Abstract
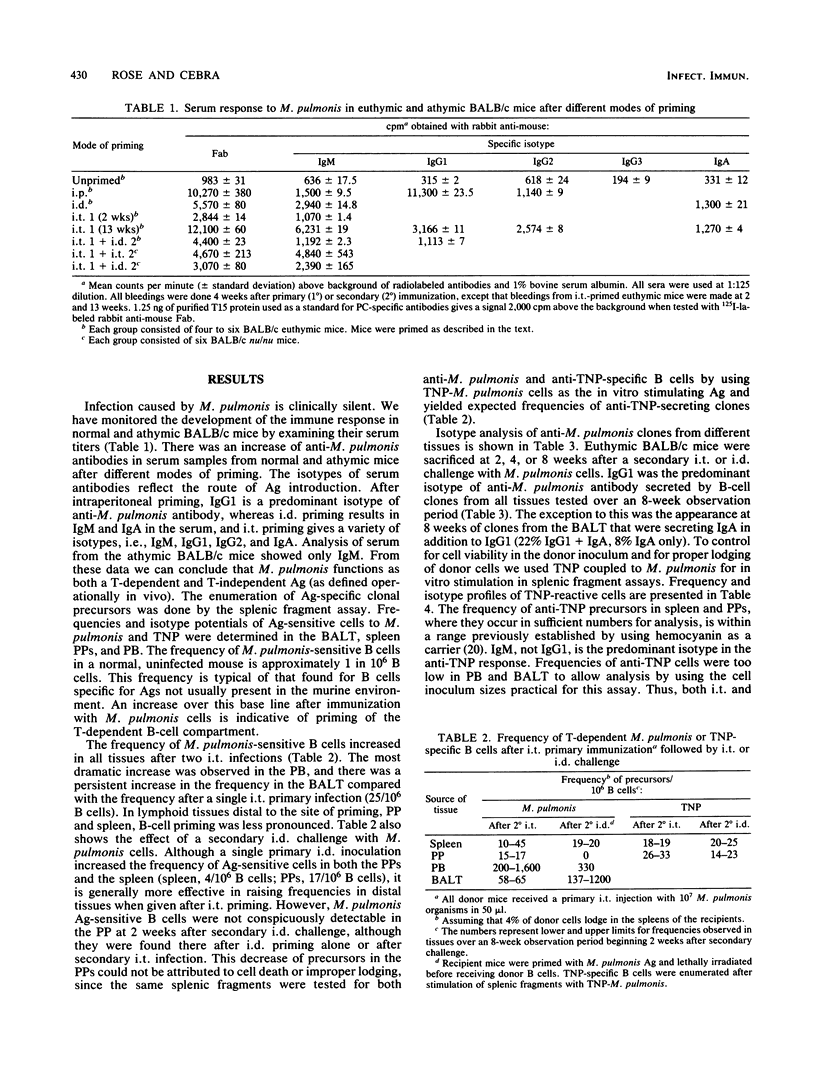
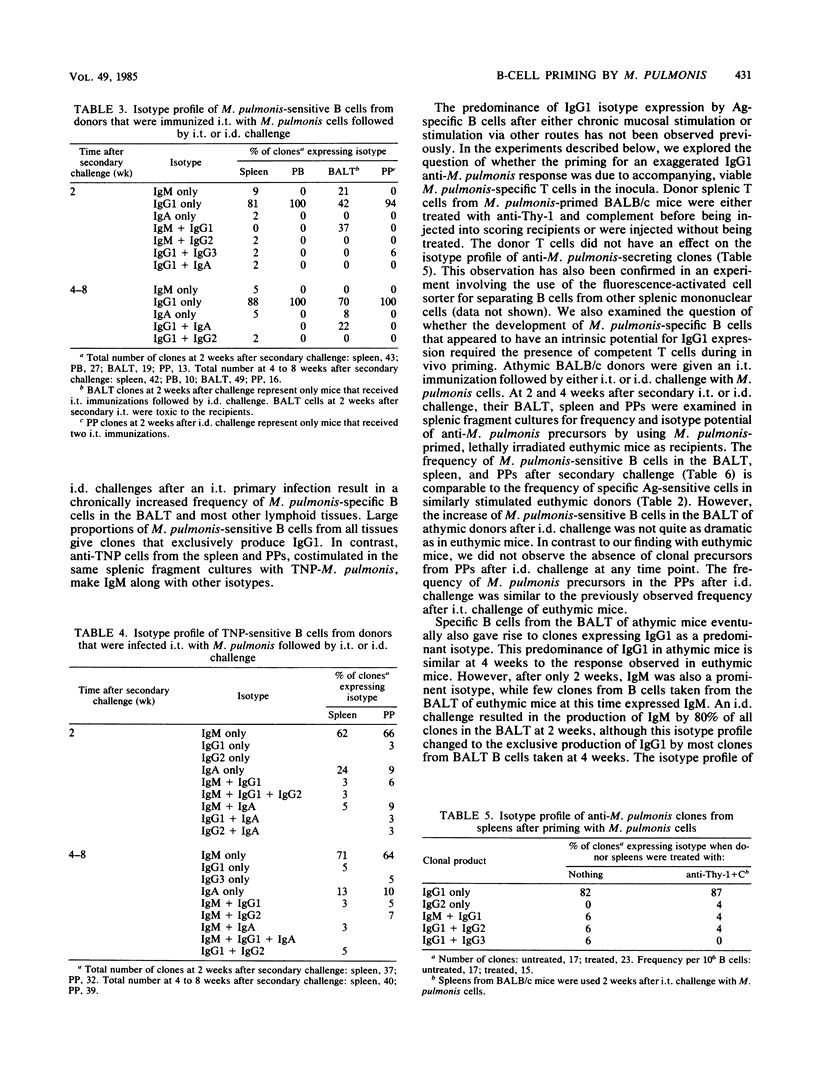
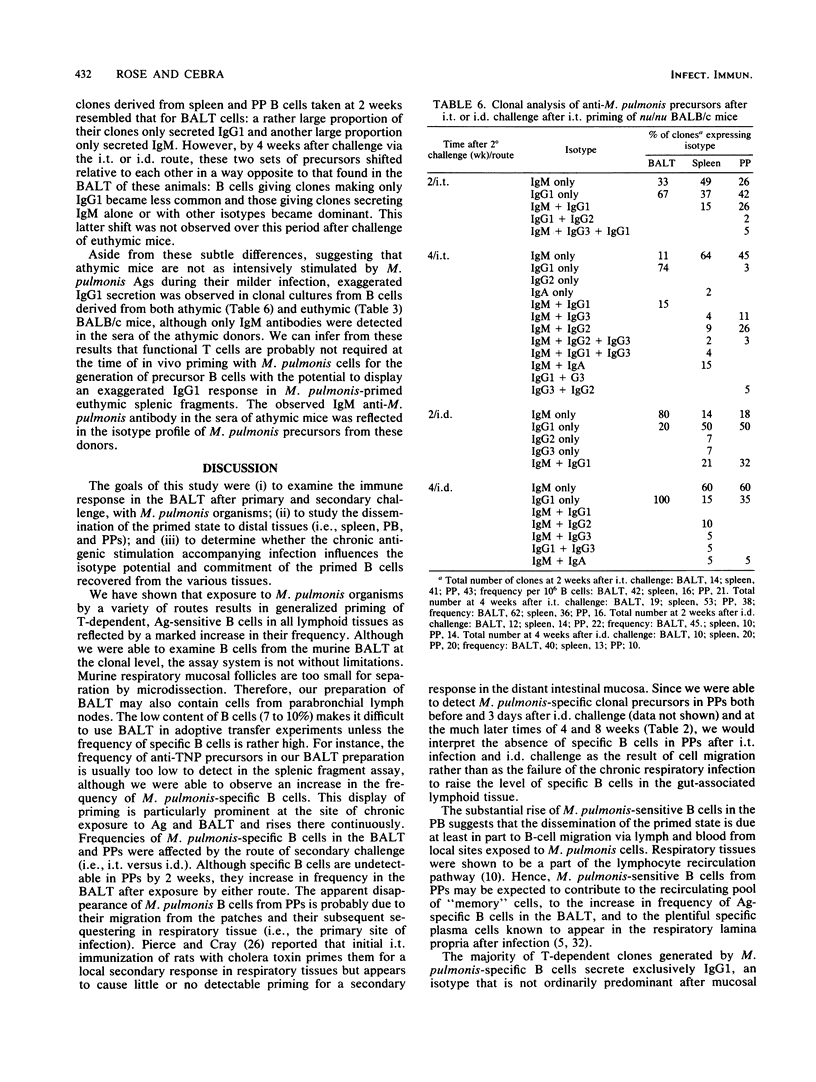
Live Mycoplasma pulmonis organisms were used to examine the immune response in the bronchus-associated lymphoid tissue after primary and secondary challenge with M. pulmonis, to study the dissemination of the primed state to distal tissues (i.e., spleen, peripheral blood, and Peyer's patches), and to determine whether the chronic antigenic stimulation accompanying infection influences the isotype potential and commitment of the primed B cells recovered from the various tissues. We have shown that exposure to M. pulmonis by a variety of routes results in a generalized rise in frequency of T-dependent, antigen-sensitive B cells in all lymphoid tissues. The route of secondary exposure to M. pulmonis was found to markedly increase the frequency of M. pulmonis-specific B cells in the bronchus-associated lymphoid tissue relative to that in the Peyer's patches after intraduodenal but not intratracheal challenge. A substantial rise in the number of M. pulmonis-sensitive B cells in the peripheral blood suggests that the dissemination of the primed state, at least in part, is due to B-cell migration via lymph and blood from local sites exposed to M. pulmonis. The majority of T-dependent clones generated by M. pulmonis-specific B cells secrete exclusively immunoglobulin G1 (IgG1). We have demonstrated that the exaggerated IgG1 response was not due to the accompanying viable donor T cells in the inoculum. The predominance of IgG1 was also demonstrated in clones from the bronchus-associated lymphoid tissue of athymic BALB/c mice that were primed with M. pulmonis. Thus, we can infer that functional T cells are not required for the development of specific B cells with the potential for IgG1 expression at the time of in vivo priming. When anti-trinitrophenyl- and anti-M. pulmonis-specific clones were generated in the same splenic fragment cultures stimulated by trinitrophenylated M. pulmonis, only the M. pulmonis-specific clones showed exaggerated IgG1 expression. Therefore, we conclude that the exaggerated IgG1 response accompanying M. pulmonis infection of euthymic mice seems to be dependent, at least in part, on an intrinsic property of the B cells that develop during this antigenic stimulation.
