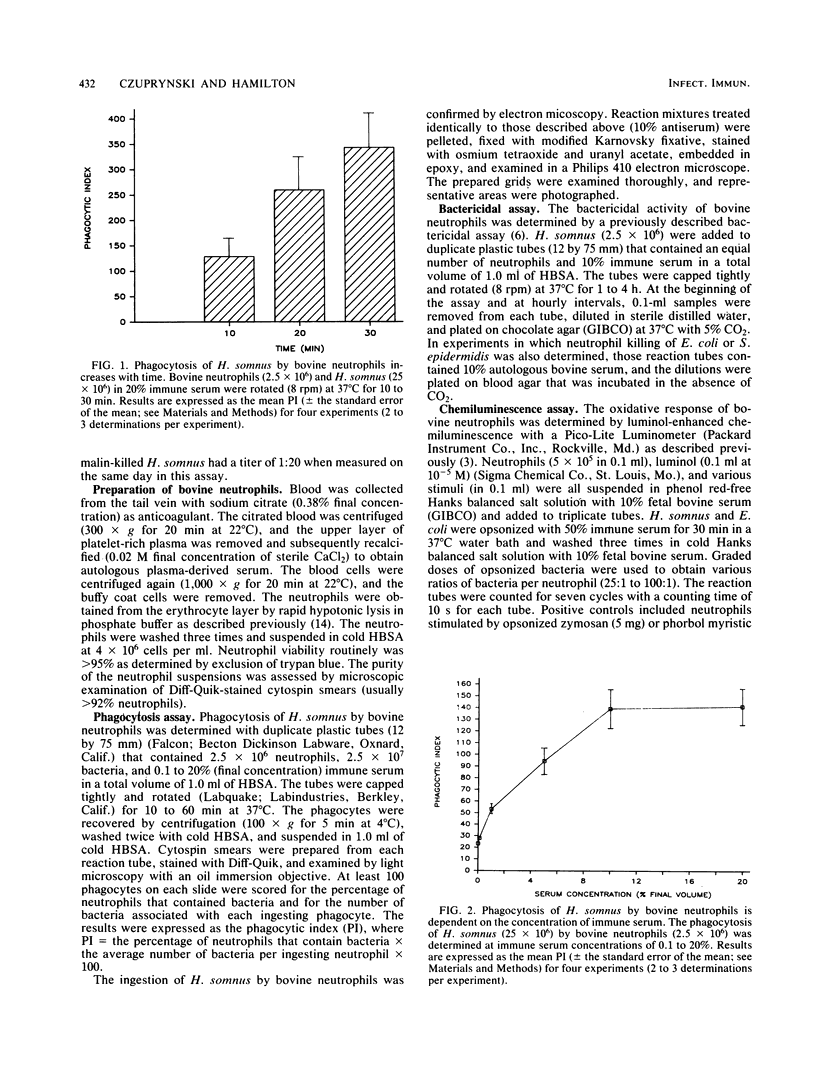
Abstract
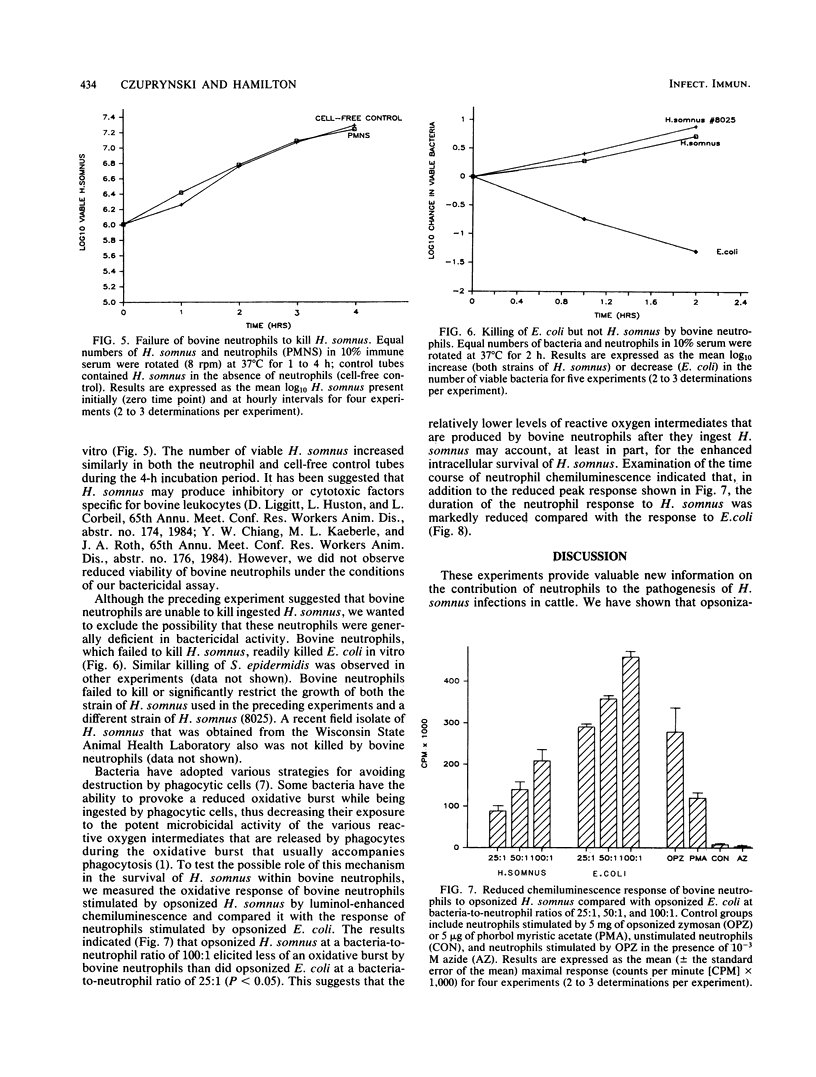
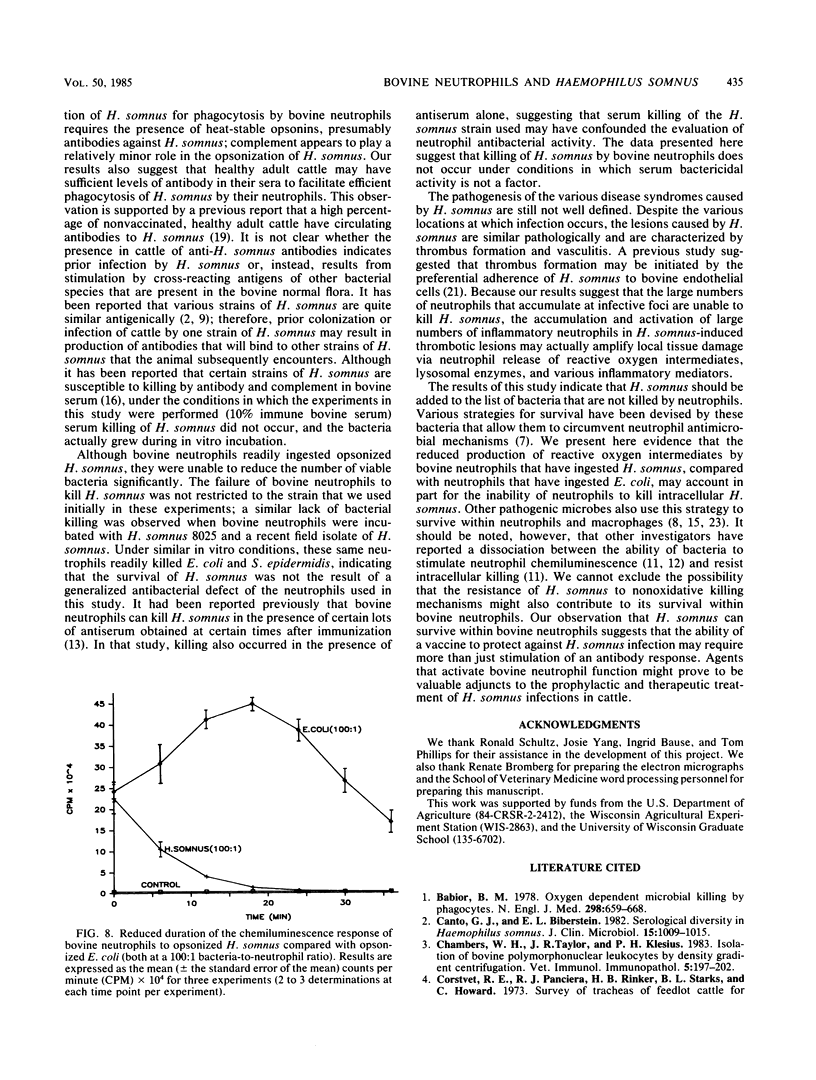
Phagocytosis of Haemophilus somnus by bovine blood neutrophils required opsonization of the bacteria with antibodies against H. somnus. Few bacteria were phagocytosed in the absence of serum; in addition, absorption of immune serum with Formalin-killed H. somnus significantly reduced ingestion of H. somnus. Heat inactivation of antiserum (56 degrees C for 30 min) to eliminate complement activity had little effect on its ability to opsonize H. somnus for uptake by bovine neutrophils. Antiserum from an H. somnus-immunized calf and autologous sera from adult cattle supported equivalent phagocytosis of H. somnus by bovine neutrophils, suggesting that normal, healthy cattle may contain sufficient antibodies in their sera to facilitate phagocytosis of H. somnus. Although bovine neutrophils readily ingested H. somnus, they were unable to kill the bacterium in vitro. These same neutrophils readily killed opsonized Escherichia coli and Staphylococcus epidermidis, suggesting that H. somnus is able to survive and perhaps multiply within bovine neutrophils. Because bovine neutrophils stimulated with opsonized H. somnus demonstrated a reduced oxidative burst (as measured by chemiluminescence) compared with neutrophils stimulated by opsonized E. coli, we suggest that reduced production of reactive oxygen intermediates during the phagocytosis of H. somnus may account, in part, for the enhanced survival of H. somnus in bovine neutrophils.
