Abstract
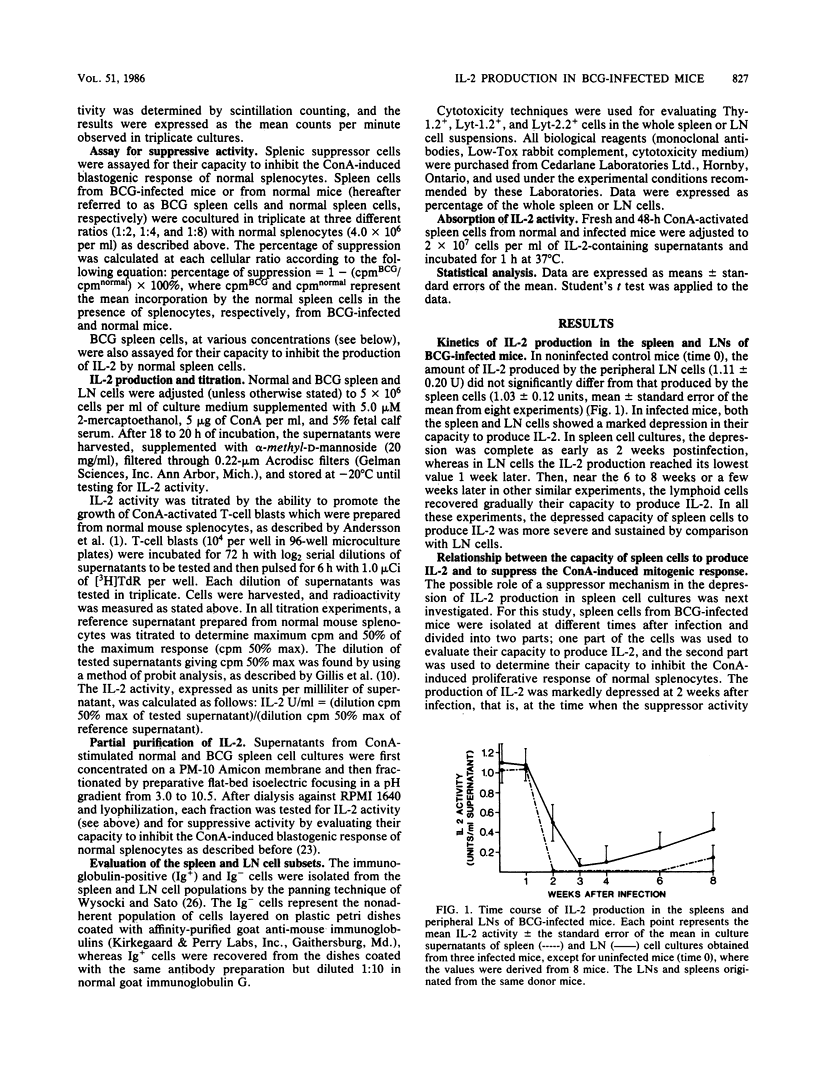
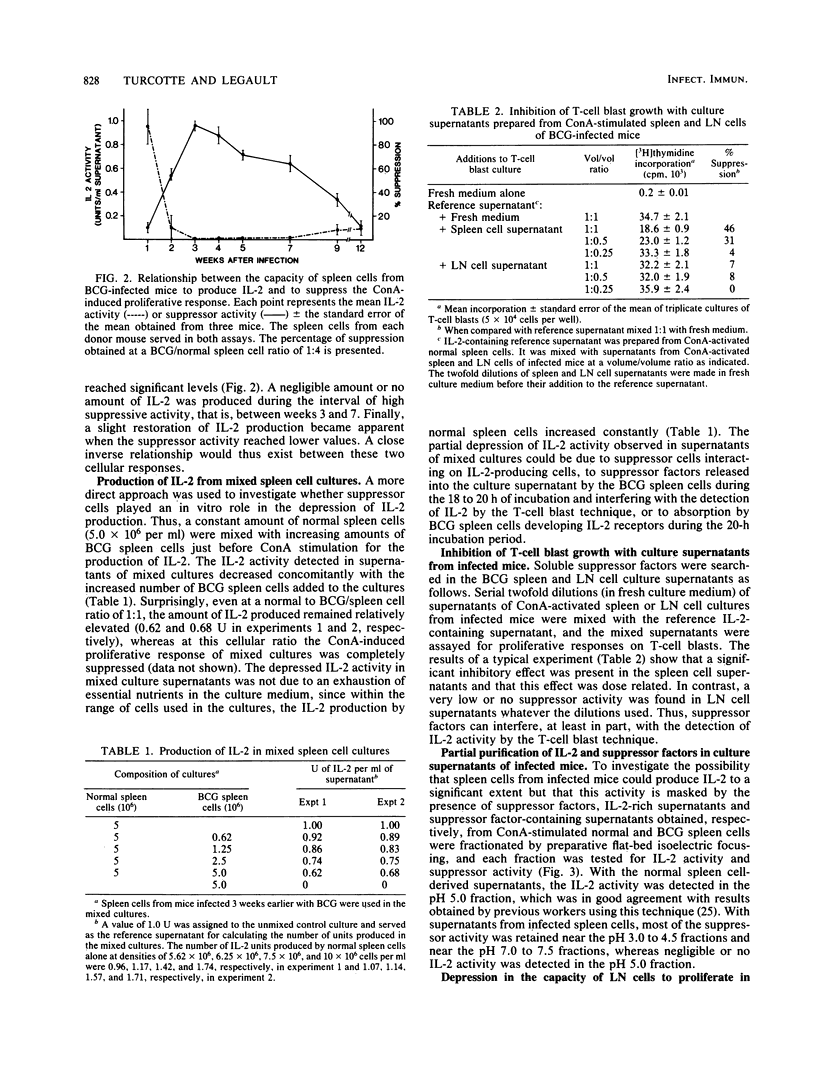
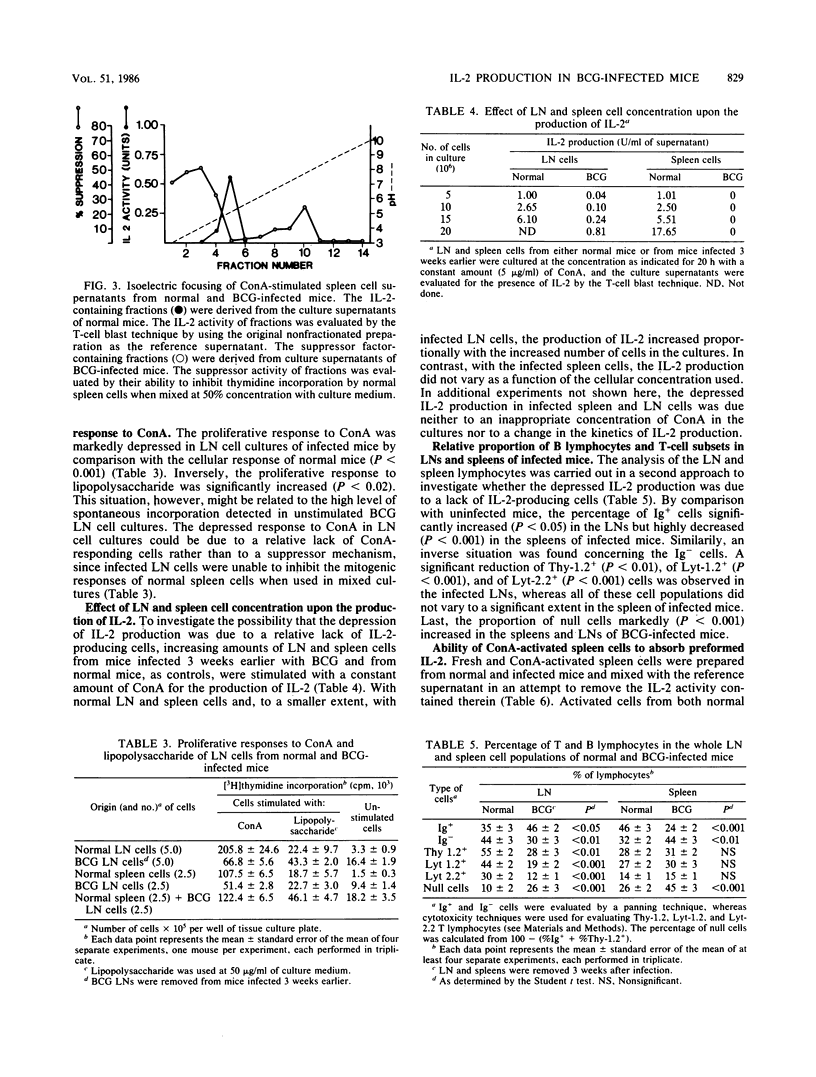
Mice were infected intravenously with 1.0 mg of Mycobacterium bovis BCG. At various times thereafter, spleen and peripheral lymph node cells were stimulated with concanavalin A for 18 to 20 h, and their capacity to produce interleukin-2 (IL-2) was evaluated by means of a T-cell blast proliferation technique. A depression of IL-2 production that was complete in the spleen but partial in lymph node cell cultures occurred at 2 to 3 weeks and persisted till weeks 8 to 10 after infection. No direct evidence was found for an active suppressor mechanism depressing in vitro the production of IL-2. In spleen cell cultures the suppression of IL-2 production would result from a functional defect of the IL-2-producing T-cell subset, whereas in lymph node cell cultures the depression mainly results from a relative lack of IL-2-producing cells caused by an accumulation of immunoglobulin-positive and "null" cells. Spleen cells from BCG-infected mice maintained their capacity to acquire IL-2 receptors when activated by concanavalin A.
Full text
PDF


Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Andersson J., Grönvik K. O., Larsson E. L., Coutinho A. Studies on T lymphocyte activation. I. Requirements for the mitogen-dependent production of T cell growth factors. Eur J Immunol. 1979 Aug;9(8):581–587. doi: 10.1002/eji.1830090802. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Andrus L., Granelli-Piperno A., Reich E. Cytotoxic T cells both produce and respond to interleukin 2. J Exp Med. 1984 Feb 1;159(2):647–652. doi: 10.1084/jem.159.2.647. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Brown C. A., Brown I. N., Sljivić V. S. Suppressed or enhanced antibody responses in vitro after BCG treatment of mice: importance of BCG viability. Immunology. 