Abstract
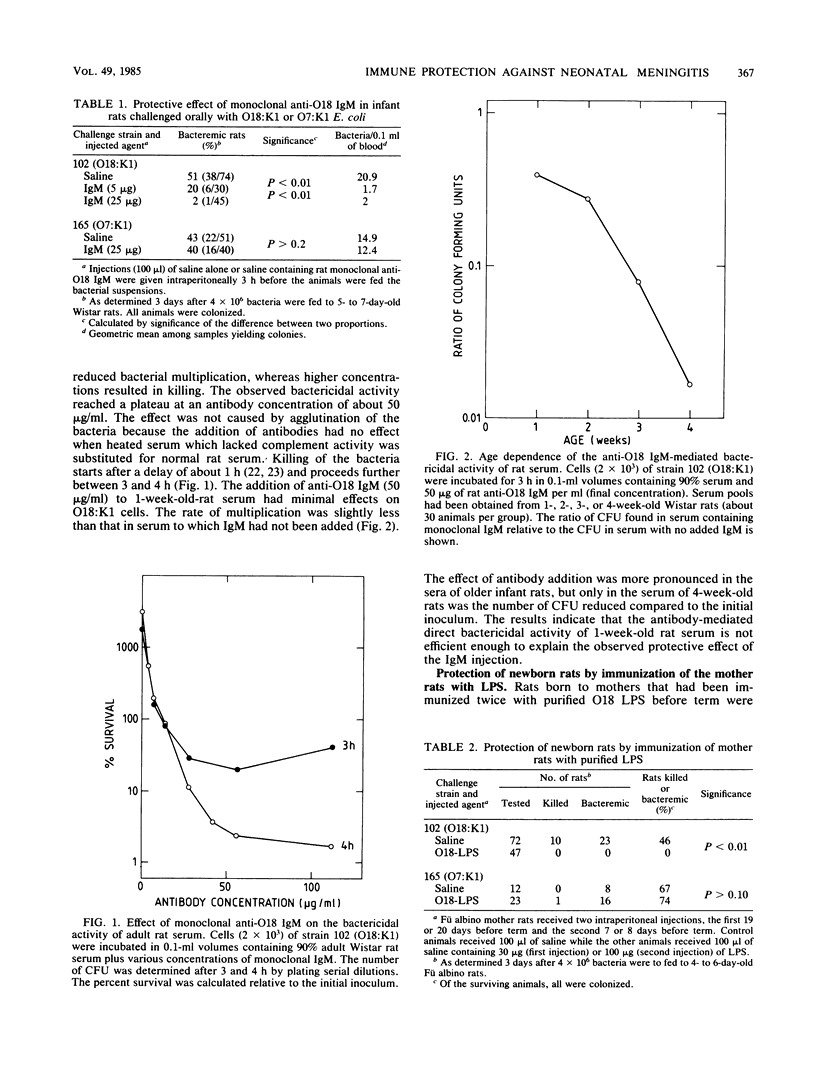
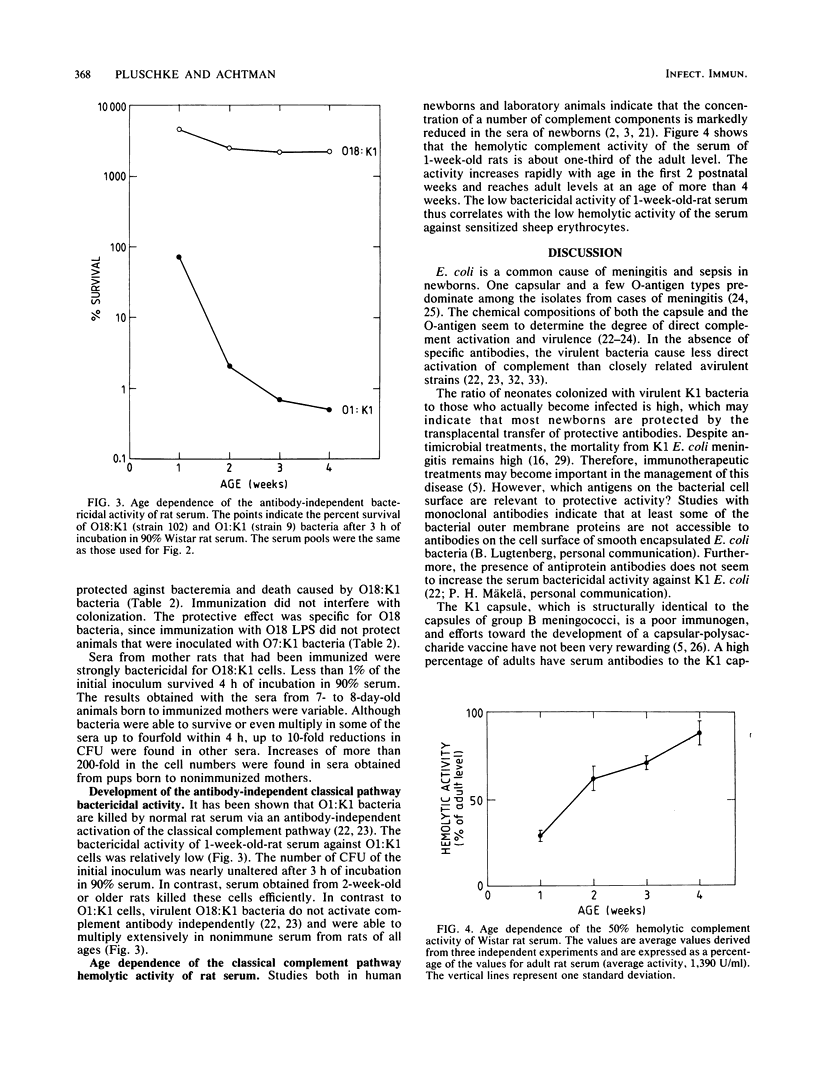
Monoclonal IgM specific for the O18 antigen conferred passive protection to 1-week-old rats against bacteremia and killing after oral challenge with O18:K1 Escherichia coli. Specific protection of the pups was also achieved by immunizing the pregnant rats with purified O18 lipopolysaccharide. We suppose that most human newborns that are colonized by potentially invasive K1 E. coli are protected by the transplacental transfer of anti-lipopolysaccharide immunoglobulin G, and we suggest that treatment with such antibodies might in the future be considered a therapeutic option. Rat serum from 1-week-old animals had only about one-third of the complement hemolytic activity of adult rat serum. This low level of hemolytic activity correlated with a relatively poor bactericidal activity in antibody-dependent and antibody-independent bactericidal in vitro assays. Monoclonal anti-O18 immunoglobulin M, although protective in vivo and bactericidal when added to adult rat serum, only poorly inhibited the multiplication of O18:K1 cells in serum from 1-week-old rats. This suggests that other elements of host defense besides complement participate in antibody-mediated in vivo protection.
Full text
PDF



Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Achtman M., Mercer A., Kusecek B., Pohl A., Heuzenroeder M., Aaronson W., Sutton A., Silver R. P. Six widespread bacterial clones among Escherichia coli K1 isolates. Infect Immun. 1983 Jan;39(1):315–335. doi: 10.1128/iai.39.1.315-335.1983. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bortolussi R., Ferrieri P., Björkstén B., Quie P. G. Capsular K1 polysaccharide of Escherichia coli: relationship to virulence in newborn rats and resistance to phagocytosis. Infect Immun. 1979 Jul;25(1):293–298. doi: 10.1128/iai.25.1.293-298.1979. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Cross A. S., Zollinger W., Mandrell R., Gemski P., Sadoff J. Evaluation of immunotherapeutic approaches for the potential treatment of infections caused by K1-positive Escherichia coli. J Infect Dis. 1983 Jan;147(1):68–76. doi: 10.1093/infdis/147.1.68. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Finne J., Leinonen M., Mäkelä P. H. Antigenic similarities between brain components and bacteria causing meningitis. Implications for vaccine development and pathogenesis. Lancet. 1983 Aug 13;2(8346):355–357. doi: 10.1016/s0140-6736(83)90340-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Galfre G., Howe S. C., Milstein C., Butcher G. W., Howard J. C. Antibodies to major histocompatibility antigens produced by hybrid cell lines. Nature. 1977 Apr 7;266(5602):550–552. doi: 10.1038/266550a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Glode M. P., Sutton A., Moxon E. R., Robbins J. B. Pathogenesis of neonatal Escherichia coli meningitis: induction of bacteremia and meningitis in infant rats fed E. coli K1. Infect Immun. 1977 Apr;16(1):75–80. doi: 10.1128/iai.16.1.75-80.1977. