Abstract
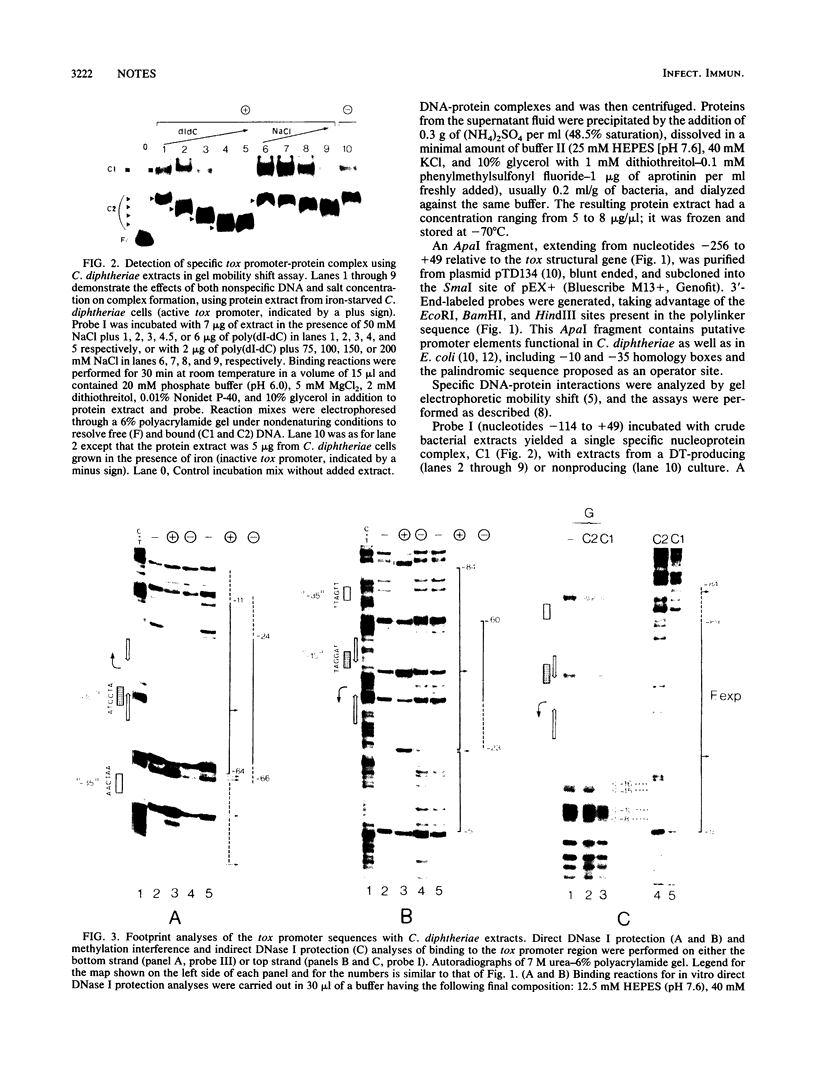
Previous studies provided indirect evidence that in Corynebacterium diphtheriae regulation of diphtheria toxin gene (tox) transcription by iron is mediated by a bacterial repressor. By performing in vitro protein-DNA binding experiments, we establish that a corynebacterial Fe2+-sensitive protein, named DtoxR, can bind to a palindromic motif present in the tox promoter region. Binding of this factor prevents the interaction of the transcription initiation machinery with presumptive critical promoter elements, providing evidence that DtoxR is responsible for the repression of toxinogenesis observed in iron-containing growth medium.
