Abstract
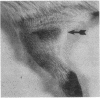
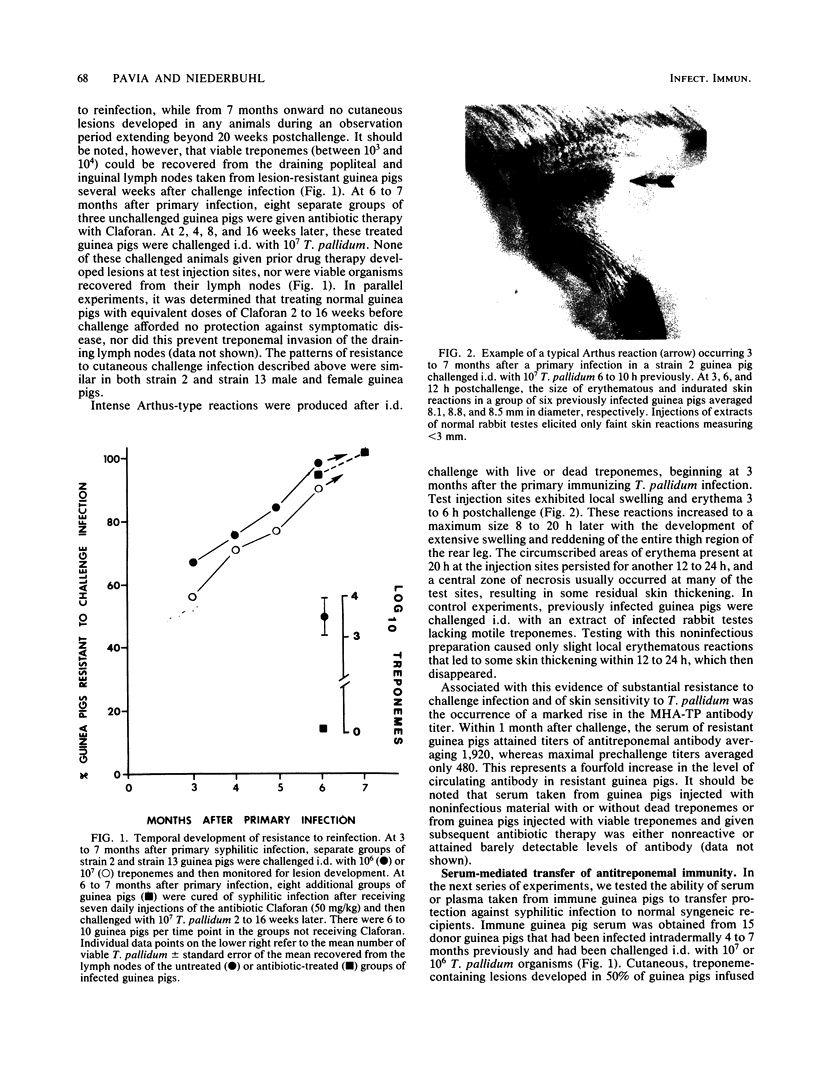
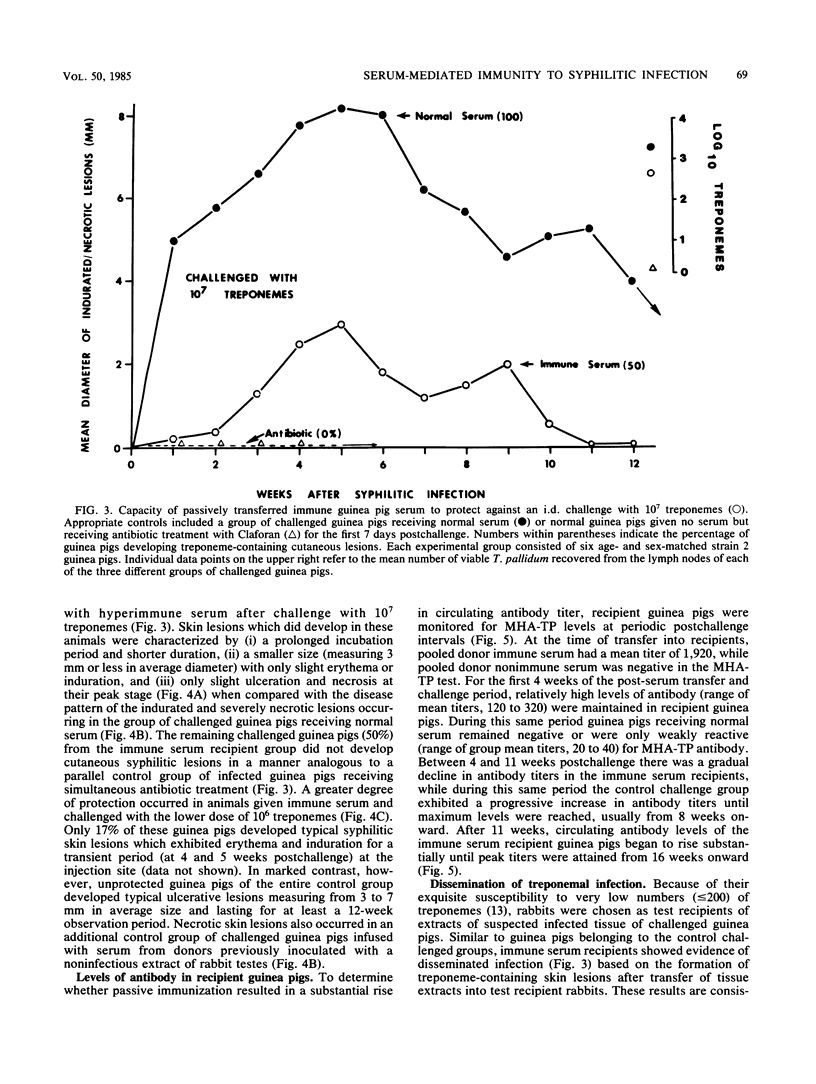
Resistance to cutaneous syphilitic reinfection in strain 2 and strain 13 guinea pigs developed gradually 3 to 7 months after primary infection and reached maximum levels at 6 to 7 months after the induction of primary cutaneous disease. Associated with this acquired resistance was the occurrence of Arthus reactions and anamnestic-type antibody responses. Passive transfer of immune serum containing high-titered treponemal antibody into normal strain 2 guinea pigs significantly delayed the appearance and markedly diminished the severity and duration of skin lesions that developed after these recipients were challenged with treponemes but did not prevent the dissemination of organisms to the draining lymph nodes. These findings provide direct evidence that syphilitic infection elicits the formation of serum factors that are, at least, partially protective against symptomatic disease.
Full text
PDF

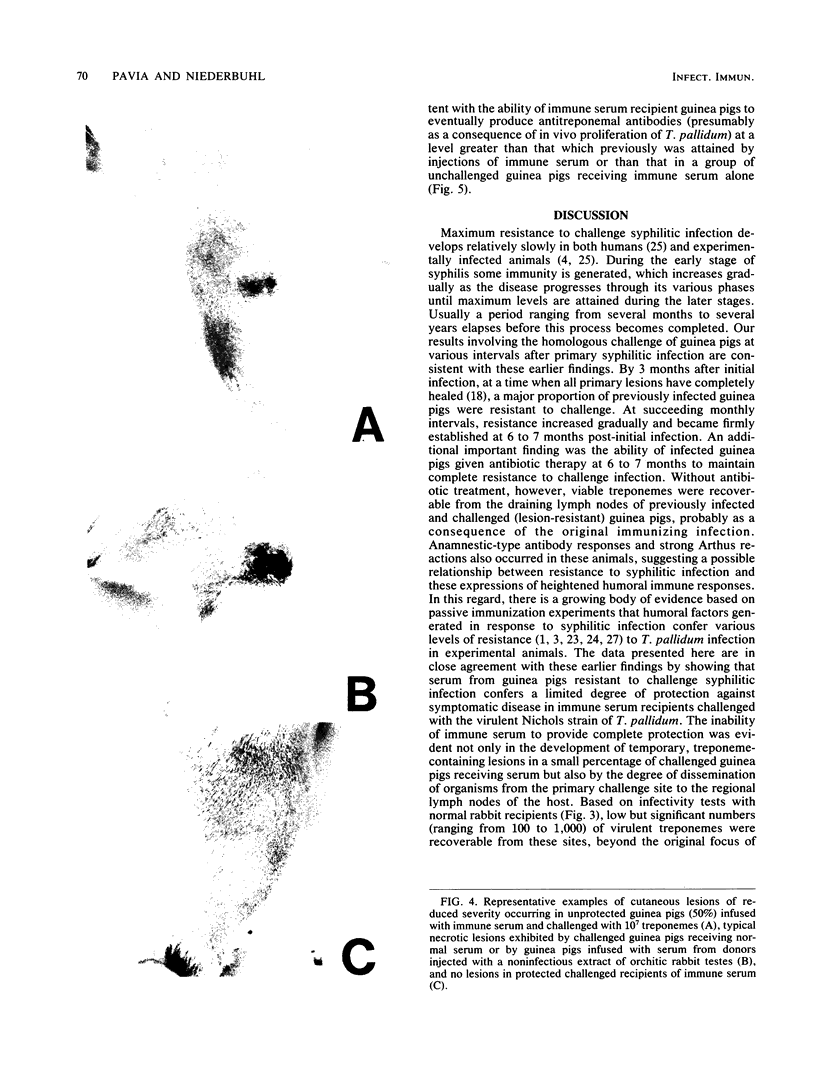
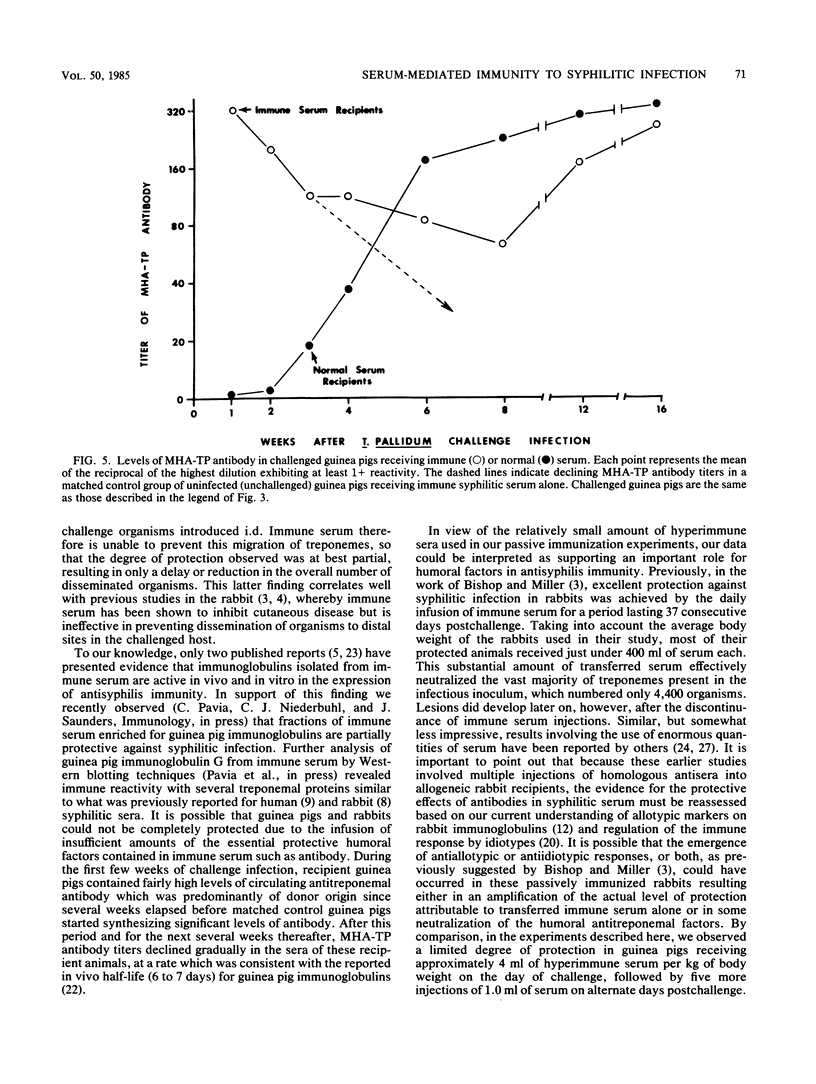

Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Azadegan A. A., Schell R. F., LeFrock J. L. Immune serum confers protection against syphilitic infection on hamsters. Infect Immun. 1983 Oct;42(1):42–47. doi: 10.1128/iai.42.1.42-47.1983. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Baughn R. E., Musher D. M. Reappraisal of lymphocyte responsiveness to concanavalin A during experimental syphilis: evidence that glycosaminoglycans in the sera and tissues interfere ith active binding sites on the lectin and not with the lymphocytes. Infect Immun. 1982 Feb;35(2):552–559. doi: 10.1128/iai.35.2.552-559.1982. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bishop N. H., Miller J. N. Humoral immunity in experimental syphilis. I. The demonstration of resistance conferred by passive immunization. J Immunol. 1976 Jul;117(1):191–196. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bishop N. H., Miller J. N. Humoral immunity in experimental syphilis. II. The relationship of neutralizing factors in immune serum to acquired resistance. J Immunol. 1976 Jul;117(1):197–207. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Blanco D. R., Miller J. N., Hanff P. A. Humoral immunity in experimental syphilis: the demonstration of IgG as a treponemicidal factor in immune rabbit serum. J Immunol. 1984 Nov;133(5):2693–2697. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Collart P., Franceschini P., Durel P. Experimental rabbit syphilis. Br J Vener Dis. 1971 Dec;47(6):389–400. doi: 10.1136/sti.47.6.389. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Fieldsteel A. H., Becker F. A., Stout J. G. Prolonged survival of virulent Treponema pallidum (Nichols strain) in cell-free and tissue culture systems. Infect Immun. 1977 Oct;18(1):173–182. doi: 10.1128/iai.18.1.173-182.1977. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hanff P. A., Bishop N. H., Miller J. N., Lovett M. A. Humoral immune response in experimental syphilis to polypeptides of Treponema pallidum. J Immunol. 1983 Oct;131(4):1973–1977. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hanff P. A., Fehniger T. E., Miller J. N., Lovett M. A. Humoral immune response in human syphilis to polypeptides of Treponema pallidum. J Immunol. 1982 Sep;129(3):1287–1291. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Izzat N. N., Knox J. M., Dacres W. G., Smith E. B. Resistance and serological changes in rabbits immunized with virulent Treponema pallidum sonicate. Acta Derm Venereol. 1971;51(2):157–160. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Izzat N. N., Yazdi E. Immunological studies on treponemal cellular antigens. I. Serological changes and resistance to infection in rabbits immunized with treponemal nucleic acids. Br J Vener Dis. 1973 Aug;49(4):338–341. doi: 10.1136/sti.49.4.338. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kindt T. J. Rabbit immunoglobulin allotypes: structure, immunology, and genetics. Adv Immunol. 1975;21:35–86. doi: 10.1016/s0065-2776(08)60218-7. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Miller J. N. Immunity in experimental syphilis. VI. Successful vaccination of rabbits with Treponema pallidum, Nichols strain, attenuated by -irradiation. J Immunol. 1973 May;110(5):1206–1215. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Pavia C. S., Folds J. D., Baseman J. B. Depression of lymphocyte response to concanavalin A in rabbits infected with Treponema pallidum (Nichols strain). Infect Immun. 1976 Jul;14(1):320–322. doi: 10.1128/iai.14.1.320-322.1976. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Pavia C. S., Folds J. D., Baseman J. B. Selective in vitro response of thymus-derived lymphocytes from Treponema pallidum-infected rabbits. Infect Immun. 1977 Dec;18(3):603–611. doi: 10.1128/iai.18.3.603-611.1977. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Pavia C. S., Niederbuhl C. J. Experimental infection of inbred guinea pigs with Treponema pallidum: development of lesions and formation of antibodies. Genitourin Med. 1985 Apr;61(2):75–81. doi: 10.1136/sti.61.2.75. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Pavis C. S., Folds J. D., Baseman J. B. Cell-mediated immunity during syphilis. Br J Vener Dis. 1978 Jun;54(3):144–150. doi: 10.1136/sti.54.3.144. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Pierce C. S., Wicher K., Nakeeb S. Experimental syphilis: guinea pig model. Br J Vener Dis. 1983 Jun;59(3):157–168. doi: 10.1136/sti.59.3.157. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- SELL S. EVIDENCE FOR SPECIES' DIFFERENCES IN THE EFFECT OF SERUM GAMMA-GLOBULIN CONCENTRATION ON GAMMA-GLOBULIN CATABOLISM. J Exp Med. 1964 Nov 1;120:967–986. doi: 10.1084/jem.120.5.967. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Titus R. G., Weiser R. S. Experimental syphilis in the rabbit: passive transfer of immunity with immunoglobulin G from immune serum. J Infect Dis. 1979 Dec;140(6):904–913. doi: 10.1093/infdis/140.6.904. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Turner T. B., Hardy P. H., Jr, Newman B., Nell E. E. Effects of passive immunization on experimental syphilis in the rabbit. Johns Hopkins Med J. 1973 Nov;133(5):241–251. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Weiser R. S., Erickson D., Perine P. L., Pearsall N. N. Immunity to syphilis: passive transfer in rabbits using serial doses of immune serum. Infect Immun. 1976 May;13(5):1402–1407. doi: 10.1128/iai.13.5.1402-1407.1976. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wicher K., Wicher V., Gruhn R. F. Differences in susceptibility to infection with Treponema pallidum (Nichols) between five strains of guinea pig. Genitourin Med. 1985 Feb;61(1):21–26. doi: 10.1136/sti.61.1.21. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]