Abstract
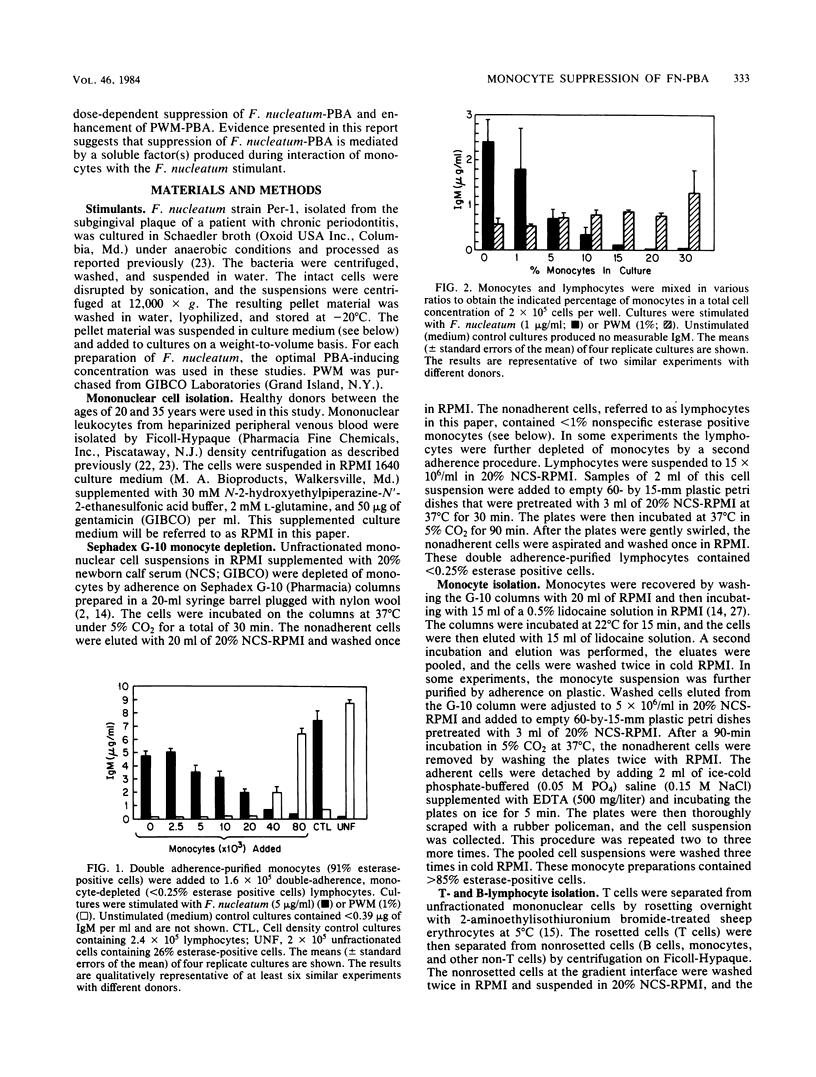
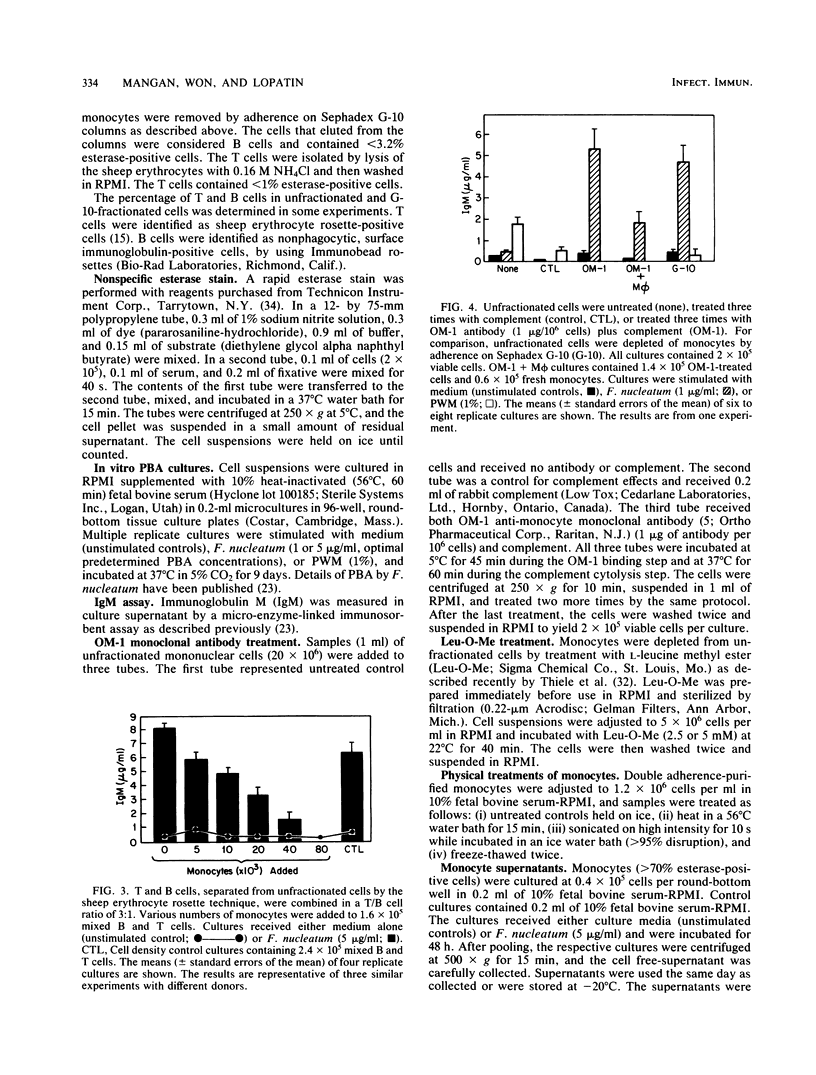
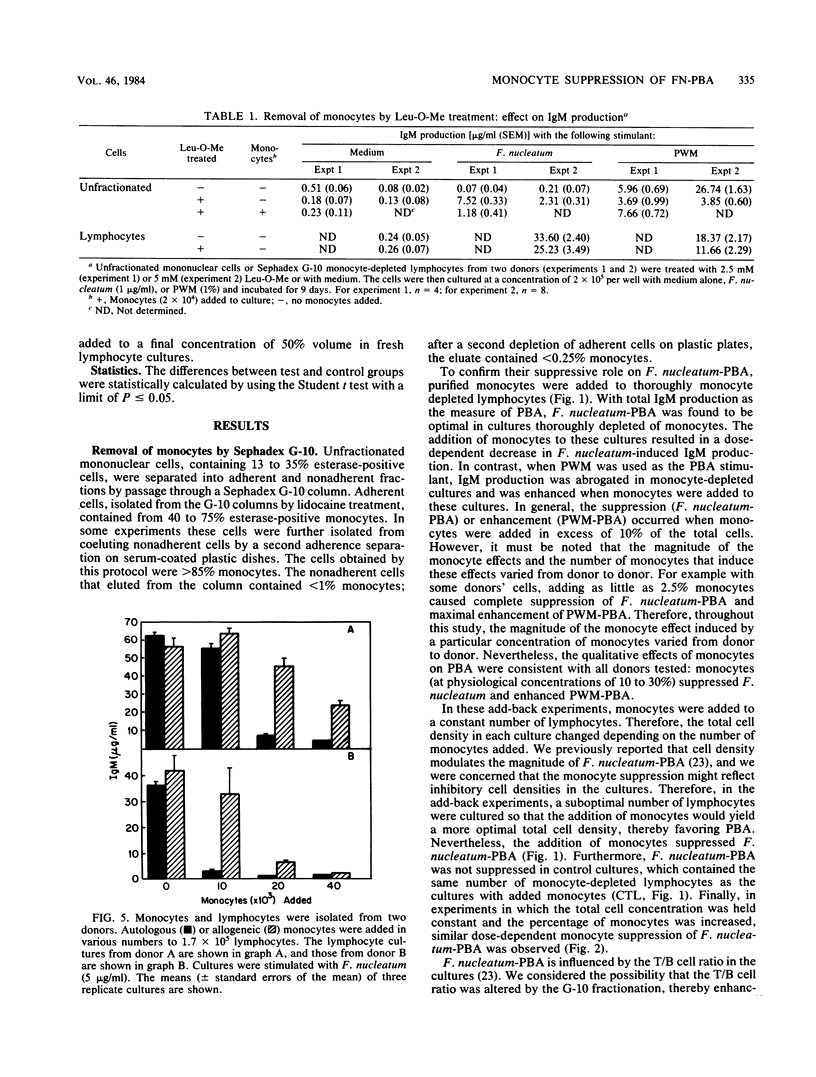
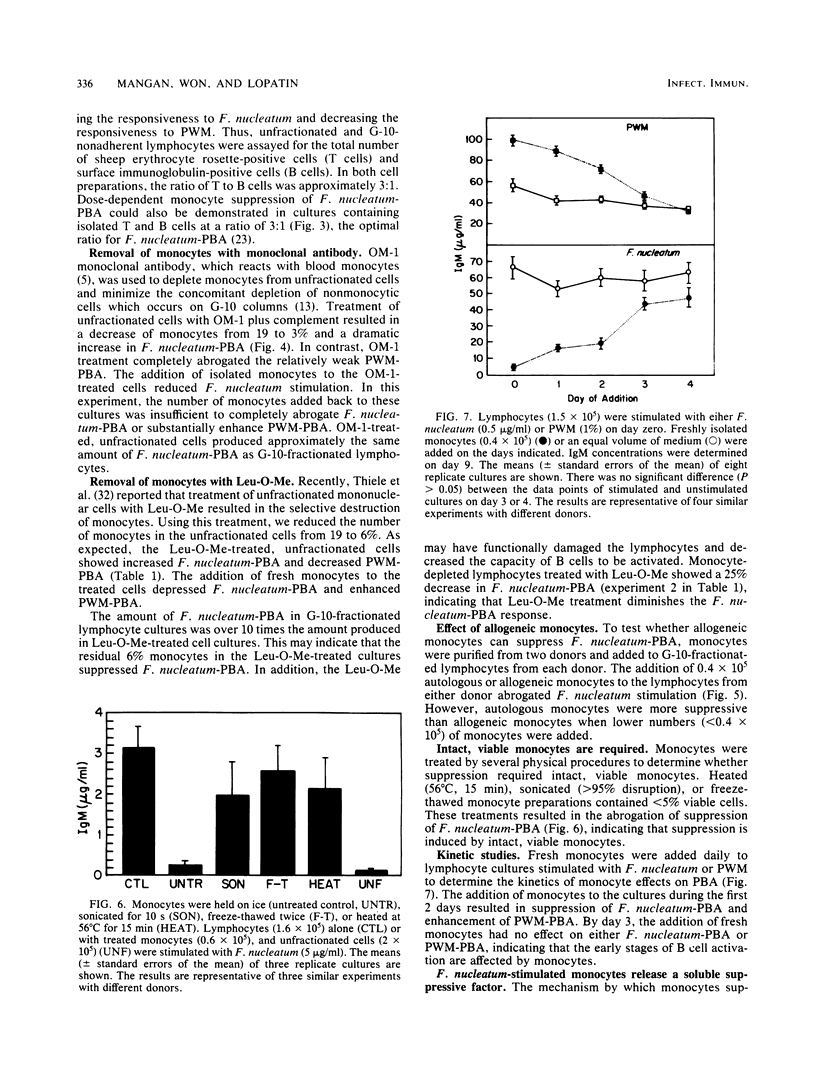
Previous studies reported that Fusobacterium nucleatum induced polyclonal B-lymphocyte activation (PBA) as determined by immunoglobulin M production in cultures of human peripheral blood mononuclear cells. However, the PBA response was greatly enhanced when the cells were depleted of esterase-positive, adherent cells (i.e., monocytes). The purpose of this study was to confirm and further examine the suppression of F. nucleatum-induced PBA (F. nucleatum-PBA) by blood monocytes. For comparison, PBA induced by pokeweed mitogen (PWM-PBA), which is enhanced by monocytes, was assessed in some experiments. We found the removal of monocytes from unfractionated cells by (i) Sephadex G-10, (ii) anti-monocyte