Abstract
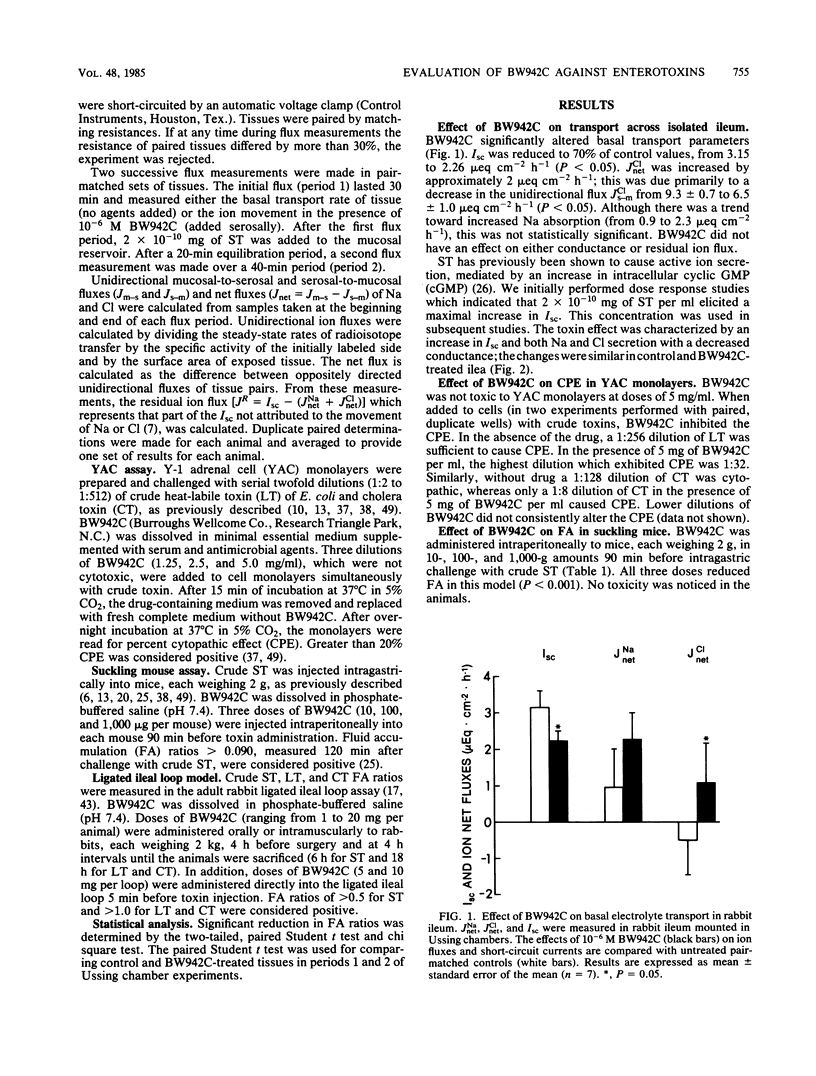
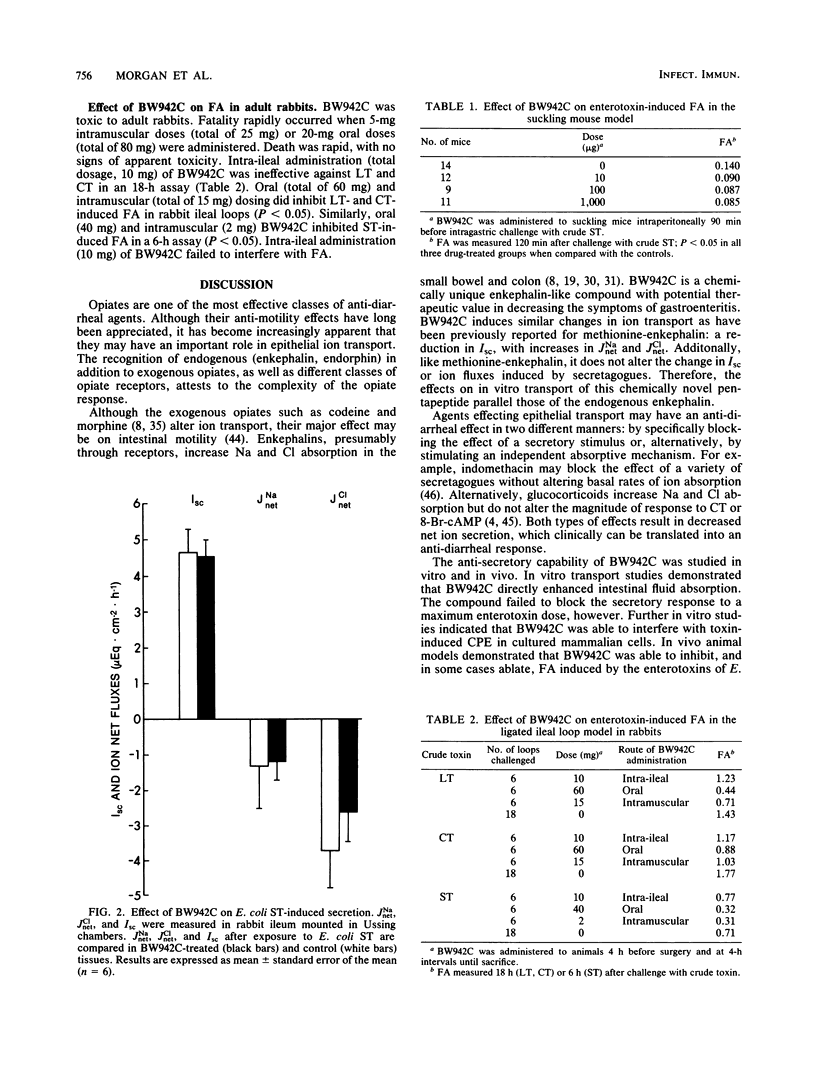
BW942C, an enkephalin-like pentapeptide with anti-diarrheal activity, was tested against crude toxins of Escherichia coli and Vibrio cholerae in the Y-1 adrenal cell assay, rabbit ileal loop assay, and suckling mouse assay. The effects of BW942C on in vitro ion transport were measured in rabbit ileum mounted in Ussing chambers. In vitro, BW942C decreased basal short-circuit current (2.26 and 3.15 mueq cm-2 h-1 in experimental samples and controls, respectively; n = 7, P less than 0.05) and increased basal net Cl absorption (1.59 and 0.50 mueq cm-2 h-1 in experimental samples and controls, respectively; P less than 0.025). Net Na absorption was also increased, but not significantly. BW942C did not block the secretory response to a maximal dose of purified heat-stable toxin. BW942C directly enhanced intestinal fluid absorption. In the Y-1 adrenal cell assay, 5 mg of BW942C per ml inhibited the cytopathic effect caused by cholera toxin or heat-labile enterotoxin of E. coli. In the rabbit ileal loop assay, E. coli heat-stable toxin, E. coli heat-labile enterotoxin, and cholera toxin were inhibited 35 to 70% by administration of BW942C. With the suckling mouse model, the fluid accumulation caused by E. coli heat-stable toxin was ablated by prior treatment with BW942C. The drug is currently being evaluated in patients with acute secretory diarrhea to determine its effect on clinical symptoms.
Full text
PDF


Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Abbey D. M., Knoop F. C. Effect of chlorpromazine on the secretory activity of Escherichia coli heat-stable enterotoxin. Infect Immun. 1979 Dec;26(3):1000–1003. doi: 10.1128/iai.26.3.1000-1003.1979. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Brostrom M. A., Brostrom C. O., Huang S. C., Wolff D. J. Cholera toxin-stimulated cyclic AMP accumulation in glial tumor cells: modulation by Ca2+. Mol Pharmacol. 1981 Jul;20(1):59–67. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Charney A. N., Donowitz M. Prevention and reversal of cholera enterotoxin-induced intestinal secretion by methylprednisolone induction of Na+-K+-ATPase. J Clin Invest. 1976 Jun;57(6):1590–1599. doi: 10.1172/JCI108429. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Cuatrecasas P. Interaction of Vibrio cholerae enterotoxin with cell membranes. Biochemistry. 1973 Aug 28;12(18):3547–3558. doi: 10.1021/bi00742a031. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Dean A. G., Ching Y. C., Williams R. G., Harden L. B. Test for Escherichia coli enterotoxin using infant mice: application in a study of diarrhea in children in Honolulu. J Infect Dis. 1972 Apr;125(4):407–411. doi: 10.1093/infdis/125.4.407. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Dietz J., Field M. Ion transport in rabbit ileal mucosa. IV. Bicarbonate secretion. Am J Physiol. 1973 Oct;225(4):858–861. doi: 10.1152/ajplegacy.1973.225.4.858. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Dobbins J., Racusen L., Binder H. J. Effect of D-alanine methionine enkephalin amide on ion transport in rabbit ileum. J Clin Invest. 