Abstract
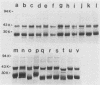
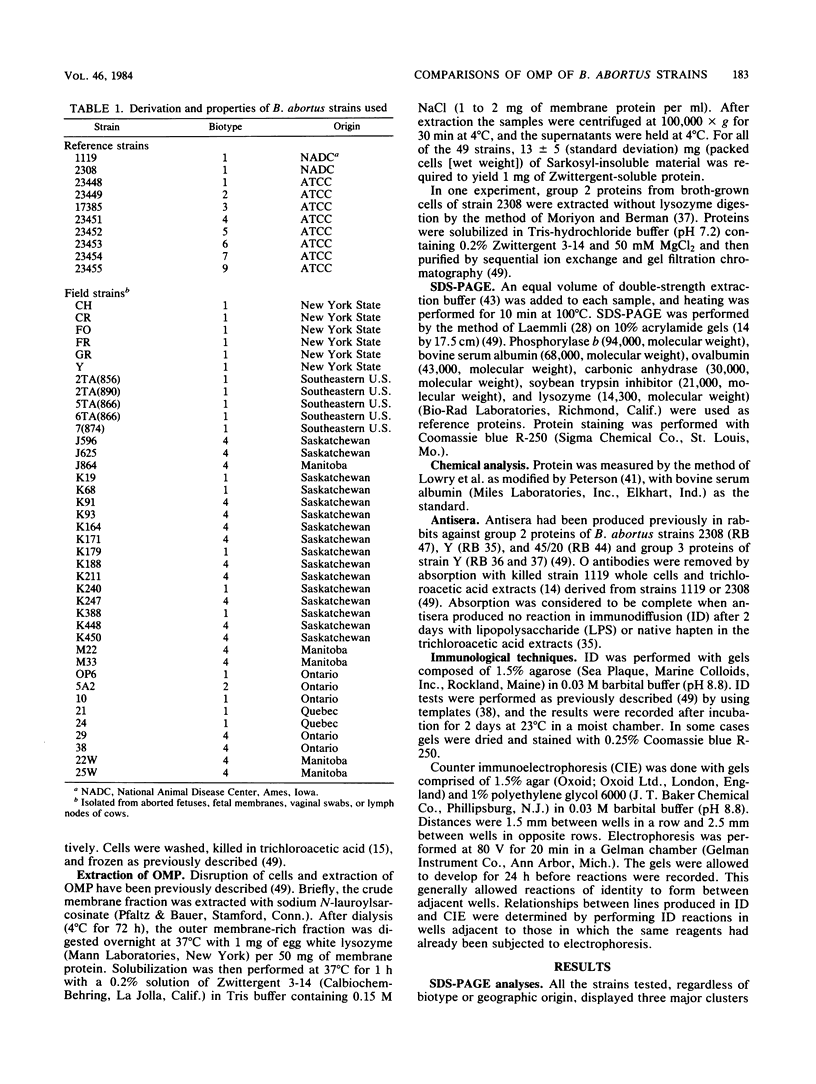
Outer membrane proteins were solubilized from 49 strains of Brucella abortus by sequential extraction of physically disrupted cells with N-lauroylsarcosinate and a dipolar ionic detergent (Verstreate et al., Infect. Immun. 35:979-989, 1982). The strains tested included standard agglutination test strain 1119, virulent strain 2308, and eight reference strains representing each of the biotypes; the remainder were isolates from cattle in North America with natural infections and included biotypes 1, 2, and 4. Three principal protein groups with apparent molecular weights of 88,000 to 94,000 (group 1), 35,000 to 40,000 (group 2, now established as porins [Douglas et al., Infect. Immun. 44:16-21, 1984]), and 25,000 to 30,000 (group 3) were observed in every strain. Some variability in banding patterns occurred among strains, but intrastrain variation was sufficient to preclude the use of sodium dodecyl sulfate-polyacrylamide gel electrophoresis profiles of outer membrane proteins for differentiating among strains of B. abortus. One antigen ([b]) was shared among the porin proteins, and three others ([c], ([d], and ([ e]) were shared among the group 3 proteins of all of the strains tested, indicating that these relationships are probably species wide. These results suggest that it may be possible to use outer membrane proteins from a representative strain of B. abortus in a vaccine for species-wide immunization.