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Jehanli A., Hough D. A rapid procedure for the isolation of human IgM myeloma proteins. J Immunol Methods. 1981;44(2):199–204. doi: 10.1016/0022-1759(81)90347-1. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Joiner K. A., Goldman R. C., Hammer C. H., Leive L., Frank M. M. Studies of the mechanism of bacterial resistance to complement-mediated killing. V. IgG and F(ab')2 mediate killing of E. coli 0111B4 by the alternative complement pathway without increasing C5b-9 deposition. J Immunol. 1983 Nov;131(5):2563–2569. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Joiner K. A., Goldman R. C., Hammer C. H., Leive L., Frank M. M. Studies on the mechanism of bacterial resistance to complement-mediated killing. VI. IgG increases the bactericidal efficiency of C5b-9 for E. coli 0111B4 by acting at a step before C5 cleavage. J Immunol. 1983 Nov;131(5):2570–2575. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Joiner K. A., Goldman R., Schmetz M., Berger M., Hammer C. H., Frank M. M., Leive L. A quantitative analysis of C3 binding to O-antigen capsule, lipopolysaccharide, and outer membrane protein of E. coli 0111B4. J Immunol. 1984 Jan;132(1):369–375. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kusecek B., Wloch H., Mercer A., Vaisänen V., Pluschke G., Korhonen T., Achtman M. Lipopolysaccharide, capsule, and fimbriae as virulence factors among O1, O7, O16, O18, or O75 and K1, K5, or K100 Escherichia coli. Infect Immun. 1984 Jan;43(1):368–379. doi: 10.1128/iai.43.1.368-379.1984. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- McCracken G. H., Jr, Mize S. G., Threlkeld N. Intraventricular gentamicin therapy in gram-negative bacillary meningitis of infancy. Report of the Second Neonatal Meningitis Cooperative Study Group. Lancet. 1980 Apr 12;1(8172):787–791. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Moreno C., Hewitt J., Hastings K., Brown D. Immunological properties of monoclonal antibodies specific for meningococcal polysaccharides: the protective capacity of IgM antibodies specific for polysaccharide group B. J Gen Microbiol. 1983 Aug;129(8):2451–2456. doi: 10.1099/00221287-129-8-2451. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ochman H., Selander R. K. Evidence for clonal population structure in Escherichia coli. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1984 Jan;81(1):198–201. doi: 10.1073/pnas.81.1.198. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Olling S., Hanson L. A., Holmgren J., Jodal U., Lincoln K., Lindberg U. The bactericidal effect of normal human serum on E. coli strains from normals and from patients with urinary tract infections. Infection. 1973;1(1):24–28. doi: 10.1007/BF01638251. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Orskov F., Sorenson K. B. Escherichia coli serogroups in breast-fed and bottle-fed infants. Acta Pathol Microbiol Scand B. 1975 Feb;83(1):25–30. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Pabst H. F., Kreth H. W. Ontogeny of the immune response as a basis of childhood disease. J Pediatr. 