Abstract
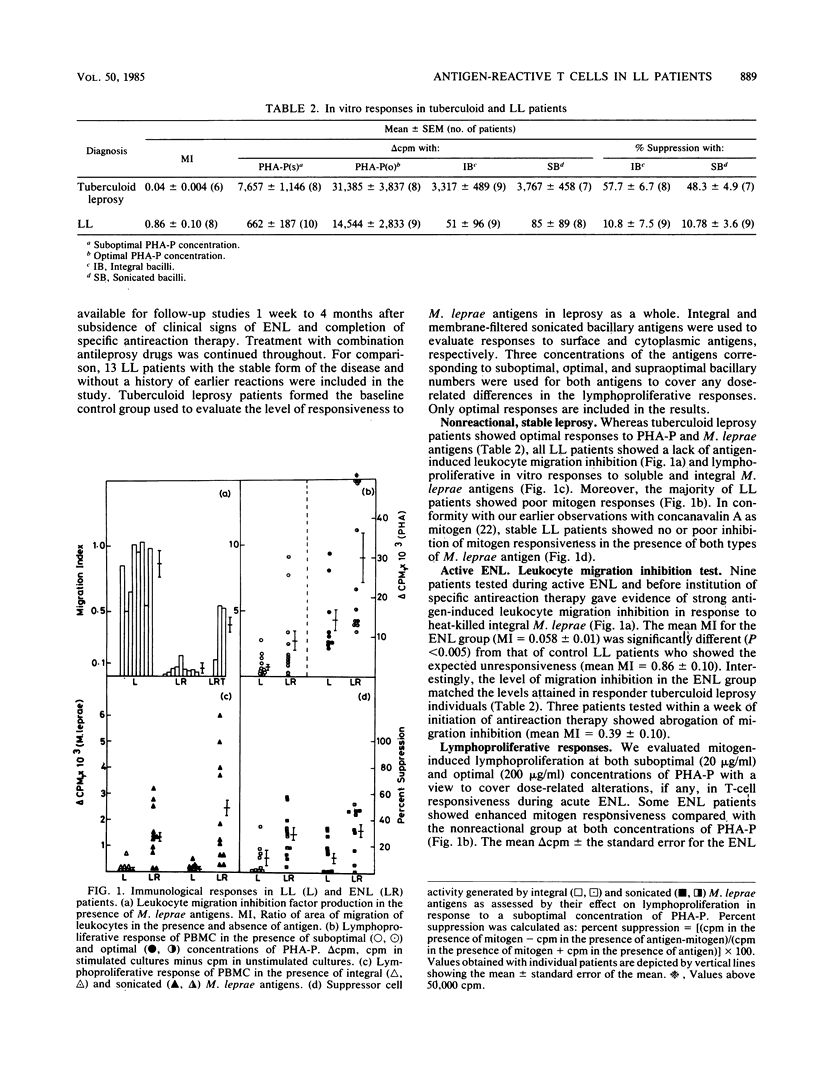
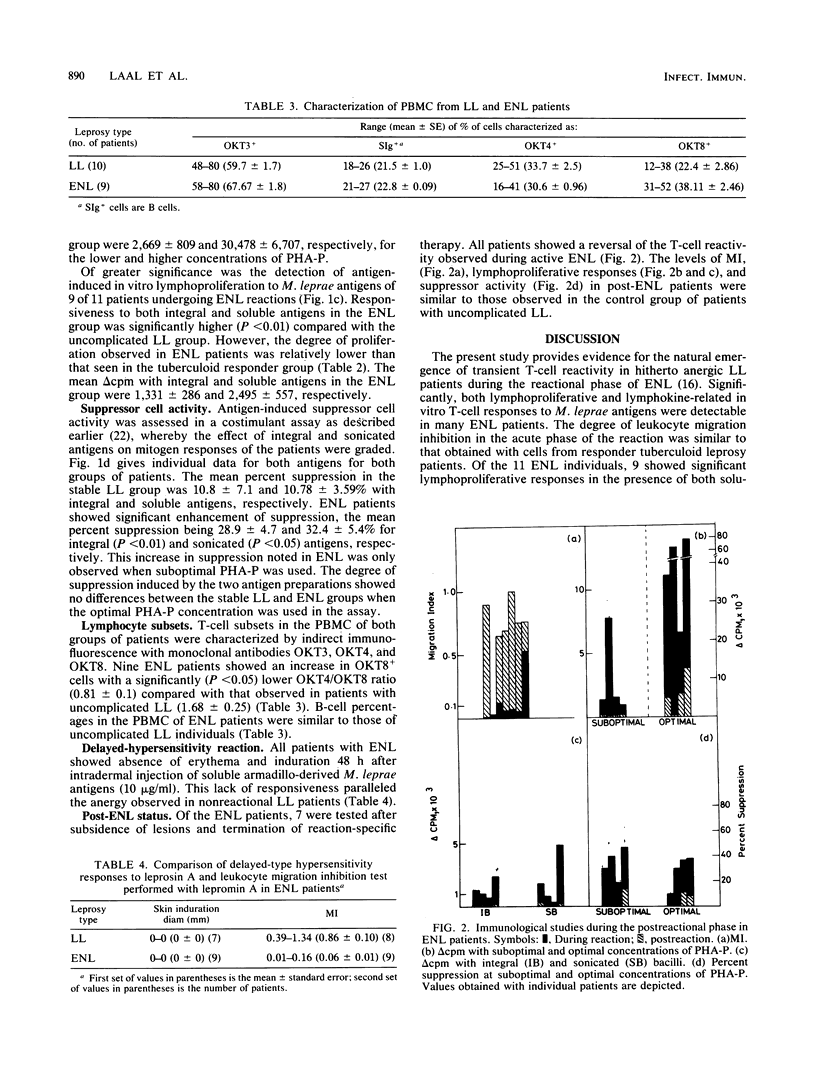
Fifteen lepromatous leprosy (LL) patients undergoing erythema nodosum leprosum (ENL) reactions were compared with 13 stable, uncomplicated, anergic individuals of the same leprosy background. ENL patients showed significant antigen-induced leukocyte migration inhibition (migration index = 0.058 +/- 0.01), paralleling the values obtained with a responder tuberculoid leprosy population (migration index = 0.04 +/- 0.004). Both phytohemagglutinin-induced general T-cell proliferation and, more significantly, antigen-induced lymphoproliferation were enhanced during the acute phase of the reaction. Suppressor cell activity, monitored by a costimulant assay, showed enhanced antigen-stimulated suppression of mitogen responses. Interestingly, the improvement in in vitro T-cell responses was not reflected in dermal reactivity, since 48-h delayed-type hypersensitivity responses after intradermal injection of soluble Mycobacterium leprae antigens continued to be poor. After subsidence of reactional lesions, leukocyte migration inhibition, lymphoproliferation, and suppressor cell activity were reduced to the unresponsive state seen in stable LL patients. Significantly, perturbations of T-cell reactivity are detectable in ENL reactions, indicating the natural but transient emergence of antigen-induced T cells in LL.
Full text
PDF



Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Bjorvatn B., Barnetson R. S., Kronvall G., Zubler R. H., Lambert P. H. Immune complexes and complement hypercatabolism in patients with leprosy. Clin Exp Immunol. 1976 Dec;26(3):388–396. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bullock W. E., Jr, Fasal P. Studies of immune mechanisms in leprosy. 3. The role of cellular and humoral factors in impairment of the in vitro immune response. J Immunol. 1971 Apr;106(4):888–899. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bullock W. E., Watson S., Nelson K. E., Schauf V., Makonkawkeyoon S., Jacobson R. R. Aberrant immunoregulatory control of B lymphocyte function in lepromatous leprosy. Clin Exp Immunol. 1982 Jul;49(1):105–114. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Böyum A. Isolation of mononuclear cells and granulocytes from human blood. Isolation of monuclear cells by one centrifugation, and of granulocytes by combining centrifugation and sedimentation at 1 g. Scand J Clin Lab Invest Suppl. 1968;97:77–89. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Chakrabarty A. K., Maire M. A., Lambert P. H. SDS-PAGE analysis of M. leprae protein antigens reacting with antibodies from sera from lepromatous patients and infected armadillos. Clin Exp Immunol. 1982 Sep;49(3):523–531. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gelber R. H., Drutz D. J., Epstein W. V., Fasal P. Clinical correlates of C1Q-precipitating substances in the sera of patients with leprosy. Am J Trop Med Hyg. 1974 May;23(3):471–475. doi: 10.4269/ajtmh.1974.23.471. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Godal T. Immunological aspects of leprosy--present status. Prog Allergy. 1978;25:211–242. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- HANKS J. H., CHATTERJEE B. R., LECHAT M. F. A GUIDE TO THE COUNTING OF MYCOBACTERIA IN CLINICAL AND EXPERIMENTAL MATERIALS. Int J Lepr. 1964 Apr-Jun;32:156–167. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Haregewoin A., Godal T., Mustafa A. S., Belehu A., Yemaneberhan T. T-cell conditioned media reverse T-cell unresponsiveness in lepromatous leprosy. Nature. 1983 May 26;303(5915):342–344. doi: 10.1038/303342a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mehra V. L., Talwar G. P., Balakrishnan K., Bhutani L. K. Influence of chemotherapy and serum factors on the mitogenic response of peripheral leucocytes of leprosy patients to phytohaemagglutinin. Clin Exp Immunol. 1972 Oct;12(2):205–213. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mehra V., Mason L. H., Rothman W., Reinherz E., Schlossman S. F., Bloom B. R. Delineation of a human T cell subset responsible for lepromin-induced suppression in leprosy patients. J Immunol. 1980 Sep;125(3):1183–1188. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Moran C. J., Ryder G., Turk J. L., Waters M. F. Evidence for circulating immune complexes in lepromatous leprosy. Lancet. 1972 Sep 16;2(7777):572–573. doi: 10.1016/s0140-6736(72)91962-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mshana R. N., Haregewoin A., Harboe M., Belehu A. Thymus dependent lymphocytes in leprosy. I. T lymphocyte subpopulations defined by monoclonal antibodies. Int J Lepr Other Mycobact Dis. 1982 Sep;50(3):291–296. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Myrvang B., Godal T., Ridley D. S., Fröland S. S., Song Y. K. Immune responsiveness to Mycobacterium leprae and other mycobacterial antigens throughout the clinical and histopathological spectrum of leprosy. Clin Exp Immunol. 1973 Aug;14(4):541–553. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Narayanan R. B., Laal S., Sharma A. K., Bhutani L. K., Nath I. Differences in predominant T cell phenotypes and distribution pattern in reactional lesions of tuberculoid and lepromatous leprosy. Clin Exp Immunol. 1984 Mar;55(3):623–628. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Nath I., Curtis J., Sharma A. K., Talwar G. P. Circulating T-cell numbers and their mitogenic potential in leprosy--correlation with mycobacterial load. Clin Exp Immunol. 1977 Sep;29(3):393–400. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Nath I., Narayanan R. B., Mehra N. K., Sharma A. K., Gupte M. D. Concanavalin A induced suppressor activity in human leprosy. J Clin Lab Immunol. 1979 Nov;2(4):319–324. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Nath I., Sathish M., Jayaraman T., Bhutani L. K., Sharma A. K. Evidence for the presence of M. leprae reactive T lymphocytes in patients with lepromatous leprosy. Clin Exp Immunol. 1984 Dec;58(3):522–530. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Nath I., Singh R. The suppressive effect of M. leprae on the in vitro proliferative responses of lymphocytes from patients with leprosy. Clin Exp Immunol. 1980 Sep;41(3):406–414. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Nath I., Van Rood J. J., Mehra N. K., Vaidya M. C. Natural suppressor cells in human leprosy: the role of HLA-D-identical peripheral lymphocytes and macrophages in the in vitro modulation of lymphoproliferative responses. Clin Exp Immunol. 