Full text
PDF



Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Adamus G., Mulczyk M., Witkowska D., Romanowska E. Protection against keratoconjunctivitis shigellosa induced by immunization with outer membrane proteins of Shigella spp. Infect Immun. 1980 Nov;30(2):321–324. doi: 10.1128/iai.30.2.321-324.1980. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Blaser M. J., Hopkins J. A., Berka R. M., Vasil M. L., Wang W. L. Identification and characterization of Campylobacter jejuni outer membrane proteins. Infect Immun. 1983 Oct;42(1):276–284. doi: 10.1128/iai.42.1.276-284.1983. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bratthall D., Gibbons R. J. Antigenic variation of Streptococcus mutans colonizing gnotobiotic rats. Infect Immun. 1975 Dec;12(6):1231–1236. doi: 10.1128/iai.12.6.1231-1236.1975. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bratthall D., Gibbons R. J. Changing agglutination activities of salivary immunoglobulin A preparations against oral streptococci. Infect Immun. 1975 Mar;11(3):603–606. doi: 10.1128/iai.11.3.603-606.1975. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bretscher M. S. Major human erythrocyte glycoprotein spans the cell membrane. Nat New Biol. 1971 Jun 23;231(25):229–232. doi: 10.1038/newbio231229a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Buchanan T. M., Hildebrandt J. F. Antigen-specific serotyping of Neisseria gonorrhoeae: characterization based upon principal outer membrane protein. Infect Immun. 1981 Jun;32(3):985–994. doi: 10.1128/iai.32.3.985-994.1981. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Caldwell H. D., Kromhout J., Schachter J. Purification and partial characterization of the major outer membrane protein of Chlamydia trachomatis. Infect Immun. 1981 Mar;31(3):1161–1176. doi: 10.1128/iai.31.3.1161-1176.1981. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Caldwell H. D., Perry L. J. Neutralization of Chlamydia trachomatis infectivity with antibodies to the major outer membrane protein. Infect Immun. 1982 Nov;38(2):745–754. doi: 10.1128/iai.38.2.745-754.1982. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Caldwell H. D., Schachter J. Antigenic analysis of the major outer membrane protein of Chlamydia spp. Infect Immun. 1982 Mar;35(3):1024–1031. doi: 10.1128/iai.35.3.1024-1031.1982. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Corbeil L. B., Schurig G. G., Bier P. J., Winter A. J. Bovine veneral vibriosis: antigenic variation of the bacterium during infection. Infect Immun. 1975 Feb;11(2):240–244. doi: 10.1128/iai.11.2.240-244.1975. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Craven D. E., Frasch C. E. Protection against group B meningococcal disease: evaluation of serotype 2 protein vaccines in a mouse bacteremia model. Infect Immun. 1979 Oct;26(1):110–117. doi: 10.1128/iai.26.1.110-117.1979. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Darveau R. P., Charnetzky W. T., Hurlbert R. E. Outer membrane protein composition of Yersinia pestis at different growth stages and incubation temperatures. J Bacteriol. 1980 Aug;143(2):942–949. doi: 10.1128/jb.143.2.942-949.1980. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Diaz J. L., Heckels J. E. Antigenic variation of outer membrane protein II in colonial variants of Neisseria gonorrhoeae P9. J Gen Microbiol. 1982 Mar;128(3):585–591. doi: 10.1099/00221287-128-3-585. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Diaz R., Garatea P., Jones L. M., Moriyon I. Radial immunodiffusion test with a Brucella polysaccharide antigen for differentiating infected from vaccinated cattle. J Clin Microbiol. 1979 Jul;10(1):37–41. doi: 10.1128/jcm.10.1.37-41.1979. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Douglas J. T., Rosenberg E. Y., Nikaido H., Verstreate D. R., Winter A. J. Porins of Brucella species. Infect Immun. 1984 Apr;44(1):16–21. doi: 10.1128/iai.44.1.16-21.1984. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Dubray G., Bézard G. Isolation of three Brucella abortus cell-wall antigens protective in murine experimental brucellosis. Ann Rech Vet. 1980;11(4):367–373. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Dubray G., Charriaut C. Evidence of three major polypeptide species and two major polysaccharide species in the Brucella outer membrane. Ann Rech Vet. 1983;14(3):311–318. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Duckworth M., Jackson D., Zak K., Heckels J. E. Structural variations in pili expressed during gonococcal infection. J Gen Microbiol. 1983 May;129(5):1593–1596. doi: 10.1099/00221287-129-5-1593. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Fernandes P. B., Kim C., Cundy K. R., Haung N. N. Antibodies to cell envelope proteins of Pseudomonas aeruginosa in cystic fibrosis patients. Infect Immun. 1981 Aug;33(2):527–532. doi: 10.1128/iai.33.2.527-532.1981. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Frasch C. E., McNelis R. M., Gotschlich E. C. Strain-specific variation in the protein and lipopolysaccharide composition of the group B meningococcal outer membrane. J Bacteriol. 1976 Aug;127(2):973–981. doi: 10.1128/jb.127.2.973-981.1976. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gulig P. A., Frisch C. F., Hansen E. J. A set of two monoclonal antibodies specific for the cell surface-exposed 39K major outer membrane protein of Haemophilus influenzae type b defines all strains of this pathogen. Infect Immun. 1983 Nov;42(2):516–524. doi: 10.1128/iai.42.2.516-524.1983. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hansen E. J., Robertson S. M., Gulig P. A., Frisch C. F., Haanes E. J. Immunoprotection of rats against Haemophilus influenzae type B disease mediated by monoclonal antibody against a haemophilus outer-membrane protein. Lancet. 1982 Feb 13;1(8268):366–368. doi: 10.1016/s0140-6736(82)91394-0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hedstrom R. C., Pavlovskis O. R., Galloway D. R. Antibody response of infected mice to outer membrane proteins of Pseudomonas aeruginosa. Infect Immun. 1984 Jan;43(1):49–53. doi: 10.1128/iai.43.1.49-53.1984. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Johnston K. H., Holmes K. K., Gotschlich E. C. The serological classification of Neisseria gonorrhoeae. I. Isolation of the outer membrane complex responsible for serotypic specificity. J Exp Med. 1976 Apr 1;143(4):741–758. doi: 10.1084/jem.143.4.741. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kuusi N., Nurminen M., Saxen H., Valtonen M., Mäkelä P. H. Immunization with major outer membrane proteins in experimental salmonellosis of mice. Infect Immun. 1979 Sep;25(3):857–862. doi: 10.1128/iai.25.3.857-862.1979. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Laemmli U. K. Cleavage of structural proteins during the assembly of the head of bacteriophage T4. Nature. 1970 Aug 15;227(5259):680–685. doi: 10.1038/227680a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lawson G. H., Rowland A. C., Roberts L. The surface antigens of Campylobacter sputorum subspecies mucosalis. Res Vet Sci. 1977 Nov;23(3):378–382. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lee D. R., Schnaitman C. A., Pugsley A. P. Chemical heterogeneity of major outer membrane pore proteins of Escherichia coli. J Bacteriol. 1979 Jun;138(3):861–870. doi: 10.1128/jb.138.3.861-870.1979. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Loeb M. R., Smith D. H. Human antibody response to individual outer membrane proteins of Haemophilus influenzae type b. Infect Immun. 1982 Sep;37(3):1032–1036. doi: 10.1128/iai.37.3.1032-1036.1982. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Loeb M. R., Smith D. H. Outer membrane protein composition in disease isolates of Haemophilus influenzae: pathogenic and epidemiological implications. Infect Immun. 1980 Dec;30(3):709–717. doi: 10.1128/iai.30.3.709-717.1980. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mills S. D., Bradbury W. C. Human antibody response to outer membrane proteins of Campylobacter jejuni during infection. Infect Immun. 1984 Feb;43(2):739–743. doi: 10.1128/iai.43.2.739-743.1984. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Moreno E., Speth S. L., Jones L. M., Berman D. T. Immunochemical characterization of Brucella lipopolysaccharides and polysaccharides. Infect Immun. 1981 Jan;31(1):214–222. doi: 10.1128/iai.31.1.214-222.1981. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Moriyon I., Berman D. T. Effects of nonionic, ionic, and dipolar ionic detergents and EDTA on the Brucella cell envelope. J Bacteriol. 1982 Nov;152(2):822–828. doi: 10.1128/jb.152.2.822-828.1982. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Moriyon I., Berman D. T. Isolation, purification, and partial characterization of Brucella abortus matrix protein. Infect Immun. 1983 Jan;39(1):394–402. doi: 10.1128/iai.39.1.394-402.1983. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Murphy T. F., Dudas K. C., Mylotte J. M., Apicella M. A. A subtyping system for nontypable Haemophilus influenzae based on outer-membrane proteins. J Infect Dis. 1983 May;147(5):838–846. doi: 10.1093/infdis/147.5.838. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Osborn M. J., Wu H. C. Proteins of the outer membrane of gram-negative bacteria. Annu Rev Microbiol. 1980;34:369–422. doi: 10.1146/annurev.mi.34.100180.002101. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Peterson G. L. A simplification of the protein assay method of Lowry et al. which is more generally applicable. Anal Biochem. 1977 Dec;83(2):346–356. doi: 10.1016/0003-2697(77)90043-4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Poolman J. T., Hopman C. T., Zanen H. C. Immunogenicity of meningococcal antigens as detected in patient sera. Infect Immun. 1983 Apr;40(1):398–406. doi: 10.1128/iai.40.1.398-406.1983. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rosenbusch J. P. Characterization of the major envelope protein from Escherichia coli. Regular arrangement on the peptidoglycan and unusual dodecyl sulfate binding. J Biol Chem. 1974 Dec 25;249(24):8019–8029. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Santos J. M., Verstreate D. R., Perera V. Y., Winter A. J. Outer membrane proteins from rough strains of four Brucella species. Infect Immun. 1984 Oct;46(1):188–194. doi: 10.1128/iai.46.1.188-194.1984. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Shenep J. L., Munson R. S., Jr, Barenkamp S. J., Granoff D. M. Further studies of the role of noncapsular antibody in protection against experimental Haemophilus influenzae type b bacteremia. Infect Immun. 1983 Oct;42(1):257–263. doi: 10.1128/iai.42.1.257-263.1983. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Swanson J., Barrera O. Immunological characteristics of gonococcal outer membrane protein II assessed by immunoprecipitation, immunoblotting, and coagglutination. J Exp Med. 1983 May 1;157(5):1405–1420. doi: 10.1084/jem.157.5.1405. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Tsai C. M., Frasch C. E., Mocca L. F. Five structural classes of major outer membrane proteins in Neisseria meningitidis. J Bacteriol. 1981 Apr;146(1):69–78. doi: 10.1128/jb.146.1.69-78.1981. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Verstreate D. R., Creasy M. T., Caveney N. T., Baldwin C. L., Blab M. W., Winter A. J. Outer membrane proteins of Brucella abortus: isolation and characterization. Infect Immun. 1982 Mar;35(3):979–989. doi: 10.1128/iai.35.3.979-989.1982. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Winter A. J., Verstreate D. R., Hall C. E., Jacobson R. H., Castleman W. L., Meredith M. P., McLaughlin C. A. Immune response to porin in cattle immunized with whole cell, outer membrane, and outer membrane protein antigens of Brucella abortus combined with trehalose dimycolate and muramyl dipeptide adjuvants. Infect Immun. 1983 Dec;42(3):1159–1167. doi: 10.1128/iai.42.3.1159-1167.1983. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Zollinger W. D., Mandrell R. E. Type-specific antigens of group A Neisseria meningitidis: lipopolysaccharide and heat-modifiable outer membrane proteins. Infect Immun. 1980 May;28(2):451–458. doi: 10.1128/iai.28.2.451-458.1980. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]