Abstract
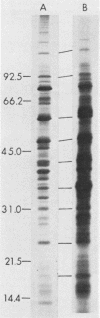
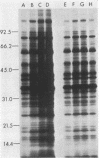
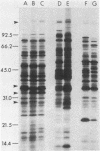
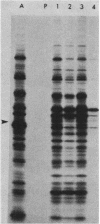
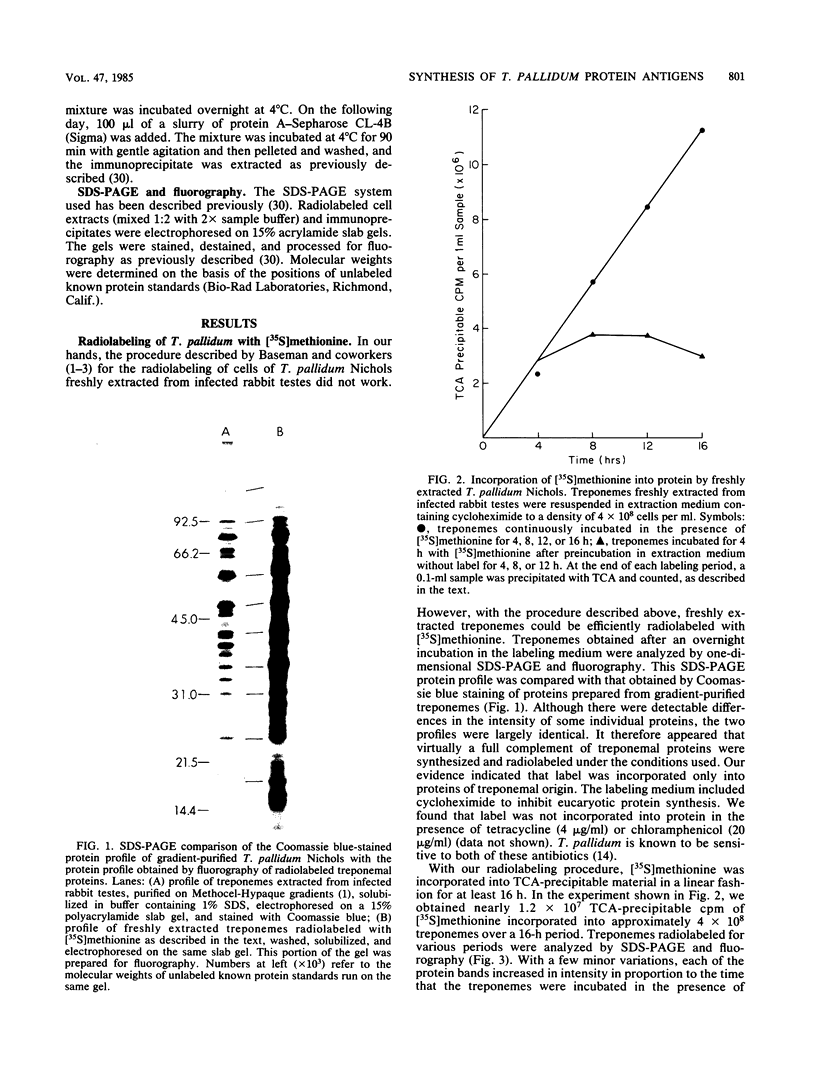
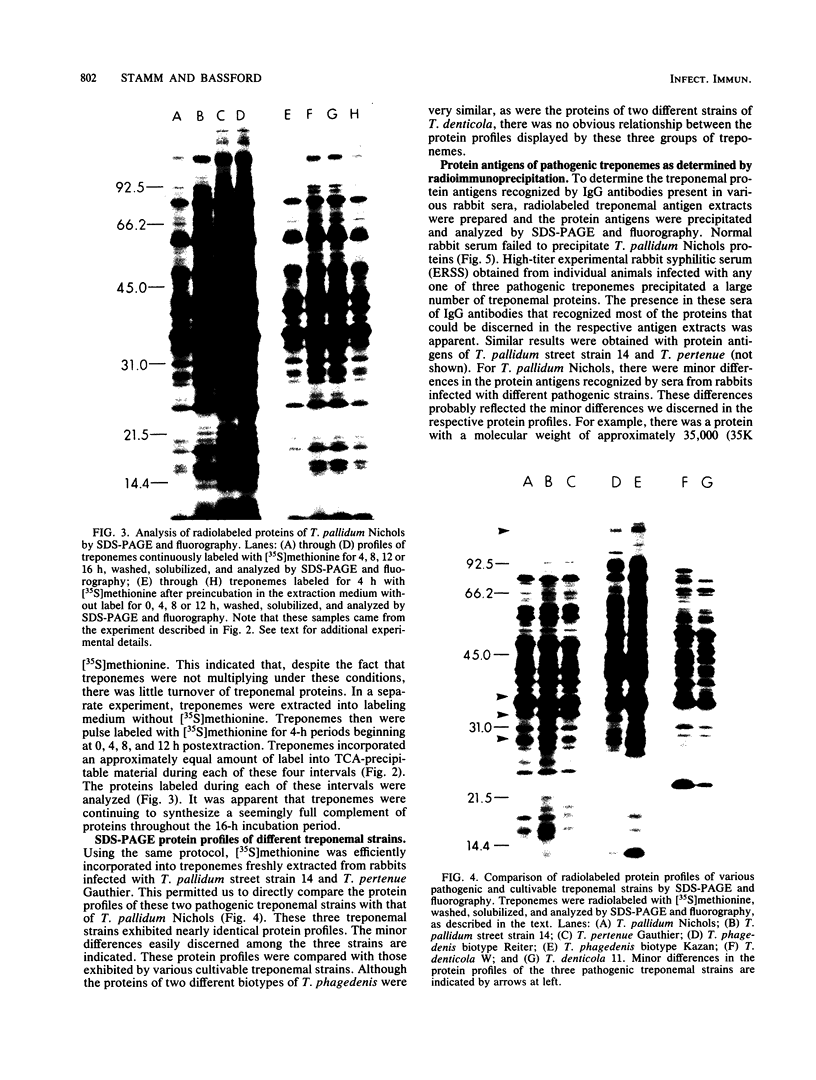
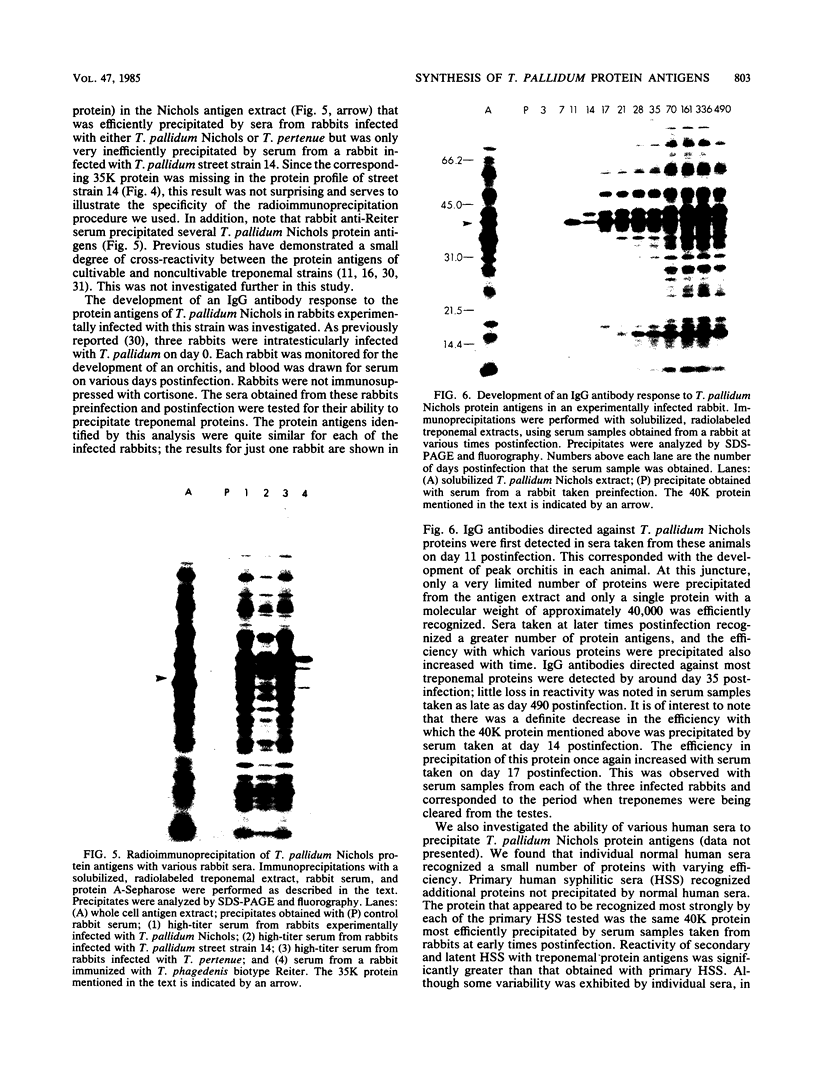
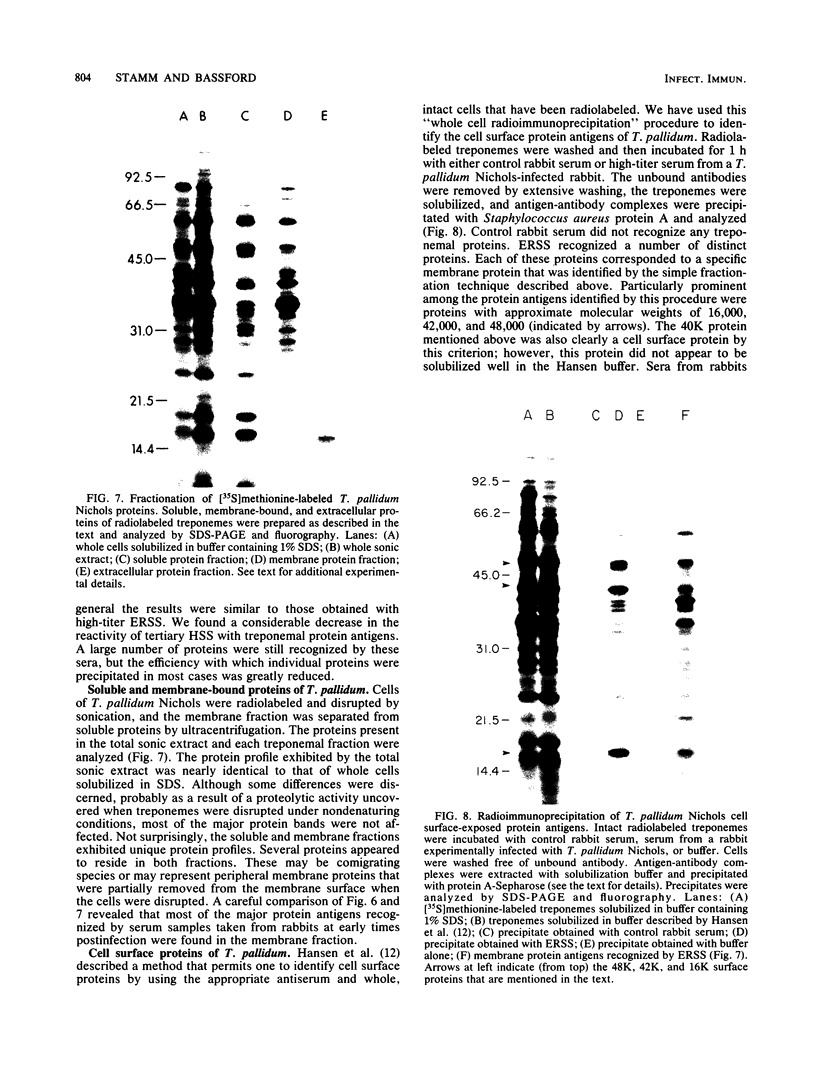
A new medium that permits radiolabeling of freshly extracted cells of Treponema pallidum with [35S]methionine very efficiently has been devised. Although treponemes were not purified free of contaminating rabbit tissue, label was incorporated exclusively into treponemal protein in a linear manner for at least the first 16 h of in vitro incubation. Throughout this period, virtually a full complement of treponemal proteins was synthesized, based on a sodium dodecyl sulfate-polyacrylamide gel electrophoresis comparison of the radiolabeled protein profile with the Coomassie blue-stained profile of gradient-purified treponemes. The radiolabeled protein profiles obtained with three pathogenic strains were very similar but not identical. Using solubilized treponemal extracts and a sensitive radioimmunoprecipitation procedure, we identified the protein antigens of T. pallidum that were recognized by immunoglobulin G antibodies in various rabbit and human syphilitic sera. A simple fractionation procedure has been used to separate soluble and membrane-bound treponemal proteins. A number of the membrane proteins are exposed on the cell surface, since intact radiolabeled treponemes bound antibodies directed against these proteins. In addition, a unique class of low-molecular-weight extracellular treponemal proteins has been identified. The cell surface-exposed proteins were among the earliest proteins recognized by immunoglobulin G antibodies after experimental infection of rabbits with T. pallidum.
