Abstract
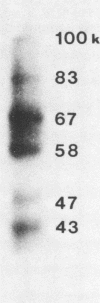
Immunologically reactive proteins in acid extracts and culture supernatants of Streptococcus equi were recognized through a combination of chromatographic and immunologic procedures. Both high- and low-molecular-weight components of each of these protein preparations were protective for mice and were, therefore, presumed to contain a variety of hydrolytic products or fragments of the M protein of S. equi. Convalescent horse sera that exhibited strong bactericidal activity for S. equi always reacted with polypeptides in the molecular weight range of 24,000 to 29,000, whereas preinfection sera did not. Rabbit antisera to affinity-purified S. equi protein also reacted with these polypeptides, as well as with a polypeptide of about 36,000 to 37,000 molecular weight. M protein in acid extract and culture supernatant did not cross-react in immunodiffusion, but rabbit antiserum to affinity-purified M protein from an acid extract of S. equi reacted strongly with culture supernatant proteins of approximate molecular weights of 67,000, 58,000, and 43,000. We suggest, therefore, that the M protein in culture supernatant is masked by other sequences that are removed by hot acid during preparation of acid extracts. Polypeptides common to acid extracts of S. equi and Streptococcus zooepidemicus were also identified. These polypeptides had molecular weights of about 55,000 and 31,000.
Full text
PDF





Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Erickson E. D., Norcross N. L. The cell surface antigens of Streptococcus equi. Can J Comp Med. 1975 Apr;39(2):110–115. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Fischetti V. A., Gotschlich E. C., Siviglia G., Zabriskie J. B. Streptococcal M protein extracted by nonionic detergent. I. Properties of the antiphagocytic and type-specific molecules. J Exp Med. 1976 Jul 1;144(1):32–53. doi: 10.1084/jem.144.1.32. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Fischetti V. A., Jones K. F., Manjula B. N., Scott J. R. Streptococcal M6 protein expressed in Escherichia coli. Localization, purification, and comparison with streptococcal-derived M protein. J Exp Med. 1984 Apr 1;159(4):1083–1095. doi: 10.1084/jem.159.4.1083. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Fox E. N., Wittner M. K. The multiple molecular structure of the M proteins of group A streptococci. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1965 Oct;54(4):1118–1125. doi: 10.1073/pnas.54.4.1118. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Johnson R. H. Characterization of group A streptococcal R-28 antigen purified by hydroxyapatite column chromatography. Infect Immun. 1975 Oct;12(4):901–909. doi: 10.1128/iai.12.4.901-909.1975. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kühnemund O., Havlicek J., Köhler W. Type-specific and non-type-specific reactions of purified M protein preparations. Z Immunitatsforsch Immunobiol. 1978 Jun;154(3):197–207. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- LANCEFIELD R. C. Differentiation of group A streptococci with a common R antigen into three serological types, with special reference to the bactericidal test. J Exp Med. 1957 Oct 1;106(4):525–544. doi: 10.1084/jem.106.4.525. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- LANCEFIELD R. C., PERLMANN G. E. Preparation and properties of a protein (R antigen) occurring in streptococci of group A, type 28 and in certain streptococci of other serological groups. J Exp Med. 1952 Jul;96(1):83–97. doi: 10.1084/jem.96.1.83. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Laemmli U. K. Cleavage of structural proteins during the assembly of the head of bacteriophage T4. Nature. 1970 Aug 15;227(5259):680–685. doi: 10.1038/227680a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Pinney A. M., Widdowson J. P. Characteristics of the extracellular M proteins of group-A streptococci. J Med Microbiol. 1977 Nov;10(4):415–429. doi: 10.1099/00222615-10-4-415. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Towbin H., Staehelin T., Gordon J. Electrophoretic transfer of proteins from polyacrylamide gels to nitrocellulose sheets: procedure and some applications. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1979 Sep;76(9):4350–4354. doi: 10.1073/pnas.76.9.4350. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Vosti K. L. The characteristics of M proteins purified by column chromatography with hydroxyapatite from acid extracts of Streptococcus pyogenes of types 1, 3, 6, 12 and 17. J Med Microbiol. 1978 Nov;11(4):453–462. doi: 10.1099/00222615-11-4-453. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Woolcock J. B. Purification and antigenicity of an M-like protein of Streptococcus equi. Infect Immun. 1974 Jul;10(1):116–122. doi: 10.1128/iai.10.1.116-122.1974. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- van de Rijn I., Fischetti V. A. Immunochemical analysis of intact M protein secreted from cell wall-less streptococci. Infect Immun. 1981 Apr;32(1):86–91. doi: 10.1128/iai.32.1.86-91.1981. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- van de Rijn I., Kessler R. E. Growth characteristics of group A streptococci in a new chemically defined medium. Infect Immun. 1980 Feb;27(2):444–448. doi: 10.1128/iai.27.2.444-448.1980. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]