Abstract
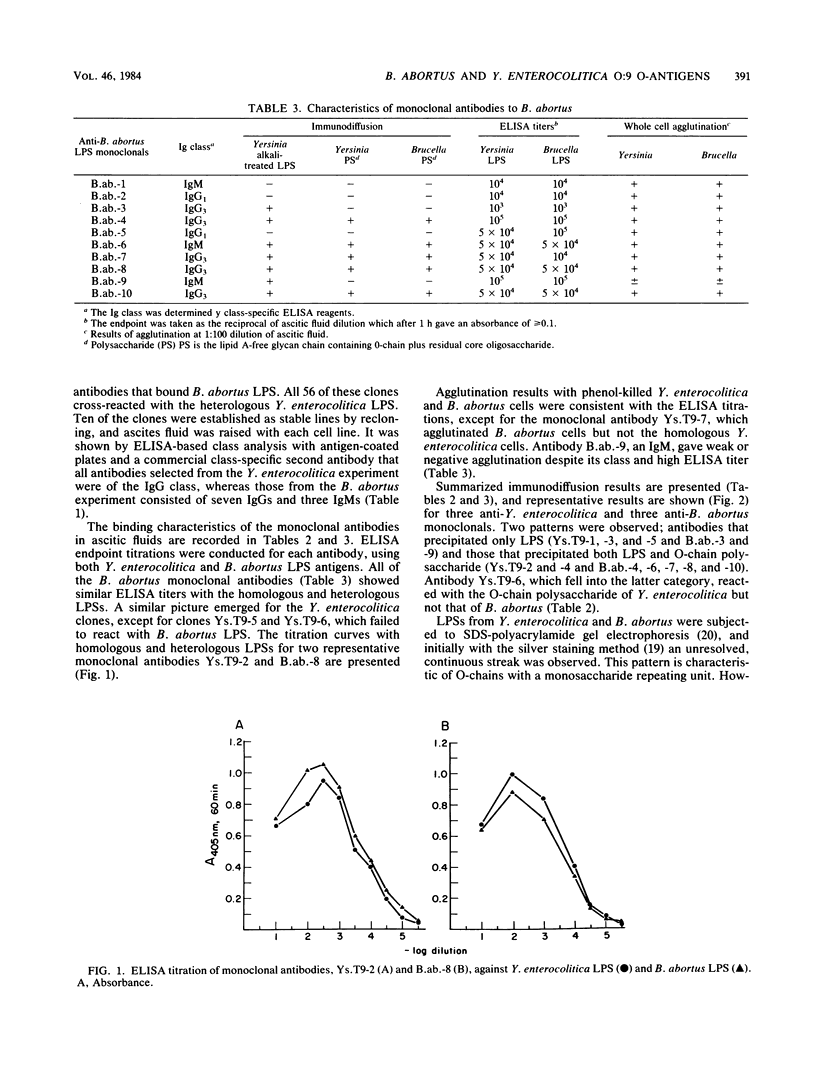
Murine monoclonal antibodies that bind the O-antigens of Yersinia enterocolitica serotype O:9 and Brucella abortus 1119-3 were generated after immunization of BALB/c mice with killed, whole cells. Highly purified lipopolysaccharide preparations from each organism were used to screen for antigen-specific antibodies. Immunization with B. abortus cells induced 56 antigen-specific hybrids, and 10 of the highest antibody-producing clones were selected for further study. Seven of these clones secreted immunoglobulin G, and three secreted immunoglobulin M antibodies. Immunization with Y. enterocolitica cells resulted after fusion in 76 antigen-specific hybrid cell lines; from these, seven immunoglobulin G-secreting clones were selected for study. The serological cross-reactivity of the B. abortus and Y. enterocolitica O-antigens was established by enzyme-linked immunosorbent assay, immunoprecipitation, and agglutination tests with the monoclonal antibodies induced by each bacterium. This serological cross-reactivity is consistent with the structural identity of the two O-antigens established by chemical analysis.