Full text
PDF




Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Alderete J. F., Baseman J. B. Analysis of serum IgG against Treponema pallidum protein antigens in experimentally infected rabbits. Br J Vener Dis. 1981 Oct;57(5):302–308. doi: 10.1136/sti.57.5.302. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Alderete J. F., Baseman J. B. Surface characterization of virulent Treponema pallidum. Infect Immun. 1980 Dec;30(3):814–823. doi: 10.1128/iai.30.3.814-823.1980. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Alderete J. F., Baseman J. B. Surface-associated host proteins on virulent Treponema pallidum. Infect Immun. 1979 Dec;26(3):1048–1056. doi: 10.1128/iai.26.3.1048-1056.1979. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Baker-Zander S. A., Lukehart S. A. Molecular basis of immunological cross-reactivity between Treponema pallidum and Treponema pertenue. Infect Immun. 1983 Nov;42(2):634–638. doi: 10.1128/iai.42.2.634-638.1983. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Baseman J. B., Hayes E. C. Molecular characterization of receptor binding proteins and immunogens of virulent Treponema pallidum. J Exp Med. 1980 Mar 1;151(3):573–586. doi: 10.1084/jem.151.3.573. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Baseman J. B., Hayes N. S. Anabolic potential of virulent Treponema pallidum. Infect Immun. 1977 Dec;18(3):857–859. doi: 10.1128/iai.18.3.857-859.1977. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Baseman J. B., Hayes N. S. Protein synthesis by Treponema pallidum extracted from infected rabbit tissue. Infect Immun. 1974 Dec;10(6):1350–1355. doi: 10.1128/iai.10.6.1350-1355.1974. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- HARDY P. H., Jr, NELL E. E. Study of the antigenic structure of Treponema pallidum by specific agglutination. Am J Hyg. 1957 Sep;66(2):160–172. doi: 10.1093/oxfordjournals.aje.a119893. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hanff P. A., Bishop N. H., Miller J. N., Lovett M. A. Humoral immune response in experimental syphilis to polypeptides of Treponema pallidum. J Immunol. 1983 Oct;131(4):1973–1977. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hanff P. A., Fehniger T. E., Miller J. N., Lovett M. A. Humoral immune response in human syphilis to polypeptides of Treponema pallidum. J Immunol. 1982 Sep;129(3):1287–1291. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hanff P. A., Miller J. N., Lovett M. A. Molecular characterization of common treponemal antigens. Infect Immun. 1983 May;40(2):825–828. doi: 10.1128/iai.40.2.825-828.1983. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hansen E. J., Frisch C. F., Johnston K. H. Detection of antibody-accessible proteins on the cell surface of Haemophilus influenzae type b. Infect Immun. 1981 Sep;33(3):950–953. doi: 10.1128/iai.33.3.950-953.1981. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Jacob E., Allen A. L., Nauman R. K. Detection of oral anaerobic spirochetes in dental plaque by the indirect fluorescent-antibody technique. J Clin Microbiol. 1979 Dec;10(6):934–936. doi: 10.1128/jcm.10.6.934-936.1979. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lukehart S. A., Baker-Zander S. A., Gubish E. R., Jr Identification of Treponema pallidum antigens: comparison with a nonpathogenic treponeme. J Immunol. 1982 Aug;129(2):833–838. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lukehart S. A., Baker-Zander S. A., Lloyd R. M., Sell S. Characterization of lymphocyte responsiveness in early experimental syphilis. II. Nature of cellular infiltration and Treponema pallidum distribution in testicular lesions. J Immunol. 1980 Jan;124(1):461–467. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Marchitto K. S., Jones S. A., Schell R. F., Holmans P. L., Norgard M. V. Monoclonal antibody analysis of specific antigenic similarities among pathogenic Treponema pallidum subspecies. Infect Immun. 1984 Sep;45(3):660–666. doi: 10.1128/iai.45.3.660-666.1984. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Miao R., Fieldsteel A. H. Genetics of Treponema: relationship between Treponema pallidum and five cultivable treponemes. J Bacteriol. 1978 Jan;133(1):101–107. doi: 10.1128/jb.133.1.101-107.1978. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Moskophidis M., Müller F. Molecular analysis of immunoglobulins M and G immune response to protein antigens of Treponema pallidum in human syphilis. Infect Immun. 1984 Jan;43(1):127–132. doi: 10.1128/iai.43.1.127-132.1984. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Norgard M. V., Miller J. N. Cloning and expression of Treponema pallidum (Nichols) antigen genes in Escherichia coli. Infect Immun. 1983 Nov;42(2):435–445. doi: 10.1128/iai.42.2.435-445.1983. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Pedersen N. S., Axelsen N. H., Petersen C. S. Antigenic analysis of Treponema pallidum: cross-reactions between individual antigens of T. pallidum and T. Reiter. Scand J Immunol. 1981;13(2):143–150. doi: 10.1111/j.1365-3083.1981.tb00120.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Penn C. W. Avoidance of host defences by Treponema pallidum in situ and on extraction from infected rabbit testes. J Gen Microbiol. 1981 Sep;126(1):69–75. doi: 10.1099/00221287-126-1-69. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Robertson S. M., Kettman J. R., Miller J. N., Norgard M. V. Murine monoclonal antibodies specific for virulent Treponema pallidum (Nichols). Infect Immun. 1982 Jun;36(3):1076–1085. doi: 10.1128/iai.36.3.1076-1085.1982. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sell S., Norris S. J. The biology, pathology, and immunology of syphilis. Int Rev Exp Pathol. 1983;24:203–276. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Stamm L. V., Bassford P. J., Jr Cloning and expression of Treponema pallidum protein antigens in Escherichia coli. DNA. 1982;1(4):329–333. doi: 10.1089/dna.1982.1.329. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Stamm L. V., Folds J. D., Bassford P. J., Jr Expression of Treponema pallidum antigens in Escherichia coli K-12. Infect Immun. 1982 Jun;36(3):1238–1241. doi: 10.1128/iai.36.3.1238-1241.1982. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Stamm L. V., Kerner T. C., Jr, Bankaitis V. A., Bassford P. J., Jr Identification and preliminary characterization of Treponema pallidum protein antigens expressed in Escherichia coli. Infect Immun. 1983 Aug;41(2):709–721. doi: 10.1128/iai.41.2.709-721.1983. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Thornburg R. W., Baseman J. B. Comparison of major protein antigens and protein profiles of Treponema pallidum and Treponema pertenue. Infect Immun. 1983 Nov;42(2):623–627. doi: 10.1128/iai.42.2.623-627.1983. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Walfield A. M., Hanff P. A., Lovett M. A. Expression of Treponema pallidum antigens in Escherichia coli. Science. 1982 Apr 30;216(4545):522–523. doi: 10.1126/science.7041257. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- van Embden J. D., van der Donk H. J., van Eijk R. V., van der Heide H. G., de Jong J. A., van Olderen M. F., Osterhaus A. B., Schouls L. M. Molecular cloning and expression of Treponema pallidum DNA in Escherichia coli K-12. Infect Immun. 1983 Oct;42(1):187–196. doi: 10.1128/iai.42.1.187-196.1983. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]