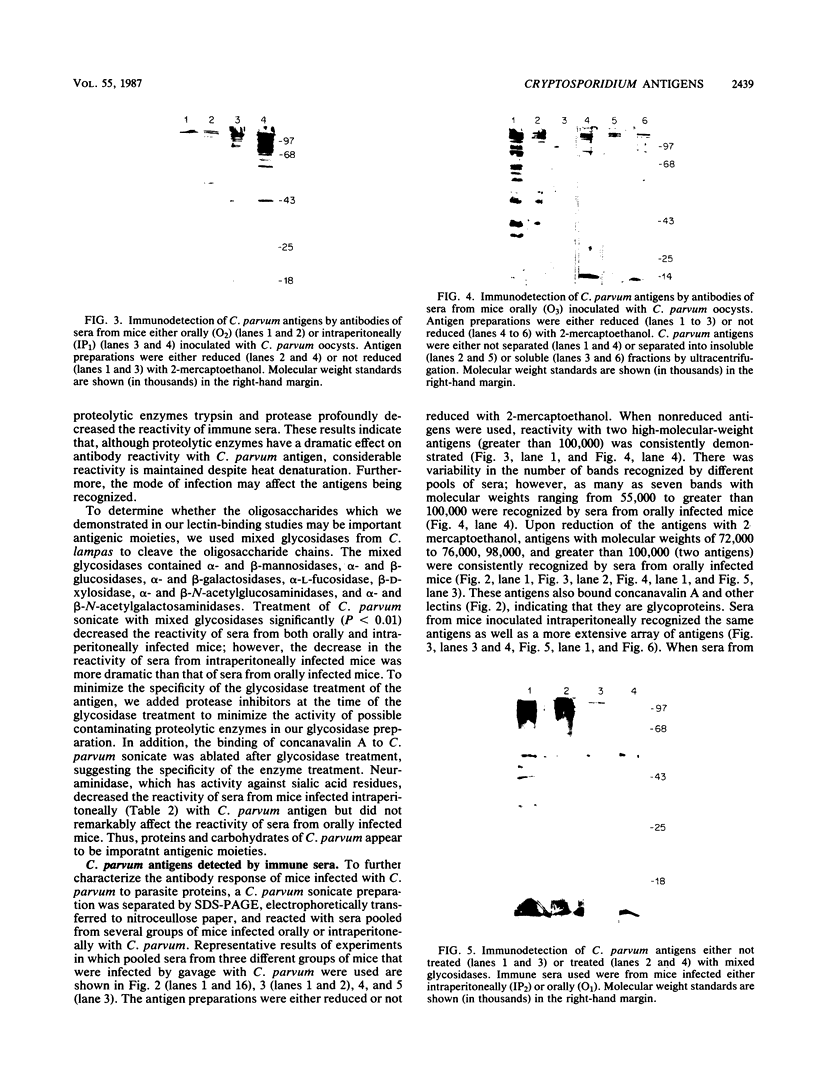
The antigenic constituents of sporulated Cryptosporidium parvum oocyst antigens were characterized with antisera from mice immunized against C. parvum. Sodium dodecyl sulfate-polyacrylamide gel electrophoresis followed by silver staining defined the major proteins. Six of seven lectins used recognized as many as 15 bands. The lectins concanavalin A, Dolichos biflorus, and wheat germ agglutinin showed strong activity against the same eight bands with molecular weights ranging from 72,000 to greater than 100,000. An enzyme-linked immunosorbent assay was used to detect antibody to C. parvum. Antibody binding was significantly decreased by heat and enzymatic treatment with trypsin, protease, and mixed glycosidases. C. parvum antigens were further defined by the reactivity of immune sera with a C. parvum sonicate preparation separated by sodium dodecyl sulfate-polyacrylamide gel electrophoresis and electrophoretically transferred to nitrocellulose paper. Antisera from orally infected mice consistently recognized four antigens with molecular weights ranging from 72,000 to greater than 100,000. These antigens also bound concanavalin A. Treatment of the antigen preparation with mixed glycosidases reduced the reactivity of antisera with most antigens with molecular weights greater than 60,000. The data suggest that the antigenic composition of C. parvum is complex and that carbohydrates alone or in association with lipids or proteins may be important in the immune response to C. parvum.