Full text
PDF



Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Ahvonen P., Jansson E., Aho K. Marked cross-agglutination between Brucellae and a subtype of Yersinia enterocolitica. Acta Pathol Microbiol Scand. 1969;75(2):291–295. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Barua D., Watanabe Y. Vibriocidal antibodies induced by Yersinia enterocolitica serotype IX. J Hyg (Lond) 1972 Mar;70(1):161–169. doi: 10.1017/s0022172400022208. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bundle D. R., Gidney M. A., Kassam N., Rahman A. F. Hybridomas specific for carbohydrates; synthetic human blood group antigens for the production, selection, and characterization of monoclonal typing reagents. J Immunol. 1982 Aug;129(2):678–672. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Caroff M., Bundle D. R., Perry M. B., Cherwonogrodzky J. W., Duncan J. R. Antigenic S-type lipopolysaccharide of Brucella abortus 1119-3. Infect Immun. 1984 Nov;46(2):384–388. doi: 10.1128/iai.46.2.384-388.1984. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Caroff M., Bundle D. R., Perry M. B. Structure of the O-chain of the phenol-phase soluble cellular lipopolysaccharide of Yersinia enterocolitica serotype O:9. Eur J Biochem. 1984 Feb 15;139(1):195–200. doi: 10.1111/j.1432-1033.1984.tb07994.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Corbell M. J. The serological relationship between Brucella spp., Yersinia enterocolitica serotype IX and Salmonella serotypes of Kauffmann-White group N. J Hyg (Lond) 1975 Aug;75(1):151–171. doi: 10.1017/s0022172400047173. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Fernandez-Lago L., Moriyon I., Toyos J., Diaz R. Immunological identity of brucella native hapten, polysaccharide B, and yersinia enterocolitica serotype 9 native hapten. Infect Immun. 1982 Nov;38(2):778–780. doi: 10.1128/iai.38.2.778-780.1982. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Galfre G., Howe S. C., Milstein C., Butcher G. W., Howard J. C. Antibodies to major histocompatibility antigens produced by hybrid cell lines. Nature. 1977 Apr 7;266(5602):550–552. doi: 10.1038/266550a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gefter M. L., Margulies D. H., Scharff M. D. A simple method for polyethylene glycol-promoted hybridization of mouse myeloma cells. Somatic Cell Genet. 1977 Mar;3(2):231–236. doi: 10.1007/BF01551818. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Holman P. J., Adams L. G., Hunter D. M., Heck F. C., Nielsen K. H., Wagner G. G. Derivation of monoclonal antibodies against Brucella abortus antigens. Vet Immunol Immunopathol. 1983 Jul;4(5-6):603–614. doi: 10.1016/0165-2427(83)90068-5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hurvell B., Lindberg A. A. Serological cross-reactions between different Brucella species and Yersinia enterocolitica. Immunochemical studies on phenol-water extracted lipopolysaccharides from Brucella abortus and Yersinia enterocolitica type IX. Acta Pathol Microbiol Scand B Microbiol Immunol. 1973 Feb;81(1):113–119. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kenne L., Lindberg B., Unger P., Gustafsson B., Holme T. Structural studies of the Vibrio cholerae O-antigen. Carbohydr Res. 1982 Mar 1;100:341–349. doi: 10.1016/s0008-6215(00)81047-2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kennett R. H., Denis K. A., Tung A. S., Klinman N. R. Hybrid plasmacytoma production: fusions with adult spleen cells, monoclonal spleen fragments, neonatal spleen cells and human spleen cells. Curr Top Microbiol Immunol. 1978;81:77–91. doi: 10.1007/978-3-642-67448-8_13. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lindberg A. A., Haeggman S., Karlson K., Carlsson H. E., Mair N. S. Enzyme immunoassay of the antibody response to Brucella and Yersinia enterocolitica 09 infections in humans. J Hyg (Lond) 1982 Apr;88(2):295–307. doi: 10.1017/s0022172400070157. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sandulache R., Marx A. Immunochemical studies on a Yersinia enterocolitica O:9 lipopolysaccharide cross-reacting with Brucella abortus and Vibrio cholerae extracts. Ann Microbiol (Paris) 1978 Oct;129 B(3):425–435. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Schalch W., Wright J. K., Rodkey L. S., Braun D. G. Distinct functions of monoclonal IgG antibody depend on antigen-site specificities. J Exp Med. 1979 Apr 1;149(4):923–937. doi: 10.1084/jem.149.4.923. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Schurig G. G., Hammerberg C., Finkler B. R. Monoclonal antibodies to Brucella surface antigens associated with the smooth lipopolysaccharide complex. Am J Vet Res. 1984 May;45(5):967–971. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Shulman M., Wilde C. D., Köhler G. A better cell line for making hybridomas secreting specific antibodies. Nature. 1978 Nov 16;276(5685):269–270. doi: 10.1038/276269a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Towbin H., Staehelin T., Gordon J. Electrophoretic transfer of proteins from polyacrylamide gels to nitrocellulose sheets: procedure and some applications. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1979 Sep;76(9):4350–4354. doi: 10.1073/pnas.76.9.4350. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Tsai C. M., Frasch C. E. A sensitive silver stain for detecting lipopolysaccharides in polyacrylamide gels. Anal Biochem. 1982 Jan 1;119(1):115–119. doi: 10.1016/0003-2697(82)90673-x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]