specific OM-1 monoclonal antibody plus complement, or (iii) L-leucine methyl ester, a compound which selectively kills lysosome-rich cells, resulted in a population of cells responsive to F. nucleatum-PBA and unresponsive to PWM-PBA. The addition of double adherence-purified monocytes (greater than 85% esterase-positive cells), particularly in concentrations of greater than 10%, to lymphocytes depleted of monocytes by G-10, OM-1, or L-leucine methyl ester treatments, suppressed F. nucleatum-PBA and enhanced PWM-PBA. Monocytes also suppressed a mixture of isolated T and B cells combined in a T/B cell ratio of 3:1, which is an optimal ratio for F. nucleatum-PBA. Allogeneic monocytes suppressed F. nucleatum-PBA, although at low numbers these cells were not as suppressive as autologous monocytes. Heating at 56 degrees C for 15 min, sonicating, or freeze-thawing the monocyte preparations resulted in an abrogation of monocyte-induced suppression of F. nucleatum-PBA. Kinetic studies in which fresh monocytes were added daily to lymphocytes stimulated with F. nucleatum or PWM showed that the monocytes must be added within the first 2 days of culture to suppress F. nucleatum-PBA or enhance PWM-PBA. Monocytes incubated with F. nucleatum for 48 h released into the culture medium a soluble factor that suppressed F. nucleatum-PBA. The results from this study demonstrate a potent mechanism by which the host might prevent exaggerated nonspecific immunoglobulin responses when exposed to PBA-inducing concentrations of F. nucleatum. On the other hand, the induction of suppressive monocytes (or monocyte-mediated suppressive factors) by interaction with F. nucleatum might result in the inhibition of host protective immune reactions.