1980 Jul;66(1):19–28. doi: 10.1172/JCI109830. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Donowitz M., Charney A. N. Propranolol prevention of cholera enterotoxin-induced intestinal secretion in the rat. Gastroenterology. 1979 Mar;76(3):482–491. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Donta S. T., Smith D. M. Stimulation of steroidogenesis in tissue culture by enterotoxigenic Escherichia coli and its neutralization by specific antiserum. Infect Immun. 1974 Mar;9(3):500–505. doi: 10.1128/iai.9.3.500-505.1974. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Dreyfus L. A., Jaso-Friedmann L., Robertson D. C. Characterization of the mechanism of action of Escherichia coli heat-stable enterotoxin. Infect Immun. 1984 May;44(2):493–501. doi: 10.1128/iai.44.2.493-501.1984. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- DuPont H. L., Olarte J., Evans D. G., Pickering L. K., Galindo E., Evans D. J. Comparative susceptibility of latin american and united states students to enteric pathogens. N Engl J Med. 1976 Dec 30;295(27):1520–1521. doi: 10.1056/NEJM197612302952707. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- DuPont H. L., Sullivan P., Evans D. G., Pickering L. K., Evans D. J., Jr, Vollet J. J., Ericsson C. D., Ackerman P. B., Tjoa W. S. Prevention of traveler's diarrhea (emporiatric enteritis). Prophylactic administration of subsalicylate bismuth). JAMA. 1980 Jan 18;243(3):237–241. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- DuPont H. L., Sullivan P., Pickering L. K., Haynes G., Ackerman P. B. Symptomatic treatment of diarrhea with bismuth subsalicylate among students attending a Mexican university. Gastroenterology. 1977 Oct;73(4 Pt 1):715–718. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ericsson C. D., Evans D. G., DuPont H. L., Evans D. J., Jr, Pickering L. K. Bismuth subsalicylate inhibits activity of crude toxins of Escherichia coli and Vibrio cholerae. J Infect Dis. 1977 Nov;136(5):693–696. doi: 10.1093/infdis/136.5.693. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Evans D. G., Evans D. J., Jr, Pierce N. F. Differences in the response of rabbit small intestine to heat-labile and heat-stable enterotoxins of Escherichia coli. Infect Immun. 1973 Jun;7(6):873–880. doi: 10.1128/iai.7.6.873-880.1973. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Field M. Mechanisms of action of cholera and Escherichia coli enterotoxins. Am J Clin Nutr. 1979 Jan;32(1):189–196. doi: 10.1093/ajcn/32.1.189. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Fogel R., Kaplan R. B. Role of enkephalins in regulation of basal intestinal water and ion absorption in the rat. Am J Physiol. 1984 Apr;246(4 Pt 1):G386–G392. doi: 10.1152/ajpgi.1984.246.4.G386. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Giannella R. A. Suckling mouse model for detection of heat-stable Escherichia coli enterotoxin: characteristics of the model. Infect Immun. 1976 Jul;14(1):95–99. doi: 10.1128/iai.14.1.95-99.1976. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gill D. M., Meren R. ADP-ribosylation of membrane proteins catalyzed by cholera toxin: basis of the activation of adenylate cyclase. