Abstract
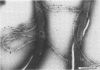
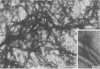
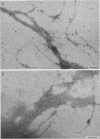
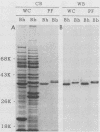
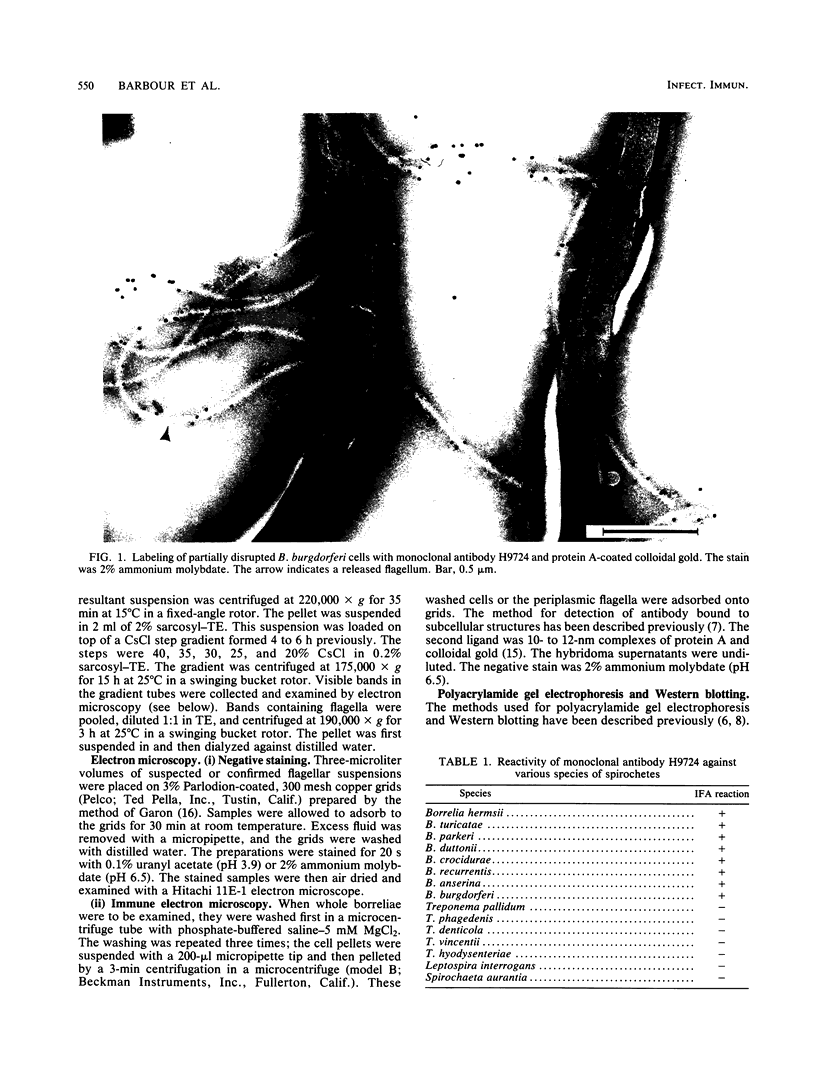
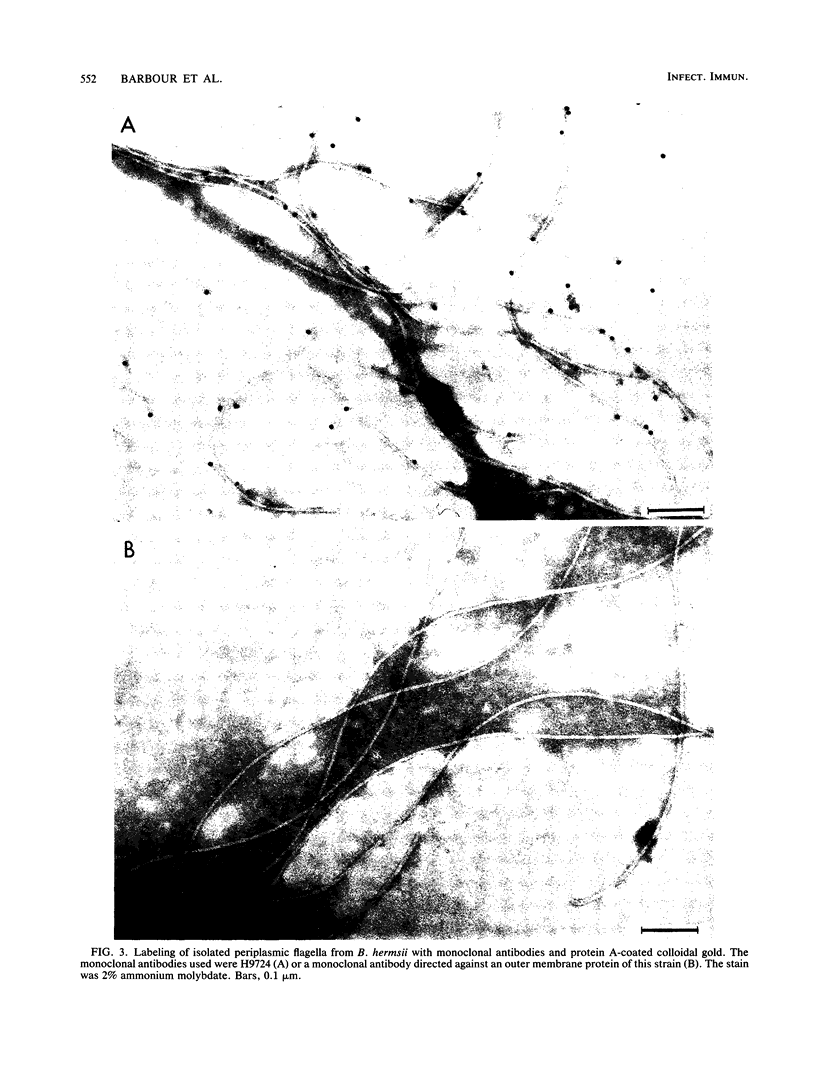
In immunofluorescence assays monoclonal antibody H9724 recognized eight species of the spirochetal genus Borrelia but not representatives of the genera Treponema, Leptospira, and Spirochaeta. We examined the reactivity of H9724 against subcellular components of Borrelia hermsii, an agent of relapsing fever, and B. burgdorferi, the cause of Lyme disease. H9724 bound to isolated periplasmic flagella of the two borreliae. In Western blots the antibody reacted with the predominant protein in flagellar preparations from B. hermsii and B. burgdorferi; the apparent molecular weights of these flagellins were 39,000 and 41,000, respectively.
