Abstract
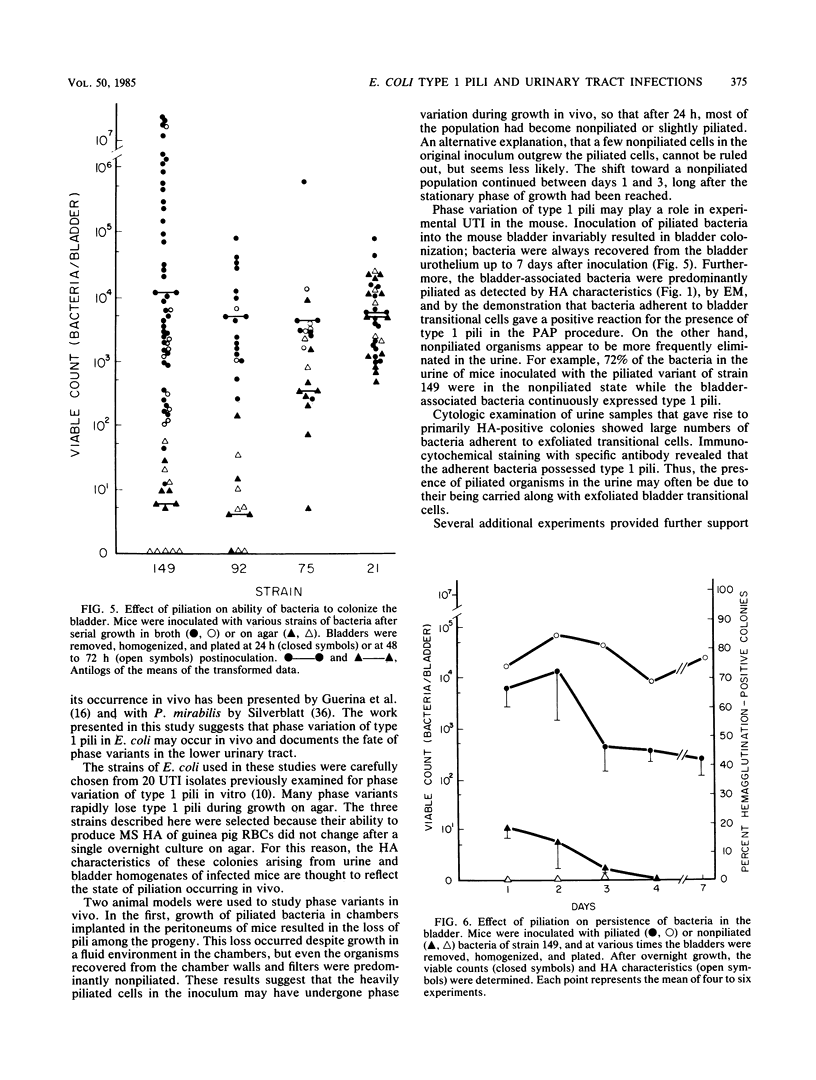
Phase variation of type 1 pili (fimbriae) was studied during the in vivo growth of Escherichia coli in two animal models. In the first, a heavily piliated urinary tract isolate (strain 149) was placed in 1-cm polypropylene chambers sealed with 0.22-micron-pore-size filters. The chambers were surgically implanted intraperitoneally in mice and recovered at various times. Piliation, as determined by electron microscopy and by measuring the minimum number of bacteria needed to produce mannose-sensitive hemagglutination, gradually decreased, and by day 5, most of the organisms were nonpiliated. In the second model, piliated and nonpiliated E. coli phase variants were inoculated into the bladders of BALB/c mice via urinary catheters, and their fate in the lower urinary tract was studied. Viable counts of bladder homogenates revealed that piliated phase variants were significantly more effective in colonizing the bladder urothelium than were their nonpiliated counterparts. Specific antibody to type 1 pili prevented colonization by the piliated organisms. After inoculation of piliated variants, the bladder-associated bacteria gave rise to approximately 80% mannose-sensitive hemagglutination-positive colonies, and immunocytochemistry of bladder lavages revealed large numbers of type 1 piliated bacteria adhering to the bladder transitional cells. Electron microscopy confirmed the presence of piliated bacteria in association with the bladder urothelium. The urine of these mice, whose bladders were colonized with piliated bacteria, frequently showed no growth, and when bacteria were present, strain 149 yielded less than 30% hemagglutination-positive colonies. The results suggest that for some E. coli strains, phase variation may be a factor in determining the fate of the E. coli in the urinary tract and that the urine may not necessarily reflect the bacteriologic state of the bladder mucosa.
