Abstract
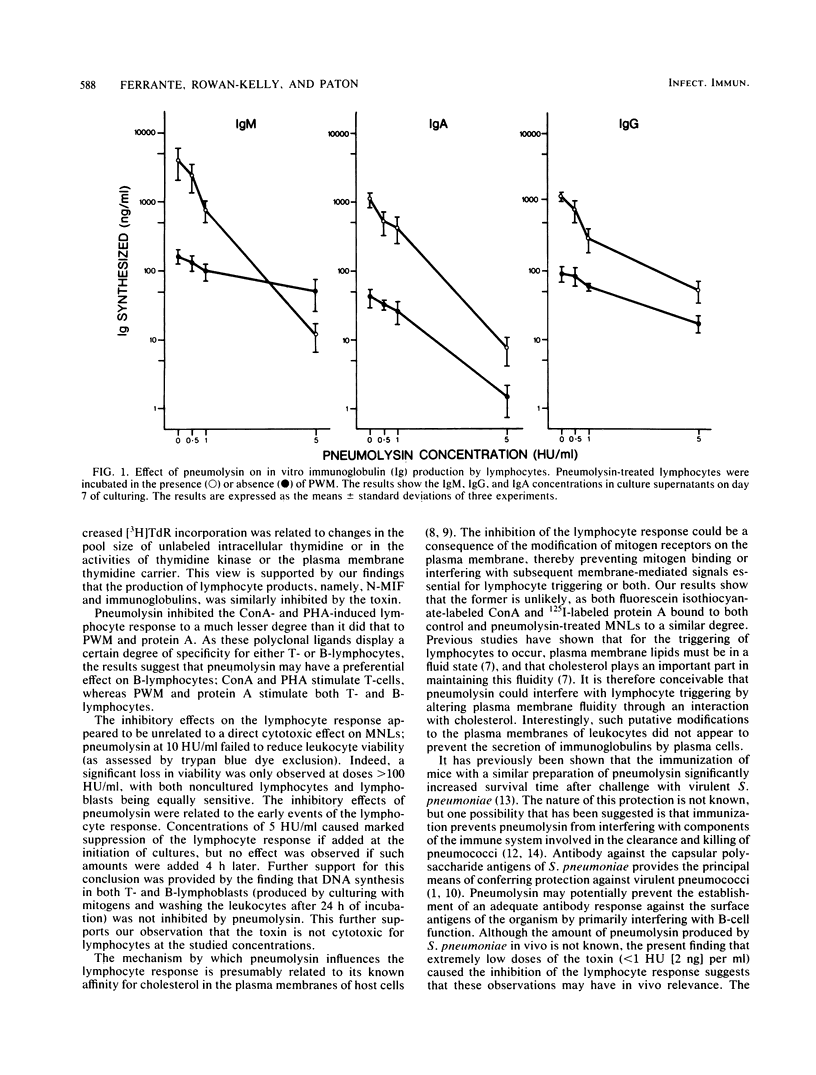
The effects of pneumolysin, a sulfhydryl-activated cytolytic toxin produced by Streptococcus pneumoniae, on the in vitro human lymphocyte response was examined. The toxin, at concentrations of one to five hemolytic units per ml, caused marked inhibition of the response of lymphocytes to concanavalin A, phytohemagglutinin, pokeweed mitogen, and protein A. The response was assessed by measuring both [3H]thymidine incorporation and the ability of lymphocytes to produce immunoglobulins and lymphokine activity. The effects of pneumolysin were irreversible, could be prevented by pretreatment of the toxin with cholesterol, and were not related to a direct cytotoxic effect on the lymphocytes. Pneumolysin appeared to act at the initiation phase of the immune response and had no effect on lymphocytes committed to DNA synthesis or to the synthesis and secretion of immunoglobulins. Furthermore, pneumolysin-mediated inhibition of the lymphocyte response was not due to the inhibition of binding of mitogens to leukocytes and is likely to be related to effects on membrane-mediated signals essential for lymphocyte triggering. This may be one means by which pneumolysin plays a role in the pathogenesis of pneumococcal infections.
Full text
PDF



Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Ferrante A., Beard L. J., Thong Y. H. Early decay of human neutrophil chemotactic responsiveness following isolation from peripheral blood. Clin Exp Immunol. 1980 Feb;39(2):532–537. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ferrante A., Mocatta T. J. Human neutrophils require activation by mononuclear leucocyte conditioned medium to kill the pathogenic free-living amoeba, Naegleria fowleri. Clin Exp Immunol. 1984 Jun;56(3):559–566. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ferrante A., Rowan-Kelly B., Thong Y. H. Suppression of immunological responses in mice by treatment with amphotericin B. Clin Exp Immunol. 1979 Oct;38(1):70–76. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ferrante A., Thong Y. H. Optimal conditions for simultaneous purification of mononuclear and polymorphonuclear leucocytes from human blood by the Hypaque-Ficoll method. J Immunol Methods. 1980;36(2):109–117. doi: 10.1016/0022-1759(80)90036-8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ferrante A., Thong Y. H. Separation of mononuclear and polymorphonuclear leucocytes from human blood by the one-step Hypaque-Ficoll method is dependent on blood column height. J Immunol Methods. 1982;48(1):81–85. doi: 10.1016/0022-1759(82)90212-5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Johnson M. K., Boese-Marrazzo D., Pierce W. A., Jr Effects of pneumolysin on human polymorphonuclear leukocytes and platelets. Infect Immun. 1981 Oct;34(1):171–176. doi: 10.1128/iai.34.1.171-176.1981. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Johnson M. K., Geoffroy C., Alouf J. E. Binding of cholesterol by sulfhydryl-activated cytolysins. Infect Immun. 1980 Jan;27(1):97–101. doi: 10.1128/iai.27.1.97-101.1980. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Johnston R. B., Jr The host response to invasion by Streptococcus pneumoniae: protection and the pathogenesis to tissue damage. Rev Infect Dis. 1981 Mar-Apr;3(2):282–288. doi: 10.1093/clinids/3.2.282. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Nelson R. D., Quie P. G., Simmons R. L. Chemotaxis under agarose: a new and simple method for measuring chemotaxis and spontaneous migration of human polymorphonuclear leukocytes and monocytes. J Immunol. 1975 Dec;115(6):1650–1656. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Paton J. C., Ferrante A. Inhibition of human polymorphonuclear leukocyte respiratory burst, bactericidal activity, and migration by pneumolysin. Infect Immun. 1983 Sep;41(3):1212–1216. doi: 10.1128/iai.41.3.1212-1216.1983. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Paton J. C., Lock R. A., Hansman D. J. Effect of immunization with pneumolysin on survival time of mice challenged with Streptococcus pneumoniae. Infect Immun. 1983 May;40(2):548–552. doi: 10.1128/iai.40.2.548-552.1983. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Paton J. C., Rowan-Kelly B., Ferrante A. Activation of human complement by the pneumococcal toxin pneumolysin. Infect Immun. 1984 Mar;43(3):1085–1087. doi: 10.1128/iai.43.3.1085-1087.1984. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Thong Y. H., Ferrante A. Inhibition of mitogen-induced human lymphocyte proliferative responses by tetracycline analogues. Clin Exp Immunol. 1979 Mar;35(3):443–446. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]