Full text
PDF


Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Babior B. M. Oxygen-dependent microbial killing by phagocytes (first of two parts). N Engl J Med. 1978 Mar 23;298(12):659–668. doi: 10.1056/NEJM197803232981205. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Canto G. J., Biberstein E. L. Serological diversity in Haemophilus somnus. J Clin Microbiol. 1982 Jun;15(6):1009–1015. doi: 10.1128/jcm.15.6.1009-1015.1982. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Chambers W. H., Taylor J. R., Klesius P. H. Isolation of bovine polymorphonuclear leukocytes by density gradient centrifugation. Vet Immunol Immunopathol. 1983 Dec;5(2):197–202. doi: 10.1016/0165-2427(83)90020-x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Crandell R. A., Smith A. R., Kissil M. Colonization and transmission of Haemophilus somnus in cattle. Am J Vet Res. 1977 Nov;38(11):1749–1751. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Czuprynski C. J., Henson P. M., Campbell P. A. Killing of Listeria monocytogenes by inflammatory neutrophils and mononuclear phagocytes from immune and nonimmune mice. J Leukoc Biol. 1984 Feb;35(2):193–208. doi: 10.1002/jlb.35.2.193. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Densen P., Mandell G. L. Phagocyte strategy vs. microbial tactics. Rev Infect Dis. 1980 Sep-Oct;2(5):817–838. doi: 10.1093/clinids/2.5.817. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gangadharam P. R., Edwards C. K., 3rd Release of superoxide anion from resident and activated mouse peritoneal macrophages infected with Mycobacterium intracellulare. Am Rev Respir Dis. 1984 Nov;130(5):834–838. doi: 10.1164/arrd.1984.130.5.834. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Garcia-Delgado G. A., Little P. B., Barnum D. A. A comparison of various Haemophilus somnus strains. Can J Comp Med. 1977 Oct;41(4):380–388. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- KENNEDY P. C., BIBERSTEIN E. L., HOWARTH J. A., FRAZIER L. M., DUNGWORTH D. L. Infectious meningo-encephalitis in cattle, caused by a haemophilus-like organism. Am J Vet Res. 1960 Mar;21:403–409. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kossack R. E., Guerrant R. L., Densen P., Schadelin J., Mandell G. L. Diminished neutrophil oxidative metabolism after phagocytosis of virulent Salmonella typhi. Infect Immun. 1981 Feb;31(2):674–678. doi: 10.1128/iai.31.2.674-678.1981. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Miller R. M., Garbus J., Hornick R. B. Lack of enhanced oxygen consumption by polymorphonuclear leukocytes on phagocytosis of virulent Salmonella typhi. Science. 1972 Mar 3;175(4025):1010–1011. doi: 10.1126/science.175.4025.1010. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Pennell J. R., Renshaw H. W. Haemophilus somnus complex: in vitro interactions of Haemophilus somnus, leukocytes, complement, and antiserums produced from vaccination of cattle with fractions of the organism. Am J Vet Res. 1977 Jun;38(6):759–769. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Roth J. A., Kaeberle M. L. Evaluation of bovine polymorphonuclear leukocyte function. Vet Immunol Immunopathol. 1981 Apr;2(2):157–174. doi: 10.1016/0165-2427(81)90047-7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sasada M., Johnston R. B., Jr Macrophage microbicidal activity. Correlation between phagocytosis-associated oxidative metabolism and the killing of Candida by macrophages. J Exp Med. 1980 Jul 1;152(1):85–98. doi: 10.1084/jem.152.1.85. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Simonson R. R., Maheswaran S. K. Host humoral factors in natural resistance to Haemophilus somnus. Am J Vet Res. 1982 Jul;43(7):1160–1164. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
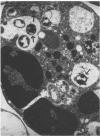
- Stephens L. R., Little P. B. Ultrastructure of Haemophilus somnus, causative agent of bovine infectious thromboembolic meningoencephalitis. Am J Vet Res. 1981 Sep;42(9):1638–1640. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Stephens L. R., Little P. B., Wilkie B. N., Barnum D. A. Infectious thromboembolic meningoencephalitis in cattle: a review. J Am Vet Med Assoc. 1981 Feb 15;178(4):378–384. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Stephens L. R., Little P. B., Wilkie B. N., Barnum D. A. Isolation of Haemophilus somnus antigens and their use as vaccines for prevention of bovine thromboembolic meningoencephalitis. Am J Vet Res. 1984 Feb;45(2):234–239. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Thompson K. G., Little P. B. Effect of Haemophilus somnus on bovine endothelial cell in organ culture. Am J Vet Res. 1981 May;42(5):748–754. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Williams J. M., Smith G. L., Murdock F. M. Immunogenicity of a Haemophilus somnus bacterin in cattle. Am J Vet Res. 1978 Nov;39(11):1756–1762. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wilson C. B., Tsai V., Remington J. S. Failure to trigger the oxidative metabolic burst by normal macrophages: possible mechanism for survival of intracellular pathogens. J Exp Med. 1980 Feb 1;151(2):328–346. doi: 10.1084/jem.151.2.328. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]