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1978 Jul;75(7):3050–3054. doi: 10.1073/pnas.75.7.3050. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gorbach S. L., Kean B. H., Evans D. G., Evans D. J., Jr, Bessudo D. Travelers' diarrhea and toxigenic Escherichia coli. N Engl J Med. 1975 May 1;292(18):933–936. doi: 10.1056/NEJM197505012921801. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gots R. E., Formal S. B., Giannella R. A. Indomethacin inhibition of Salmonella typhimurium, Shigella flexneri, and cholera-mediated rabbit ileal secretion. J Infect Dis. 1974 Sep;130(3):280–284. doi: 10.1093/infdis/130.3.280. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Greenberg R. N., Dunn J. A. Evaluation of low-dose pharmacological combinations for inhibition of the effects of Escherichia coli heat-stable enterotoxin in suckling mice. J Infect Dis. 1984 Feb;149(2):280–280. doi: 10.1093/infdis/149.2.280. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Greenberg R. N., Murad F., Chang B., Robertson D. C., Guerrant R. L. Inhibition of Escherichia coli heat-stable enterotoxin by indomethacin and chlorpromazine. Infect Immun. 1980 Sep;29(3):908–913. doi: 10.1128/iai.29.3.908-913.1980. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Guandalini S., Rao M. C., Smith P. L., Field M. cGMP modulation of ileal ion transport: in vitro effects of Escherichia coli heat-stable enterotoxin. Am J Physiol. 1982 Jul;243(1):G36–G41. doi: 10.1152/ajpgi.1982.243.1.G36. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Guerrant R. L., Hughes J. M., Chang B., Robertson D. C., Murad F. Activation of intestinal guanylate cyclase by heat-stable enterotoxin of Escherichia coli: studies of tissue specificity, potential receptors, and intermediates. J Infect Dis. 1980 Aug;142(2):220–228. doi: 10.1093/infdis/142.2.220. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Holmgren J., Lange S., Lönnroth I. Reversal of cyclic AMP-mediated intestinal secretion in mice by chlorpromazine. Gastroenterology. 1978 Dec;75(6):1103–1108. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kachur J. F., Miller R. J. Characterization of the opiate receptor in the guinea-pig ileal mucosa. Eur J Pharmacol. 1982 Jul 9;81(2):177–183. doi: 10.1016/0014-2999(82)90435-6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kachur J. F., Miller R. J., Field M. Control of guinea pig intestinal electrolyte secretion by a delta-opiate receptor. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1980 May;77(5):2753–2756. doi: 10.1073/pnas.77.5.2753. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Knoop F. C., Abbey D. M. Effect of chemical and pharmacological agents on the secretory activity induced by Escherichia coli heat-stable enterotoxin. Can J Microbiol. 1981 Aug;27(8):754–758. doi: 10.1139/m81-117. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Knoop F. C., Thomas D. D. Effect of lodoxamide on the secretory response induced by Escherichia coli and Vibrio cholerae enterotoxins in infant mice. Infect Immun. 1984 May;44(2):406–408. doi: 10.1128/iai.44.2.406-408.1984. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Madsen G. L., Knoop F. C. Inhibition of the secretory activity of Escherichia coli heat-stable enterotoxin by indomethacin. Infect Immun. 1978 Oct;22(1):143–147. doi: 10.1128/iai.22.1.143-147.1978. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- McKay J. S., Linaker B. D., Turnberg L. A. Influence of opiates on ion transport across rabbit ileal mucosa. Gastroenterology. 1981 Feb;80(2):279–284. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Miller G. C., Murgo A. J., Plotnikoff N. P. Enkephalins--enhancement of active T-cell rosettes from lymphoma patients. Clin Immunol Immunopathol. 1983 Mar;26(3):446–451. doi: 10.1016/0090-1229(83)90131-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Morgan D. R., DuPont H. L., Wood L. V., Ericsson C. D. Comparison of methods to detect Escherichia coli heat-labile enterotoxin in stool and cell-free culture supernatants. J Clin Microbiol. 1983 Oct;18(4):798–802. doi: 10.1128/jcm.18.4.798-802.1983. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Newsome P. M., Burgess M. N., Mullan N. A. Effect of Escherichia coli heat-stable enterotoxin on cyclic GMP levels in mouse intestine. Infect Immun. 1978 Oct;22(1):290–291. doi: 10.1128/iai.22.1.290-291.1978. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Pelemans W., Vantrappen F. A double blind crossover comparison of loperamide with diphenoxylate in the symptomatic treatment of chronic diarrhea. Gastroenterology. 1976 Jun;70(6):1030–1034. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Pierce N. F., Wallace C. K. Stimulation of jejunal secretion by a crude Escherichia coli enterotixin. Gastroenterology. 1972 Sep;63(6):439–448. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Schiller L. R., Santa Ana C. A., Morawski S. G., Fordtran J. S. Mechanism of the antidiarrheal effect of loperamide. Gastroenterology. 1984 Jun;86(6):1475–1480. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sellin J. H., Field M. Physiologic and pharmacologic effects of glucocorticoids on ion transport across rabbit ileal mucosa in vitro. J Clin Invest. 1981 Mar;67(3):770–778. doi: 10.1172/JCI110094. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Smith P. L., Blumberg J. B., Stoff J. S., Field M. Antisecretory effects of indomethacin on rabbit ileal mucosa in vitro. Gastroenterology. 1981 Feb;80(2):356–365. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Steffen R., van der Linde F., Gyr K., Schär M. Epidemiology of diarrhea in travelers. JAMA. 1983 Mar 4;249(9):1176–1180. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Thomas D. D., Knoop F. C. The effect of calcium and prostaglandin inhibitors on the intestinal fluid response to heat-stable enterotoxin of Escherichia coli. J Infect Dis. 1982 Feb;145(2):141–147. doi: 10.1093/infdis/145.2.141. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wood L. V., Wolfe W. H., Ruiz-Palacios G., Foshee W. S., Corman L. I., McCleskey F., Wright J. A., DuPont H. L. An outbreak of gastroenteritis due to a heat-labile enterotoxin-producing strain of Escherichia coli. Infect Immun. 1983 Sep;41(3):931–934. doi: 10.1128/iai.41.3.931-934.1983. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]