Full text
PDF



Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Allison A. C. Mechanisms by which activated macrophages inhibit lymphocyte responses. Immunol Rev. 1978;40:3–27. doi: 10.1111/j.1600-065x.1978.tb00399.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Alonso C. M., Bernabé R. R., Moreno E., Diaz de Espada F. Depletion of monocytes from human peripheral blood leucocytes by passage through sephadex G-10 columns. J Immunol Methods. 1978;22(3-4):361–368. doi: 10.1016/0022-1759(78)90043-1. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bick P. H., Carpenter A. B., Holdeman L. V., Miller G. A., Ranney R. R., Palcanis K. G., Tew J. G. Polyclonal B-cell activation induced by extracts of Gram-negative bacteria isolated from periodontally diseased sites. Infect Immun. 1981 Oct;34(1):43–49. doi: 10.1128/iai.34.1.43-49.1981. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bona C., Broder S., Dimitriu A., Waldmann T. A. Polyclonal activation of human B lymphocytes by Nocardia water soluble mitogen (NWSM). Immunol Rev. 1979;45:69–92. doi: 10.1111/j.1600-065x.1979.tb00273.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Breard J., Reinherz E. L., Kung P. C., Goldstein G., Schlossman S. F. A monoclonal antibody reactive with human peripheral blood monocytes. J Immunol. 1980 Apr;124(4):1943–1948. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Broder S., Humphrey R., Durm M., Blackman M., Meade B., Goldman C., Strober W., Waldmann T. Impaired synthesis of polyclonal (non-paraprotein) immunoglobulins by circulating lymphocytes from patients with multiple myeloma Role of suppressor cells. N Engl J Med. 1975 Oct 30;293(18):887–892. doi: 10.1056/NEJM197510302931801. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Carpenter A. B., Sully E. C., Palcanis K. G., Bick P. H. Role of monocytes in polyclonal immunoglobulin production stimulated by sonicates of periodontally associated bacteria. Infect Immun. 1983 Dec;42(3):853–862. doi: 10.1128/iai.42.3.853-862.1983. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Delfraissy J. F., Galanaud P., Dormont J., Wallon C. Primary in vitro antibody response of human peripheral blood lymphocytes: role of phagocytic mononuclear cells. J Immunol. 1978 Apr;120(4):1283–1288. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ellner J. J. Suppressor adherent cells in human tuberculosis. J Immunol. 1978 Dec;121(6):2573–2579. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gerrard T. L., Fauci A. S. Activation and immunoregulation of antigen-specific human b lymphocyte responses: multifaceted role of the monocyte. J Immunol. 1982 May;128(5):2367–2372. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gmelig-Meyling F., Waldmann T. A. Human B cell activation in vitro: augmentation and suppression by monocytes of the immunoglobulin production induced by various B cell stimulants. J Immunol. 1981 Feb;126(2):529–537. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hoffmann M. K., Pollack S., Krown S. E., Mittler R. S. Deletion of active human suppressor T lymphocytes from peripheral blood by Sephadex G-10 filtration. J Immunol Methods. 1982 Dec 30;55(3):327–336. doi: 10.1016/0022-1759(82)90092-8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Jerrells T. R., Dean J. H., Richardson G. L., Herberman R. B. Depletion of monocytes from human peripheral blood mononuclear leukocytes: comparison of the sephadex G-10 column method with other commonly used techniques. J Immunol Methods. 1980;32(1):11–29. doi: 10.1016/0022-1759(80)90113-1. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Katz P., Fauci A. S. Inhibition of polyclonal B-cell activation by suppressor monocytes in patients with sarcoidosis. Clin Exp Immunol. 1978 Jun;32(3):554–562. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Katz P., Goldstein R. A., Fauci A. S. Immunoregulation in infection caused by Mycobacterium tuberculosis: the presence of suppressor monocytes and the alteration of subpopulations of T lymphocytes. J Infect Dis. 1979 Jul;140(1):12–21. doi: 10.1093/infdis/140.1.12. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Knapp W., Baumgartner G. Monocyte-mediated suppression of human B lymphocyte differentiation in vitro. J Immunol. 1978 Sep;121(3):1177–1183. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Laughter A. H., Lidsky M. D., Twomey J. J. Suppression of immunoglobulin synthesis by monocytes in health and in patients with systemic lupus erythematosus. Clin Immunol Immunopathol. 1979 Dec;14(4):435–440. doi: 10.1016/0090-1229(79)90095-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Levitt D., Duber-Stull D., Lawton A. R. T-cell-dependent and independent plasma cell differentiation induced by Escherichia coli Lipopolysaccharide in human peripheral blood lymphocytes. Clin Immunol Immunopathol. 1981 Mar;18(3):309–321. doi: 10.1016/0090-1229(81)90124-0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mackler B. F., Frostad K. B., Robertson P. B., Levy B. M. Immunoglobulin bearing lymphocytes and plasma cells in human periodontal disease. J Periodontal Res. 1977 Jan;12(1):37–45. doi: 10.1111/j.1600-0765.1977.tb00107.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mangan D. F., Lopatin D. E. In vitro stimulation of immunoglobulin production from human peripheral blood lymphocytes by a soluble preparation of Actinomyces viscosus. Infect Immun. 1981 Jan;31(1):236–244. doi: 10.1128/iai.31.1.236-244.1981. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mangan D. F., Lopatin D. E. Polyclonal activation of human peripheral blood B lymphocytes by Fusobacterium nucleatum. Infect Immun. 1983 Jun;40(3):1104–1111. doi: 10.1128/iai.40.3.1104-1111.1983. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mangan D. F., Won T., Lopatin D. E. Nonspecific induction of immunoglobulin M antibodies to periodontal disease-associated microorganisms after polyclonal human B-lymphocyte activation by Fusobacterium nucleatum. Infect Immun. 1983 Sep;41(3):1038–1045. doi: 10.1128/iai.41.3.1038-1045.1983. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Montazeri G., Chiorazzi N., Fu S. M., Kunkel H. G. Regulatory role of circulating monocytes in the differentiative and proliferative responses of human B lymphocytes. Clin Immunol Immunopathol. 1980 May;16(1):1–10. doi: 10.1016/0090-1229(80)90160-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Page R. C., Davies P., Allison A. C. Participation of mononuclear phagocytes in chronic inflammatory diseases. J Reticuloendothel Soc. 1974 May;15(5):413–438. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rosenberg S. A., Lipsky P. E. Monocyte dependence of pokeweed mitogen-induced differentiation of immunoglobulin-secreting cells from human peripheral blood mononuclear cells. J Immunol. 1979 Mar;122(3):926–931. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Seymour G. J., Greenspan J. S. The phenotypic characterization of lymphocyte subpopulations in established human periodontal disease. J Periodontal Res. 1979 Jan;14(1):39–46. doi: 10.1111/j.1600-0765.1979.tb00216.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Stobo J. D. Immunosuppression in man: suppression by macrophages can be mediated by interactions with regulatory T cells. J Immunol. 1977 Sep;119(3):918–924. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Thiele D. L., Kurosaka M., Lipsky P. E. Phenotype of the accessory cell necessary for mitogen-stimulated T and B cell responses in human peripheral blood: delineation by its sensitivity to the lysosomotropic agent, L-leucine methyl ester. J Immunol. 1983 Nov;131(5):2282–2290. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Tsokos G. C., Christian C. B., Balow J. E. Induction of monocytic suppression after stimulation of peripheral human mononuclear cells with staphylococcal protein A and Staphylococcus aureus. Cell Immunol. 1983 May;78(1):144–151. doi: 10.1016/0008-8749(83)90267-8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Tucker S. B., Pierre R. V., Jordon R. E. Rapid identification of monocytes in a mixed mononuclear cell preparation. J Immunol Methods. 1977;14(3-4):267–269. doi: 10.1016/0022-1759(77)90137-5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]