Full text
PDF




Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Angus K. W., Appleyard W. T., Menzies J. D., Campbell I., Sherwood D. An outbreak of diarrhoea associated with cryptosporidiosis in naturally reared lambs. Vet Rec. 1982 Feb 6;110(6):129–130. doi: 10.1136/vr.110.6.129. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Blagburn B. L., Current W. L. Accidental infection of a researcher with human Cryptosporidium. J Infect Dis. 1983 Oct;148(4):772–773. doi: 10.1093/infdis/148.4.772. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Current W. L., Reese N. C., Ernst J. V., Bailey W. S., Heyman M. B., Weinstein W. M. Human cryptosporidiosis in immunocompetent and immunodeficient persons. Studies of an outbreak and experimental transmission. N Engl J Med. 1983 May 26;308(21):1252–1257. doi: 10.1056/NEJM198305263082102. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hasin M., Rottem S., Razin S. The outer membrane of Proteus mirabilis. I. Isolation and characterization of the outer and cytoplasmic membrane fractions. Biochim Biophys Acta. 1975 Feb 14;375(3):381–394. doi: 10.1016/0005-2736(75)90354-5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Laemmli U. K. Cleavage of structural proteins during the assembly of the head of bacteriophage T4. Nature. 1970 Aug 15;227(5259):680–685. doi: 10.1038/227680a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Liebler E. M., Pohlenz J. F., Woodmansee D. B. Experimental intrauterine infection of adult BALB/c mice with Cryptosporidium sp. Infect Immun. 1986 Oct;54(1):255–259. doi: 10.1128/iai.54.1.255-259.1986. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lis H., Sharon N. The biochemistry of plant lectins (phytohemagglutinins). Annu Rev Biochem. 1973;42(0):541–574. doi: 10.1146/annurev.bi.42.070173.002545. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Naot Y., Guptill D. R., Mullenax J., Remington J. S. Characterization of Toxoplasma gondii antigens that react with human immunoglobulin M and immunoglobulin G antibodies. Infect Immun. 1983 Jul;41(1):331–338. doi: 10.1128/iai.41.1.331-338.1983. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ramasamy R., Reese R. T. A role for carbohydrate moieties in the immune response to malaria. J Immunol. 1985 Mar;134(3):1952–1955. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rottem S., Razin S. Electrophoretic patterns of membrane proteins of Mycoplasma. J Bacteriol. 1967 Aug;94(2):359–364. doi: 10.1128/jb.94.2.359-364.1967. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sharma S. D., Mullenax J., Araujo F. G., Erlich H. A., Remington J. S. Western Blot analysis of the antigens of Toxoplasma gondii recognized by human IgM and IgG antibodies. J Immunol. 1983 Aug;131(2):977–983. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Soave R., Danner R. L., Honig C. L., Ma P., Hart C. C., Nash T., Roberts R. B. Cryptosporidiosis in homosexual men. Ann Intern Med. 1984 Apr;100(4):504–511. doi: 10.7326/0003-4819-100-4-504. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Towbin H., Staehelin T., Gordon J. Electrophoretic transfer of proteins from polyacrylamide gels to nitrocellulose sheets: procedure and some applications. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1979 Sep;76(9):4350–4354. doi: 10.1073/pnas.76.9.4350. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ungar B. L., Nash T. E. Quantification of specific antibody response to Cryptosporidium antigens by laser densitometry. Infect Immun. 1986 Jul;53(1):124–128. doi: 10.1128/iai.53.1.124-128.1986. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wray W., Boulikas T., Wray V. P., Hancock R. Silver staining of proteins in polyacrylamide gels. Anal Biochem. 1981 Nov 15;118(1):197–203. doi: 10.1016/0003-2697(81)90179-2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]