Abstract
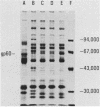
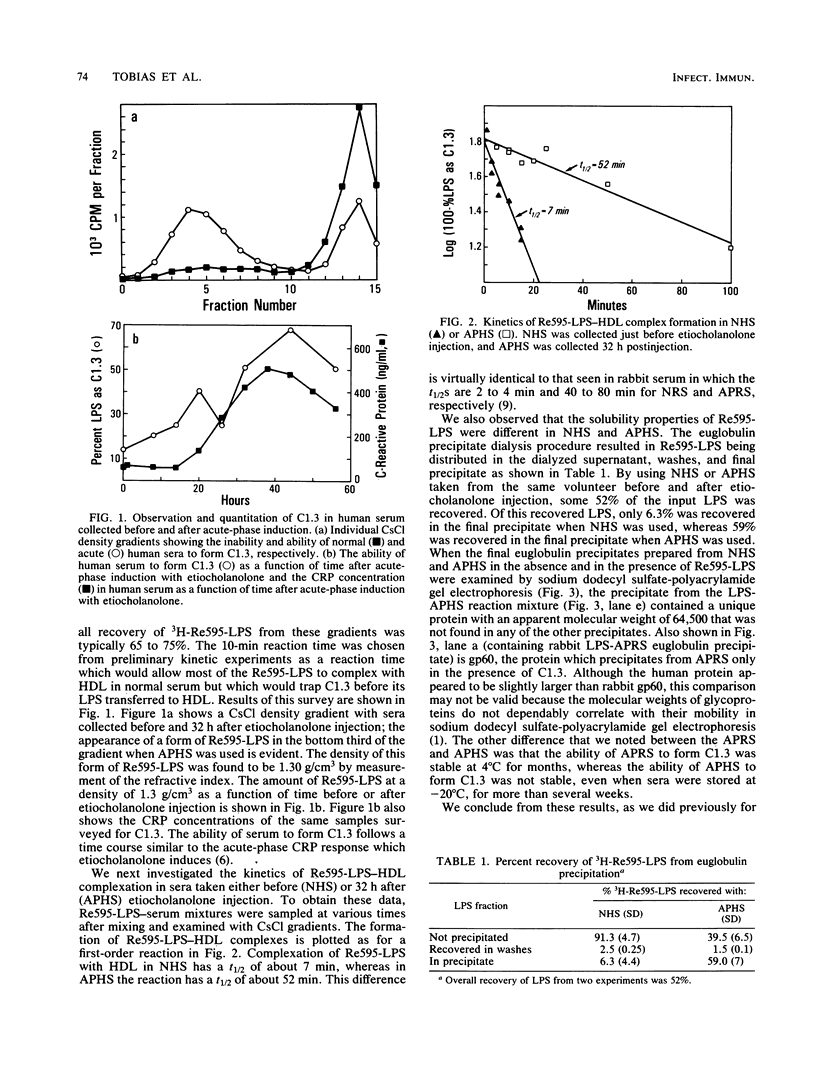
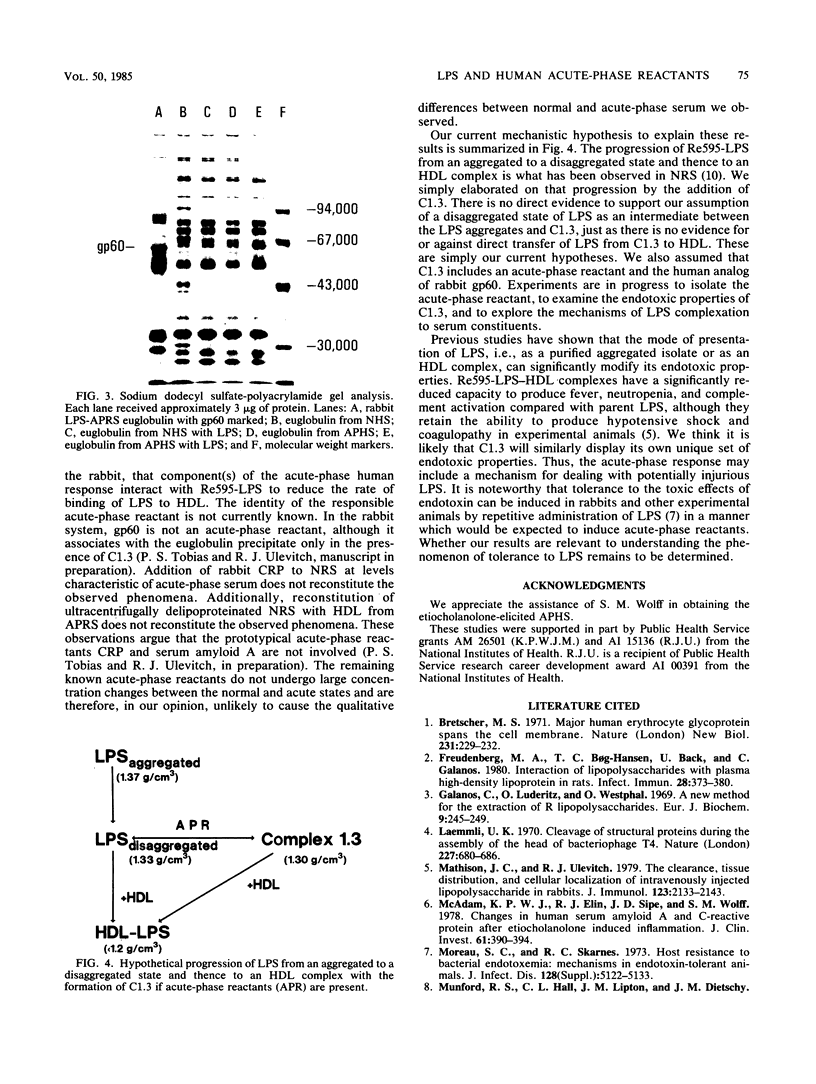
We have recently described several phenomena involving the interactions of lipopolysaccharides (LPS) from Salmonella minnesota Re595 (Re595-LPS) with rabbit serum, which are different in and unique to acute-phase serum as compared with normal serum (P.S. Tobias and R.J. Ulevitch, J. Immunol. 131:1913-1916, 1983). To determine whether these phenomena could also be observed in acute-phase human serum (APHS), we used APHS obtained from volunteers injected with etiocholanolone. As observed in acute-phase rabbit serum, we found that (i) in APHS, Re595-LPS forms a protein complex with a density of 1.3 g/cm3 which does not form in normal human serum (NHS), (ii) in APHS, the t1/2 for LPS-high-density lipoprotein (HDL) complexation is at least a factor of 10 slower than the t1/2 for LPS-HDL complexation in NHS, (iii) when Re595-LPS serum mixtures are dialyzed against a low salt buffer, Re595-LPS precipitates in less soluble form from APHS than from NHS, and (iv) the precipitate from Re595-LPS-APHS mixtures includes a protein with a molecular weight of approximately 60,000 which does not precipitate from Re595-LPS-NHS mixtures or from NHS or APHS alone. These indications of an altered status of LPS in NHS and APHS suggest that one or more acute-phase reactants interact with Re595-LPS to modify its rate of binding to HDL.
Full text
PDF

Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Bretscher M. S. Major human erythrocyte glycoprotein spans the cell membrane. Nat New Biol. 1971 Jun 23;231(25):229–232. doi: 10.1038/newbio231229a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Freudenberg M. A., Bøg-Hansen T. C., Back U., Galanos C. Interaction of lipopolysaccharides with plasma high-density lipoprotein in rats. Infect Immun. 1980 May;28(2):373–380. doi: 10.1128/iai.28.2.373-380.1980. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Galanos C., Lüderitz O., Westphal O. A new method for the extraction of R lipopolysaccharides. Eur J Biochem. 1969 Jun;9(2):245–249. doi: 10.1111/j.1432-1033.1969.tb00601.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Laemmli U. K. Cleavage of structural proteins during the assembly of the head of bacteriophage T4. Nature. 1970 Aug 15;227(5259):680–685. doi: 10.1038/227680a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mathison J. C., Ulevitch R. J. The clearance, tissue distribution, and cellular localization of intravenously injected lipopolysaccharide in rabbits. J Immunol. 1979 Nov;123(5):2133–2143. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- McAdam K. P., Elin R. J., Sipe J. D., Wolff S. M. Changes in human serum amyloid A and C-reactive protein after etiocholanolone-induced inflammation. J Clin Invest. 1978 Feb;61(2):390–394. doi: 10.1172/JCI108949. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Tobias P. S., Ulevitch R. J. Control of lipopolysaccharide-high density lipoprotein binding by acute phase protein(s). J Immunol. 1983 Oct;131(4):1913–1916. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ulevitch R. J., Johnston A. R., Weinstein D. B. New function for high density lipoproteins. Isolation and characterization of a bacterial lipopolysaccharide-high density lipoprotein complex formed in rabbit plasma. J Clin Invest. 1981 Mar;67(3):827–837. doi: 10.1172/JCI110100. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]