1979 Nov;38(3):481–488. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Colizzi V., Ferluga J., Garreau F., Malkovsky M., Asherson G. L. Suppressor cells induced by BCG release non-specific factors in vitro which inhibit DNA synthesis and interleukin-2 production. Immunology. 1984 Jan;51(1):65–71. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Collins F. M., Mackaness G. B. The relationship of delayed hypersensitivity to acquired antituberculous immunity. I. Tuberculin sensitivity and resistance to reinfection in BCG-vaccinated mice. Cell Immunol. 1970 Sep;1(3):253–265. doi: 10.1016/0008-8749(70)90047-x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Collins F. M., Watson S. R. Suppressor T-cells in BCG-infected mice. Infect Immun. 1979 Aug;25(2):491–496. doi: 10.1128/iai.25.2.491-496.1979. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Farrar J. J., Benjamin W. R., Hilfiker M. L., Howard M., Farrar W. L., Fuller-Farrar J. The biochemistry, biology, and role of interleukin 2 in the induction of cytotoxic T cell and antibody-forming B cell responses. Immunol Rev. 1982;63:129–166. doi: 10.1111/j.1600-065x.1982.tb00414.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gery I., Navok T., Stupp Y. Selective accumulation of cells with 'B' properties in stimulated lymph nodes. Immunology. 1977 Nov;33(5):727–731. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gillis S., Ferm M. M., Ou W., Smith K. A. T cell growth factor: parameters of production and a quantitative microassay for activity. J Immunol. 1978 Jun;120(6):2027–2032. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Harel-Bellan A., Joskowicz M., Fradelizi D., Eisen H. Modification of T-cell proliferation and interleukin 2 production in mice infected with Trypanosoma cruzi. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1983 Jun;80(11):3466–3469. doi: 10.1073/pnas.80.11.3466. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hoffenbach A., Lagrange P. H., Bach M. A. Influence of dose and route of Mycobacterium lepraemurium inoculation on the production of interleukin 1 and interleukin 2 in C57BL/6 mice. Infect Immun. 1984 Jun;44(3):665–671. doi: 10.1128/iai.44.3.665-671.1984. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kendall L., Sabbadini E. Effect of Bacillus Calmette-Guérin on the in vitro generation of cytotoxic T lymphocytes. I. Effect of BCG on the frequency of cytotoxic T lymphocyte precursors and on the production of helper factors. J Immunol. 1981 Jul;127(1):234–238. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Klimpel G. R., Henney C. S. BCG-induced suppressor cells. I. Demonstration of a macrophage-like suppressor cell that inhibits cytotoxic T cell generation in vitro. J Immunol. 1978 Feb;120(2):563–569. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Klimpel G. R., Okada M., Henney C. S. Inhibition of in vitro cytotoxic responses by BCG-induced macrophage-like suppressor cells. II. Suppression occurs at the level of a "helper" T cell. J Immunol. 1979 Jul;123(1):350–357. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lelchuk R., Rose G., Playfair J. H. Changes in the capacity of macrophages and T cells to produce interleukins during murine malaria infection. Cell Immunol. 1984 Apr 1;84(2):253–263. doi: 10.1016/0008-8749(84)90097-2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mizel S. B. Interleukin 1 and T cell activation. Immunol Rev. 1982;63:51–72. doi: 10.1111/j.1600-065x.1982.tb00411.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Robb R. J., Munck A., Smith K. A. T cell growth factor receptors. Quantitation, specificity, and biological relevance. J Exp Med. 1981 Nov 1;154(5):1455–1474. doi: 10.1084/jem.154.5.1455. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Stadler B. M., Dougherty S. F., Farrar J. J., Oppenheim J. J. Relationship of cell cycle to recovery of IL 2 activity from human mononuclear cells, human and mouse T cell lines. J Immunol. 1981 Nov;127(5):1936–1940. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Turcotte R. Evidence for two distinct populations of suppressor cells in the spleens of Mycobacterium bovis BCG-Sensitized mice. Infect Immun. 1981 Nov;34(2):315–322. doi: 10.1128/iai.34.2.315-322.1981. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Turcotte R., Forget A. Cutaneous unresponsiveness to Mycobacterium bovis BCG in intravenously infected mice. Infect Immun. 1983 Aug;41(2):453–461. doi: 10.1128/iai.41.2.453-461.1983. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Turcotte R., Lemieux S. Mechanisms of action of Mycobacterium bovis BCG-induced suppressor cells in mitogen-induced blastogenesis. Infect Immun. 1982 Apr;36(1):263–270. doi: 10.1128/iai.36.1.263-270.1982. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Watson J. D., Mochizuki D. Y., Gillis S. Molecular characterization of interleukin 2. Fed Proc. 1983 Jul;42(10):2747–2752. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Watson J., Mochizuki D. Interleukin 2: a class of T cell growth factors. Immunol Rev. 1980;51:257–278. doi: 10.1111/j.1600-065x.1980.tb00324.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wysocki L. J., Sato V. L. "Panning" for lymphocytes: a method for cell selection. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1978 Jun;75(6):2844–2848. doi: 10.1073/pnas.75.6.2844. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Zatz M. M. Effects of BCG on lymphocyte trapping. J Immunol. 1976 Jun;116(6):1587–1591. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]