Full text
PDF



Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Bienenstock J., Johnston N., Perey D. Y. Bronchial lymphoid tissue. I. Morphologic characteristics. Lab Invest. 1973 Jun;28(6):686–692. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Blandford G., Heath R. B. Studies on the immune response and pathogenesis of Sendai virus infection of mice. II. The immunoglobulin class of plasma cells in the bronchial sub-mucosa. Immunology. 1974 Mar;26(3):667–671. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Breeze R. G., Wheeldon E. B. The cells of the pulmonary airways. Am Rev Respir Dis. 1977 Oct;116(4):705–777. doi: 10.1164/arrd.1977.116.4.705. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bruce J., Symington F. W., McKearn T. J., Sprent J. A monoclonal antibody discriminating between subsets of T and B cells. J Immunol. 1981 Dec;127(6):2496–2501. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Cassell G. H., Lindsey J. R., Baker H. J. Immune response of pathogen-free mice inoculated intranasally with Mycoplasma pulmonis. J Immunol. 1974 Jan;112(1):124–136. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Cebra J. J., Gearhart P. J., Halsey J. F., Hurwitz J. L., Shahin R. D. Role of environmental antigens in the ontogeny of the secretory immune response. J Reticuloendothel Soc. 1980 Dec;28(Suppl):61s–71s. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Chapman C. B., Knopf P. M., Anders R. F., Mitchell G. F. IgG1 hypergammaglobulinaemia in chronic parasitic infections in mice: evidence that the response reflects chronicity of antigen exposure. Aust J Exp Biol Med Sci. 1979 Aug;57(4):389–400. doi: 10.1038/icb.1979.39. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Cooper J. M., Finlay-Jones J. J., Hill N. L., Rowley D. Local immunity to klebsiella pneumoniae in the lungs of mice. J Infect Dis. 1983 Feb;147(2):312–317. doi: 10.1093/infdis/147.2.312. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Craig S. W., Cebra J. J. Peyer's patches: an enriched source of precursors for IgA-producing immunocytes in the rabbit. J Exp Med. 1971 Jul 1;134(1):188–200. doi: 10.1084/jem.134.1.188. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Emeson E. E., Norin A. J., Veith F. J. Antigen-induced recruitment of circulating lymphocytes to the lungs and hilar lymph nodes of mice challenged intratracheally with alloantigens. Am Rev Respir Dis. 1982 Apr;125(4):453–459. doi: 10.1164/arrd.1982.125.4.453. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Fuhrman J. A., Cebra J. J. Special features of the priming process for a secretory IgA response. B cell priming with cholera toxin. J Exp Med. 1981 Mar 1;153(3):534–544. doi: 10.1084/jem.153.3.534. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gabridge M. G., Singer S. E., Esposito R. A. Cultivation of mycoplasmas in a modified tissue culture medium. Appl Environ Microbiol. 1976 Jun;31(6):986–989. doi: 10.1128/aem.31.6.986-989.1976. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gearhart P. J., Cebra J. J. Differentiated B lymphocytes. Potential to express particular antibody variable and constant regions depends on site of lymphoid tissue and antigen load. J Exp Med. 1979 Jan 1;149(1):216–227. doi: 10.1084/jem.149.1.216. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hurwitz J. L., Tagart V. B., Schweitzer P. A., Cebra J. J. Patterns of isotype expression by B cell clones responding to thymus-dependent and thymus-independent antigens in vitro. Eur J Immunol. 1982 Apr;12(4):342–348. doi: 10.1002/eji.1830120416. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Isakson P. C., Puré E., Vitetta E. S., Krammer P. H. T cell-derived B cell differentiation factor(s). Effect on the isotype switch of murine B cells. J Exp Med. 1982 Mar 1;155(3):734–748. doi: 10.1084/jem.155.3.734. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ishikawa H., Saito K. Congenitally athymic nude (nu/nu) mice have Thy-1-bearing immunocompetent helper T cells in their peritoneal cavity. J Exp Med. 1980 Apr 1;151(4):965–968. doi: 10.1084/jem.151.4.965. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kiyono H., Cooper M. D., Kearney J. F., Mosteller L. M., Michalek S. M., Koopman W. J., McGhee J. R. Isotype specificity of helper T cell clones. Peyer's patch Th cells preferentially collaborate with mature IgA B cells for IgA responses. J Exp Med. 1984 Mar 1;159(3):798–811. doi: 10.1084/jem.159.3.798. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kiyono H., McGhee J. R., Wannemuehler M. J., Frangakis M. V., Spalding D. M., Michalek S. M., Koopman W. J. In vivo immune response to a T-cell-dependent antigen by cultures of disassociated murine Peyer's patch. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1982 Jan;79(2):596–600. doi: 10.1073/pnas.79.2.596. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Klinman N. R. Antibody with homogeneous antigen binding produced by splenic foci in organ culture. Immunochemistry. 1969 Sep;6(5):757–759. doi: 10.1016/0019-2791(67)90140-1. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Klinman N. R., Press J. L. The B cell specificity repertoire: its relationship to definable subpopulations. Transplant Rev. 1975;24:41–83. doi: 10.1111/j.1600-065x.1975.tb00165.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- LOWRY O. H., ROSEBROUGH N. J., FARR A. L., RANDALL R. J. Protein measurement with the Folin phenol reagent. J Biol Chem. 1951 Nov;193(1):265–275. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ledbetter J. A., Herzenberg L. A. Xenogeneic monoclonal antibodies to mouse lymphoid differentiation antigens. Immunol Rev. 1979;47:63–90. doi: 10.1111/j.1600-065x.1979.tb00289.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Martinez-Alonso C., Coutinho A., Augustin A. A. Immunoglobulin C-gene expression. I. The commitment to IgG subclass of secretory cells is determined by the quality of the nonspecific stimuli. Eur J Immunol. 1980 Sep;10(9):698–702. doi: 10.1002/eji.1830100908. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- McDermott M. R., Bienenstock J. Evidence for a common mucosal immunologic system. I. Migration of B immunoblasts into intestinal, respiratory, and genital tissues. J Immunol. 1979 May;122(5):1892–1898. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Pierce N. F., Cray W. C., Jr Cellular dissemination of priming for a mucosal immune response to cholera toxin in rats. J Immunol. 1981 Dec;127(6):2461–2464. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Prowse S. J., Mitchell G. F., Ey P. L., Jenkin C. R. Nematospiroides dubius: susceptibility to infection and the development of resistance in hypothymic (nude) BALB/c mice. Aust J Exp Biol Med Sci. 1978 Oct;56(5):561–570. doi: 10.1038/icb.1978.62. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rudzik R., Clancy R. L., Perey D. Y., Day R. P., Bienenstock J. Repopulation with IgA-containing cells of bronchial and intestinal lamina propria after transfer of homologous Peyer's patch and bronchial lymphocytes. J Immunol. 1975 May;114(5):1599–1604. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sigal N. H., Pickard A. R., Metcalf E. S., Gearhart P. J., Klinman N. R. Expression of phosphorylcholine-specific B cells during murine development. J Exp Med. 1977 Oct 1;146(4):933–948. doi: 10.1084/jem.146.4.933. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Speck N. A., Pierce S. K. The collaborative phenotype of secondary B cells is determined by T lymphocytes during in vivo immunization. J Exp Med. 1982 Feb 1;155(2):574–586. doi: 10.1084/jem.155.2.574. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Taylor G., Howard C. J. Class-specific antibody responses to Mycoplasma pulmonis in sera and lungs of infected and vaccinated mice. Infect Immun. 1980 Sep;29(3):1160–1168. doi: 10.1128/iai.29.3.1160-1168.1980. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Taylor G. Solid-phase micro-radioimmunoassay to measure immunoglobulin class-specific antibody to Mycoplasma pulmonis. Infect Immun. 1979 Jun;24(3):701–706. doi: 10.1128/iai.24.3.701-706.1979. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]