Full text
PDF





Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Aronson M., Medalia O., Schori L., Mirelman D., Sharon N., Ofek I. Prevention of colonization of the urinary tract of mice with Escherichia coli by blocking of bacterial adherence with methyl alpha-D-mannopyranoside. J Infect Dis. 1979 Mar;139(3):329–332. doi: 10.1093/infdis/139.3.329. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- BRINTON C. C., Jr Non-flagellar appendages of bacteria. Nature. 1959 Mar 21;183(4664):782–786. doi: 10.1038/183782a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bar-Shavit Z., Goldman R., Ofek I., Sharon N., Mirelman D. Mannose-binding activity of Escherichia coli: a determinant of attachment and ingestion of the bacteria by macrophages. Infect Immun. 1980 Aug;29(2):417–424. doi: 10.1128/iai.29.2.417-424.1980. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Blumenstock E., Jann K. Adhesion of piliated Escherichia coli strains to phagocytes: differences between bacteria with mannose-sensitive pili and those with mannose-resistant pili. Infect Immun. 1982 Jan;35(1):264–269. doi: 10.1128/iai.35.1.264-269.1982. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Brinton C. C., Jr The structure, function, synthesis and genetic control of bacterial pili and a molecular model for DNA and RNA transport in gram negative bacteria. Trans N Y Acad Sci. 1965 Jun;27(8):1003–1054. doi: 10.1111/j.2164-0947.1965.tb02342.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- DUGUID J. P., SMITH I. W., DEMPSTER G., EDMUNDS P. N. Non-flagellar filamentous appendages (fimbriae) and haemagglutinating activity in Bacterium coli. J Pathol Bacteriol. 1955 Oct;70(2):335–348. doi: 10.1002/path.1700700210. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Duguid J. P., Clegg S., Wilson M. I. The fimbrial and non-fimbrial haemagglutinins of Escherichia coli. J Med Microbiol. 1979 May;12(2):213–227. doi: 10.1099/00222615-12-2-213. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Duncan J. L. Streptococcal growth and toxin production in vivo. Infect Immun. 1983 May;40(2):501–505. doi: 10.1128/iai.40.2.501-505.1983. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Edén C. S., Freter R., Hagberg L., Hull R., Hull S., Leffler H., Schoolnik G. Inhibition of experimental ascending urinary tract infection by an epithelial cell-surface receptor analogue. Nature. 1982 Aug 5;298(5874):560–562. doi: 10.1038/298560a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Eisenstein B. I., Dodd D. C. Pseudocatabolite repression of type 1 fimbriae of Escherichia coli. J Bacteriol. 1982 Sep;151(3):1560–1567. doi: 10.1128/jb.151.3.1560-1567.1982. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Eisenstein B. I. Operon fusion of the phase variation switch. A virulence factor in Escherichia coli. Infection. 1982;10(2):112–115. doi: 10.1007/BF01816739. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Eisenstein B. I. Phase variation of type 1 fimbriae in Escherichia coli is under transcriptional control. Science. 1981 Oct 16;214(4518):337–339. doi: 10.1126/science.6116279. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Fader R. C., Davis C. P. Effect of piliation on Klebsiella pneumoniae infection in rat bladders. Infect Immun. 1980 Nov;30(2):554–561. doi: 10.1128/iai.30.2.554-561.1980. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Fader R. C., Davis C. P. Klebsiella pneumoniae-induced experimental pyelitis: the effect of piliation on infectivity. J Urol. 1982 Jul;128(1):197–201. doi: 10.1016/s0022-5347(17)52817-7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Guerina N. G., Kessler T. W., Guerina V. J., Neutra M. R., Clegg H. W., Langermann S., Scannapieco F. A., Goldmann D. A. The role of pili and capsule in the pathogenesis of neonatal infection with Escherichia coli K1. J Infect Dis. 1983 Sep;148(3):395–405. doi: 10.1093/infdis/148.3.395. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hagberg L., Engberg I., Freter R., Lam J., Olling S., Svanborg Edén C. Ascending, unobstructed urinary tract infection in mice caused by pyelonephritogenic Escherichia coli of human origin. Infect Immun. 1983 Apr;40(1):273–283. doi: 10.1128/iai.40.1.273-283.1983. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hagberg L., Hull R., Hull S., Falkow S., Freter R., Svanborg Edén C. Contribution of adhesion to bacterial persistence in the mouse urinary tract. Infect Immun. 1983 Apr;40(1):265–272. doi: 10.1128/iai.40.1.265-272.1983. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Harber M. J., Chick S., Mackenzie R., Asscher A. W. Lack of adherence to epithelial cells by freshly isolated urinary pathogens. Lancet. 1982 Mar 13;1(8272):586–588. doi: 10.1016/s0140-6736(82)91749-4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hultgren S., Hidvegi D. F. Improved transmission electron microscopy technique for the study of cytologic material. Acta Cytol. 1985 Mar-Apr;29(2):179–183. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Iwahi T., Abe Y., Nakao M., Imada A., Tsuchiya K. Role of type 1 fimbriae in the pathogenesis of ascending urinary tract infection induced by escherichia coli in mice. Infect Immun. 1983 Mar;39(3):1307–1315. doi: 10.1128/iai.39.3.1307-1315.1983. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mangan D. F., Snyder I. S. Mannose-sensitive interaction of Escherichia coli with human peripheral leukocytes in vitro. Infect Immun. 1979 Nov;26(2):520–527. doi: 10.1128/iai.26.2.520-527.1979. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- McMichael J. C., Ou J. T. Structure of common pili from Escherichia coli. J Bacteriol. 1979 Jun;138(3):969–975. doi: 10.1128/jb.138.3.969-975.1979. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Nowicki B., Rhen M., Väisänen-Rhen V., Pere A., Korhonen T. K. Immunofluorescence study of fimbrial phase variation in Escherichia coli KS71. J Bacteriol. 1984 Nov;160(2):691–695. doi: 10.1128/jb.160.2.691-695.1984. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ofek I., Beachey E. H. Mannose binding and epithelial cell adherence of Escherichia coli. Infect Immun. 1978 Oct;22(1):247–254. doi: 10.1128/iai.22.1.247-254.1978. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ofek I., Mirelman D., Sharon N. Adherence of Escherichia coli to human mucosal cells mediated by mannose receptors. Nature. 1977 Feb 17;265(5595):623–625. doi: 10.1038/265623a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ofek I., Mosek A., Sharon N. Mannose-specific adherence of Escherichia coli freshly excreted in the urine of patients with urinary tract infections, and of isolates subcultured from the infected urine. Infect Immun. 1981 Dec;34(3):708–711. doi: 10.1128/iai.34.3.708-711.1981. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Old D. C., Duguid J. P. Selective outgrowth of fimbriate bacteria in static liquid medium. J Bacteriol. 1970 Aug;103(2):447–456. doi: 10.1128/jb.103.2.447-456.1970. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Old D. C. Inhibition of the interaction between fimbrial haemagglutinins and erythrocytes by D-mannose and other carbohydrates. J Gen Microbiol. 1972 Jun;71(1):149–157. doi: 10.1099/00221287-71-1-149. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Orndorff P. E., Falkow S. Identification and characterization of a gene product that regulates type 1 piliation in Escherichia coli. J Bacteriol. 1984 Oct;160(1):61–66. doi: 10.1128/jb.160.1.61-66.1984. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Orndorff P. E., Falkow S. Organization and expression of genes responsible for type 1 piliation in Escherichia coli. J Bacteriol. 1984 Aug;159(2):736–744. doi: 10.1128/jb.159.2.736-744.1984. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Salit I. E., Gotschlich E. C. Hemagglutination by purified type I Escherichia coli pili. J Exp Med. 1977 Nov 1;146(5):1169–1181. doi: 10.1084/jem.146.5.1169. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Salit I. E., Gotschlich E. C. Type I Escherichia coli pili: characterization of binding to monkey kidney cells. J Exp Med. 1977 Nov 1;146(5):1182–1194. doi: 10.1084/jem.146.5.1182. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Schaeffer A. J., Amundsen S. K., Jones J. M. Effect of carbohydrates on adherence of Escherichica coli to human urinary tract epithelial cells. Infect Immun. 1980 Nov;30(2):531–537. doi: 10.1128/iai.30.2.531-537.1980. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Silverblatt F. J., Dreyer J. S., Schauer S. Effect of pili on susceptibility of Escherichia coli to phagocytosis. Infect Immun. 1979 Apr;24(1):218–223. doi: 10.1128/iai.24.1.218-223.1979. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Silverblatt F. J. Host-parasite interaction in the rat renal pelvis: a possible role for pili in the pathogenesis of pyelonephritis. J Exp Med. 1974 Dec 1;140(6):1696–1711. doi: 10.1084/jem.140.6.1696. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Silverblatt F. J., Ofek I. Influence of pili on the virulence of Proteus mirabilis in experimental hematogenous pyelonephritis. J Infect Dis. 1978 Nov;138(5):664–667. doi: 10.1093/infdis/138.5.664. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Silverman M., Simon M. Phase variation: genetic analysis of switching mutants. Cell. 1980 Apr;19(4):845–854. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(80)90075-6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sternberger L. A., Hardy P. H., Jr, Cuculis J. J., Meyer H. G. The unlabeled antibody enzyme method of immunohistochemistry: preparation and properties of soluble antigen-antibody complex (horseradish peroxidase-antihorseradish peroxidase) and its use in identification of spirochetes. J Histochem Cytochem. 1970 May;18(5):315–333. doi: 10.1177/18.5.315. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Swaney L. M., Liu Y. P., To C. M., To C. C., Ippen-Ihler K., Brinton C. C., Jr Isolation and characterization of Escherichia coli phase variants and mutants deficient in type 1 pilus production. J Bacteriol. 1977 Apr;130(1):495–505. doi: 10.1128/jb.130.1.495-505.1977. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- van der Bosch J. F., Verboom-Sohmer U., Postma P., de Graaff J., MacLaren D. M. Mannose-sensitive and mannose-resistant adherence to human uroepithelial cells and urinary virulence of Escherichia coli. Infect Immun. 1980 Jul;29(1):226–233. doi: 10.1128/iai.29.1.226-233.1980. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]