Abstract
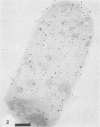
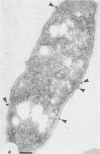
Recombinant plasmids coding for a soluble (or surface) antigen of Pasteurella haemolytica A1 were identified. Two plasmids, both containing the same 5.4 kilobase pairs of insert DNA, were recovered independently by screening a clone band of P. haemolytica A1 genomic DNA in Escherichia coli for the expression of P. haemolytica A1 soluble antigens (R. Y. C. Lo and L.A. Cameron, Can. J. Biochem. Cell Biol. 64:73-76, 1986). E. coli cells carrying the plasmids were found to be agglutinated by an antiserum raised against the P. haemolytica A1 soluble antigens. Analysis of the E. coli clones by electron microscopy revealed patches of amorphous material on the surface of the cells which were not present on the controls. Further characterization with protein A-colloidal gold labeled both these patches and the outer membranes of these cloned cells pretreated with the specific antiserum. These results indicated that the cloned antigen was expressed on the surface of the E. coli cells. The cloned antigen was found to be specific for serotype 1 when tested by slide agglutination against a collection of P. haemolytica typing antisera. Southern blot hybridization, using the cloned DNA as a probe, labeled the genomic DNA from P. haemolytica serotype 1 as well as the cross-agglutinating serotypes 2 and 7, but not DNA from the non-cross-agglutinating serotypes 3 and 4 and Pasteurella multocida. These results demonstrated that serotype specificity could be attributed to the particular antigenic determinants in the genome of the organism.
Full text
PDF





Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Adlam C., Knights J. M., Mugridge A., Lindon J. C., Baker P. R., Beesley J. E., Spacey B., Craig G. R., Nagy L. K. Purification, characterization and immunological properties of the serotype-specific capsular polysaccharide of Pasteurella haemolytica (serotype A1) organisms. J Gen Microbiol. 1984 Sep;130(9):2415–2426. doi: 10.1099/00221287-130-9-2415. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- BIBERSTEIN E. L., GILLS M., KNIGHT H. Serological types of Pasteurella hemolytica. Cornell Vet. 1960 Jul;50:283–300. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Coleman K., Dougan G., Arbuthnott J. P. Cloning, and expression in Escherichia coli K-12, of the chromosomal hemolysin (phospholipase C) determinant of Pseudomonas aeruginosa. J Bacteriol. 1983 Feb;153(2):909–915. doi: 10.1128/jb.153.2.909-915.1983. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Confer A. W., Panciera R. J., Corstvet R. E., Rummage J. A., Fulton R. W. Bovine pneumonic pasteurellosis: effect of culture age of Pasteurella haemolytica used as a live vaccine. Am J Vet Res. 1984 Dec;45(12):2543–2545. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Corstvet R. E., Gentry M. J., Newman P. R., Rummage J. A., Confer A. W. Demonstration of age-dependent capsular material on Pasteurella haemolytica serotype 1. J Clin Microbiol. 1982 Dec;16(6):1123–1126. doi: 10.1128/jcm.16.6.1123-1126.1982. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Donachie W., Burrells C., Dawson A. M. Specificity of the enzyme-linked immunosorbent assay (ELISA) for antibodies in the sera of specific pathogen-free lambs vaccinated with Pasteurella haemolytica antigens. Vet Microbiol. 1983 Apr;8(2):199–205. doi: 10.1016/0378-1135(83)90066-4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Donachie W., Gilmour N. J., Mould D. L., Poxton I. R. Comparison of cell surface antigen extracts from two serotypes of Pasteurella haemolytica. J Gen Microbiol. 1984 May;130(5):1209–1216. doi: 10.1099/00221287-130-5-1209. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Fox M. L., Thomson R. G., Magwood S. E. Pasteurella haemolytica of cattle: serotype, production of beta-galactosidase and antibacterial sensitivity. Can J Comp Med. 1971 Oct;35(4):313–317. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Frank G. H., Wessman G. E. Rapid plate agglutination procedure for serotyping Pasteurella haemolytica. J Clin Microbiol. 1978 Feb;7(2):142–145. doi: 10.1128/jcm.7.2.142-145.1978. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Friend S. C., Wilkie B. N., Thomson R. G., Barnum D. A. Bovine pneumonic pasteurellosis: experimental induction in vaccinated and nonvaccinated calves. Can J Comp Med. 1977 Jan;41(1):77–83. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gilmour N. J., Angus K. W., Donachie W., Fraser J. Vaccination against experimental pneumonic pasteurellosis. Vet Rec. 1982 May 8;110(19):450–450. doi: 10.1136/vr.110.19.450-a. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gray G. L., Smith D. H., Baldridge J. S., Harkins R. N., Vasil M. L., Chen E. Y., Heyneker H. L. Cloning, nucleotide sequence, and expression in Escherichia coli of the exotoxin A structural gene of Pseudomonas aeruginosa. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1984 May;81(9):2645–2649. doi: 10.1073/pnas.81.9.2645. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Holt S. C., Beveridge T. J. Electron microscopy: its development and application to microbiology. Can J Microbiol. 1982 Jan;28(1):1–53. doi: 10.1139/m82-001. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- LOWRY O. H., ROSEBROUGH N. J., FARR A. L., RANDALL R. J. Protein measurement with the Folin phenol reagent. J Biol Chem. 1951 Nov;193(1):265–275. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lessley B. A., Confer A. W., Mosier D. A., Gentry M. J., Durham J. A., Rummage J. A. Saline-extracted antigens of Pasteurella haemolytica: separation by chromatofocusing, preliminary characterization, and evaluation of immunogenicity. Vet Immunol Immunopathol. 1985 Nov;10(2-3):279–296. doi: 10.1016/0165-2427(85)90053-4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lo R. Y., Cameron L. A. A simple immunological detection method for the direct screening of genes from clone banks. Biochem Cell Biol. 1986 Jan;64(1):73–76. doi: 10.1139/o86-012. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lo R. Y., Shewen P. E., Strathdee C. A., Greer C. N. Cloning and expression of the leukotoxin gene of Pasteurella haemolytica A1 in Escherichia coli K-12. Infect Immun. 1985 Dec;50(3):667–671. doi: 10.1128/iai.50.3.667-671.1985. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Martin S. W., Meek A. H., Davis D. G., Johnson J. A., Curtis R. A. Factors associated with morbidity and mortality in feedlot calves: the Bruce County beef project, year two. Can J Comp Med. 1981 Apr;45(2):103–112. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Otulakowski G. L., Shewen P. E., Udoh A. E., Mellors A., Wilkie B. N. Proteolysis of sialoglycoprotein by Pasteurella haemolytica cytotoxic culture supernatant. Infect Immun. 1983 Oct;42(1):64–70. doi: 10.1128/iai.42.1.64-70.1983. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Shewen P. E., Wilkie B. N. Cytotoxin of Pasteurella haemolytica acting on bovine leukocytes. Infect Immun. 1982 Jan;35(1):91–94. doi: 10.1128/iai.35.1.91-94.1982. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wessman G. E., Hilker G. Characterization of Pasteurella hemolytica isolated from the respiratory tract of cattle. Can J Comp Med. 1968 Jul;32(3):498–504. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Yates W. D. A review of infectious bovine rhinotracheitis, shipping fever pneumonia and viral-bacterial synergism in respiratory disease of cattle. Can J Comp Med. 1982 Jul;46(3):225–263. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Yates W. D., Stockdale P. H., Babiuk L. A., Smith R. J. Prevention of experimental bovine pneumonic pasteurellosis with an extract of Pasteurella haemolytica. Can J Comp Med. 1983 Jul;47(3):250–256. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]