1980 Nov;42(2):203–210. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Nogueira N., Kaplan G., Levy E., Sarno E. N., Kushner P., Granelli-Piperno A., Vieira L., Colomer Gould V., Levis W., Steinman R. Defective gamma interferon production in leprosy. Reversal with antigen and interleukin 2. J Exp Med. 1983 Dec 1;158(6):2165–2170. doi: 10.1084/jem.158.6.2165. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Prasad H. K., Nath I. Incorporation of 3H-thymidine in Mycobacterium leprae within differentiated human macrophages. J Med Microbiol. 1981 Aug;14(3):279–293. doi: 10.1099/00222615-14-3-279. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rea T. H., Bakke A. C., Parker J. W., Modlin R. L., Horwitz D. A. Peripheral blood T lymphocyte subsets in leprosy. Int J Lepr Other Mycobact Dis. 1984 Sep;52(3):311–317. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rea T. H., Levan N. E. Variations in dinitrochlorobenzene responsivity in untreated leprosy: evidence of a beneficial role for anergy. Int J Lepr Other Mycobact Dis. 1980 Jun;48(2):120–125. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ridley D. S., Jopling W. H. Classification of leprosy according to immunity. A five-group system. Int J Lepr Other Mycobact Dis. 1966 Jul-Sep;34(3):255–273. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Salgame P. R., Mahadevan P. R., Antia N. H. Mechanism of immunosuppression in leprosy: presence of suppressor factor(s) from macrophages of lepromatous patients. Infect Immun. 1983 Jun;40(3):1119–1126. doi: 10.1128/iai.40.3.1119-1126.1983. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sathish M., Bhutani L. K., Sharma A. K., Nath I. Monocyte-derived soluble suppressor factor(s) in patients with lepromatous leprosy. Infect Immun. 1983 Dec;42(3):890–899. doi: 10.1128/iai.42.3.890-899.1983. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Shannon E. J., Powell M. D., Kirchheimer W. F., Hastings R. C. Effects of Mycobacterium leprae antigens on the in vitro responsiveness of mononuclear cells from armadillos to concanavalin-A. Lepr Rev. 1984 Mar;55(1):19–31. doi: 10.5935/0305-7518.19840003. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Stoner G. L., Mshana R. N., Touw J., Belehu A. Studies on the defect in cell-mediated immunity in lepromatous leprosy using HLA-D-identical siblings. Absence of circulating suppressor cells and evidence that the defect is in the T-lymphocyte, rather than the monocyte, population. Scand J Immunol. 1982 Jan;15(1):33–48. doi: 10.1111/j.1365-3083.1982.tb00619.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wallach D., Cottenot F., Bach M. A. Imbalances in T cell subpopulations in lepromatous leprosy. Int J Lepr Other Mycobact Dis. 1982 Sep;50(3):282–290. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Waters M. F., Turk J. L., Wemambu S. N. Mechanisms of reactions in leprosy. Int J Lepr Other Mycobact Dis. 1971 Apr-Jun;39(2):417–428. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wemambu S. N., Turk J. L., Waters M. F., Rees R. J. Erythema nodosum leprosum: a clinical manifestation of the arthus phenomenon. Lancet. 1969 Nov 1;2(7627):933–935. doi: 10.1016/s0140-6736(69)90592-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]