Full text
PDF



Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Barbour A. G., Barrera O., Judd R. C. Structural analysis of the variable major proteins of Borrelia hermsii. J Exp Med. 1983 Dec 1;158(6):2127–2140. doi: 10.1084/jem.158.6.2127. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Barbour A. G., Burgdorfer W., Grunwaldt E., Steere A. C. Antibodies of patients with Lyme disease to components of the Ixodes dammini spirochete. J Clin Invest. 1983 Aug;72(2):504–515. doi: 10.1172/JCI110998. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Barbour A. G., Heiland R. A., Howe T. R. Heterogeneity of major proteins in Lyme disease borreliae: a molecular analysis of North American and European isolates. J Infect Dis. 1985 Sep;152(3):478–484. doi: 10.1093/infdis/152.3.478. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Barbour A. G. Immunochemical analysis of Lyme disease spirochetes. Yale J Biol Med. 1984 Jul-Aug;57(4):581–586. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Barbour A. G. Isolation and cultivation of Lyme disease spirochetes. Yale J Biol Med. 1984 Jul-Aug;57(4):521–525. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Barbour A. G., Tessier S. L., Hayes S. F. Variation in a major surface protein of Lyme disease spirochetes. Infect Immun. 1984 Jul;45(1):94–100. doi: 10.1128/iai.45.1.94-100.1984. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Barbour A. G., Tessier S. L., Stoenner H. G. Variable major proteins of Borrellia hermsii. J Exp Med. 1982 Nov 1;156(5):1312–1324. doi: 10.1084/jem.156.5.1312. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Barstad P. A., Coligan J. E., Raum M. G., Barbour A. G. Variable major proteins of Borrelia hermsii. Epitope mapping and partial sequence analysis of CNBr peptides. J Exp Med. 1985 Jun 1;161(6):1302–1314. doi: 10.1084/jem.161.6.1302. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bharier M. A., Rittenberg S. C. Chemistry of axial filaments of Treponema zuezerae. J Bacteriol. 1971 Jan;105(1):422–429. doi: 10.1128/jb.105.1.422-429.1971. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bharier M., Allis D. Purification and characterization of axial filaments from Treponema phagedenis biotype reiterii (the Reiter treponeme). J Bacteriol. 1974 Dec;120(3):1434–1442. doi: 10.1128/jb.120.3.1434-1442.1974. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Chang J. Y., Brown D. M., Glazer A. N. Characterization of the subunits of the flagella of Proteus vulgaris. J Biol Chem. 1969 Oct 10;244(19):5196–5200. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Fox G. E., Stackebrandt E., Hespell R. B., Gibson J., Maniloff J., Dyer T. A., Wolfe R. S., Balch W. E., Tanner R. S., Magrum L. J. The phylogeny of prokaryotes. Science. 1980 Jul 25;209(4455):457–463. doi: 10.1126/science.6771870. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Garon C. F. Electron microscopy of nucleic acids. Gene Amplif Anal. 1981;2:573–589. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hardy P. H., Jr, Fredericks W. R., Nell E. E. Isolation and antigenic characteristics of axial filaments from the Reiter Treponeme. Infect Immun. 1975 Feb;11(2):380–386. doi: 10.1128/iai.11.2.380-386.1975. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Holt S. C. Anatomy and chemistry of spirochetes. Microbiol Rev. 1978 Mar;42(1):114–160. doi: 10.1128/mr.42.1.114-160.1978. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Johnson R. C., Hyde F. W., Rumpel C. M. Taxonomy of the Lyme disease spirochetes. Yale J Biol Med. 1984 Jul-Aug;57(4):529–537. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Nell E. E., Hardy P. H., Jr Counterimmunoelectrophoresis of Reiter Treponeme Axial filaments as a diagnostic test for syphilis. J Clin Microbiol. 1978 Aug;8(2):148–152. doi: 10.1128/jcm.8.2.148-152.1978. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Resnick D. Hyperostosis and ossification in the cervical spine. Arthritis Rheum. 1984 May;27(5):564–569. doi: 10.1002/art.1780270513. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Schmid G. P., Steigerwalt A. G., Johnson S. E., Barbour A. G., Steere A. C., Robinson I. M., Brenner D. J. DNA characterization of the spirochete that causes Lyme disease. J Clin Microbiol. 1984 Aug;20(2):155–158. doi: 10.1128/jcm.20.2.155-158.1984. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Stoenner H. G., Dodd T., Larsen C. Antigenic variation of Borrelia hermsii. J Exp Med. 1982 Nov 1;156(5):1297–1311. doi: 10.1084/jem.156.5.1297. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]