Full text
PDF



Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Bagg A., Neilands J. B. Mapping of a mutation affecting regulation of iron uptake systems in Escherichia coli K-12. J Bacteriol. 1985 Jan;161(1):450–453. doi: 10.1128/jb.161.1.450-453.1985. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bagg A., Neilands J. B. Molecular mechanism of regulation of siderophore-mediated iron assimilation. Microbiol Rev. 1987 Dec;51(4):509–518. doi: 10.1128/mr.51.4.509-518.1987. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Calderwood S. B., Mekalanos J. J. Iron regulation of Shiga-like toxin expression in Escherichia coli is mediated by the fur locus. J Bacteriol. 1987 Oct;169(10):4759–4764. doi: 10.1128/jb.169.10.4759-4764.1987. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Fried M., Crothers D. M. Equilibria and kinetics of lac repressor-operator interactions by polyacrylamide gel electrophoresis. Nucleic Acids Res. 1981 Dec 11;9(23):6505–6525. doi: 10.1093/nar/9.23.6505. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gorski K., Carneiro M., Schibler U. Tissue-specific in vitro transcription from the mouse albumin promoter. Cell. 1986 Dec 5;47(5):767–776. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(86)90519-2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ishii-Kanei C., Uchida T., Yoneda M. Mutants of Corynebacterium diphtheriae PW8 that produce toxin in medium with excess iron. Appl Environ Microbiol. 1981 Dec;42(6):1130–1131. doi: 10.1128/aem.42.6.1130-1131.1981. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Israël A., Kimura A., Kieran M., Yano O., Kanellopoulos J., Le Bail O., Kourilsky P. A common positive trans-acting factor binds to enhancer sequences in the promoters of mouse H-2 and beta 2-microglobulin genes. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1987 May;84(9):2653–2657. doi: 10.1073/pnas.84.9.2653. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kaczorek M., Delpeyroux F., Chenciner N., Streeck R. E., Murphy J. R., Boquet P., Tiollais P. Nucleotide sequence and expression of the diphtheria tox228 gene in Escherichia coli. Science. 1983 Aug 26;221(4613):855–858. doi: 10.1126/science.6348945. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kaczorek M., Zettlmeissl G., Delpeyroux F., Streeck R. E. Diphtheria toxin promoter function in Corynebacterium diphtheriae and Escherichia coli. Nucleic Acids Res. 1985 May 10;13(9):3147–3159. doi: 10.1093/nar/13.9.3147. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Leong D., Murphy J. R. Characterization of the diphtheria tox transcript in Corynebacterium diphtheriae and Escherichia coli. J Bacteriol. 1985 Sep;163(3):1114–1119. doi: 10.1128/jb.163.3.1114-1119.1985. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lichtsteiner S., Wuarin J., Schibler U. The interplay of DNA-binding proteins on the promoter of the mouse albumin gene. Cell. 1987 Dec 24;51(6):963–973. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(87)90583-6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Matsuda M., Barksdale L. System for the investigation of the bacteriophage-directed synthesis of diphtherial toxin. J Bacteriol. 1967 Feb;93(2):722–730. doi: 10.1128/jb.93.2.722-730.1967. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Murphy J. R., Michel J. L., Teng M. Evidence that the regulation of diphtheria toxin production is directed at the level of transcription. J Bacteriol. 1978 Aug;135(2):511–516. doi: 10.1128/jb.135.2.511-516.1978. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Murphy J. R., Pappenheimer A. M., Jr, de Borms S. T. Synthesis of diphtheria tox-gene products in Escherichia coli extracts. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1974 Jan;71(1):11–15. doi: 10.1073/pnas.71.1.11. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Murphy J. R., Skiver J., McBride G. Isolation and partial characterization of a corynebacteriophage beta, tox operator constitutive-like mutant lysogen of Corynebacterium diphtheriae. J Virol. 1976 Apr;18(1):235–244. doi: 10.1128/jvi.18.1.235-244.1976. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Pappenheimer A. M., Jr Diphtheria toxin. Annu Rev Biochem. 1977;46:69–94. doi: 10.1146/annurev.bi.46.070177.000441. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Russell L. M., Cryz S. J., Jr, Holmes R. K. Genetic and biochemical evidence for a siderophore-dependent iron transport system in Corynebacterium diphtheriae. Infect Immun. 1984 Jul;45(1):143–149. doi: 10.1128/iai.45.1.143-149.1984. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Schmitz A., Galas D. J. The interaction of RNA polymerase and lac repressor with the lac control region. Nucleic Acids Res. 1979 Jan;6(1):111–137. doi: 10.1093/nar/6.1.111. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Siebenlist U., Gilbert W. Contacts between Escherichia coli RNA polymerase and an early promoter of phage T7. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1980 Jan;77(1):122–126. doi: 10.1073/pnas.77.1.122. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Siebenlist U., Simpson R. B., Gilbert W. E. coli RNA polymerase interacts homologously with two different promoters. Cell. 1980 Jun;20(2):269–281. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(80)90613-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Simpson R. B. The molecular topography of RNA polymerase-promoter interaction. Cell. 1979 Oct;18(2):277–285. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(79)90047-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Singh H., Sen R., Baltimore D., Sharp P. A. A nuclear factor that binds to a conserved sequence motif in transcriptional control elements of immunoglobulin genes. Nature. 1986 Jan 9;319(6049):154–158. doi: 10.1038/319154a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Tai S. P., Holmes R. K. Iron regulation of the cloned diphtheria toxin promoter in Escherichia coli. Infect Immun. 1988 Sep;56(9):2430–2436. doi: 10.1128/iai.56.9.2430-2436.1988. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Welkos S. L., Holmes R. K. Regulation of toxinogenesis in Corynebacterium diphtheriae. I. Mutations in bacteriophage beta that alter the effects of iron on toxin production. J Virol. 1981 Mar;37(3):936–945. doi: 10.1128/jvi.37.3.936-945.1981. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- de Lorenzo V., Wee S., Herrero M., Neilands J. B. Operator sequences of the aerobactin operon of plasmid ColV-K30 binding the ferric uptake regulation (fur) repressor. J Bacteriol. 1987 Jun;169(6):2624–2630. doi: 10.1128/jb.169.6.2624-2630.1987. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]