1980 Oct;97(4):519–534. doi: 10.1016/s0022-3476(80)80003-5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Pluschke G., Achtman M. Degree of antibody-independent activation of the classical complement pathway by K1 Escherichia coli differs with O antigen type and correlates with virulence of meningitis in newborns. Infect Immun. 1984 Feb;43(2):684–692. doi: 10.1128/iai.43.2.684-692.1984. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Pluschke G., Mayden J., Achtman M., Levine R. P. Role of the capsule and the O antigen in resistance of O18:K1 Escherichia coli to complement-mediated killing. Infect Immun. 1983 Dec;42(3):907–913. doi: 10.1128/iai.42.3.907-913.1983. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Pluschke G., Mercer A., Kusećek B., Pohl A., Achtman M. Induction of bacteremia in newborn rats by Escherichia coli K1 is correlated with only certain O (lipopolysaccharide) antigen types. Infect Immun. 1983 Feb;39(2):599–608. doi: 10.1128/iai.39.2.599-608.1983. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Robbins J. B., McCracken G. H., Jr, Gotschlich E. C., Orskov F., Orskov I., Hanson L. A. Escherichia coli K1 capsular polysaccharide associated with neonatal meningitis. N Engl J Med. 1974 May 30;290(22):1216–1220. doi: 10.1056/NEJM197405302902202. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sarff L. D., McCracken G. H., Schiffer M. S., Glode M. P., Robbins J. B., Orskov I., Orskov F. Epidemiology of Escherichia coli K1 in healthy and diseased newborns. Lancet. 1975 May 17;1(7916):1099–1104. doi: 10.1016/s0140-6736(75)92496-4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Shulman M., Wilde C. D., Köhler G. A better cell line for making hybridomas secreting specific antibodies. Nature. 1978 Nov 16;276(5685):269–270. doi: 10.1038/276269a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Siegel J. D., McCracken G. H., Jr Sepsis neonatorum. N Engl J Med. 1981 Mar 12;304(11):642–647. doi: 10.1056/NEJM198103123041105. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Stephens S. Development of a sensitive solid-phase radioimmunoassay technique for quantification of class-specific Escherichia coli antibodies. J Immunol Methods. 1984 Jul 6;71(2):203–210. doi: 10.1016/0022-1759(84)90066-8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Stevens P., Huang S. N., Welch W. D., Young L. S. Restricted complement activation by Escherichia coli with the K-1 capsular serotype: a possible role in pathogenicity. J Immunol. 1978 Dec;121(6):2174–2180. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Stevens P., Young L. S., Adamu S. Opsonization of various capsular (K) E. coli by the alternative complement pathway. Immunology. 1983 Nov;50(3):497–502. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Söderström T., Stein K., Brinton C. C., Jr, Hosea S., Burch C., Hansson H. A., Karpas A., Schneerson R., Sutton A., Vann W. I. Serological and functional properties of monoclonal antibodies to Escherichia coli type I pilus and capsular antigens. Prog Allergy. 1983;33:259–274. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]


