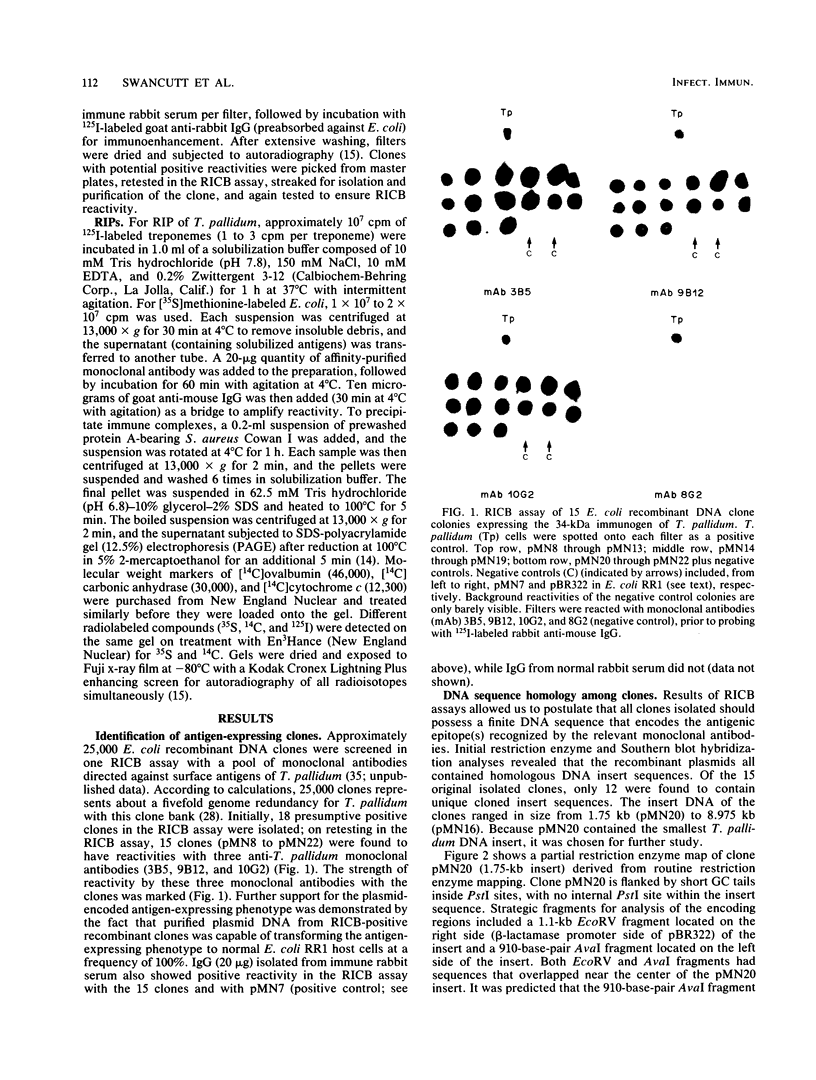
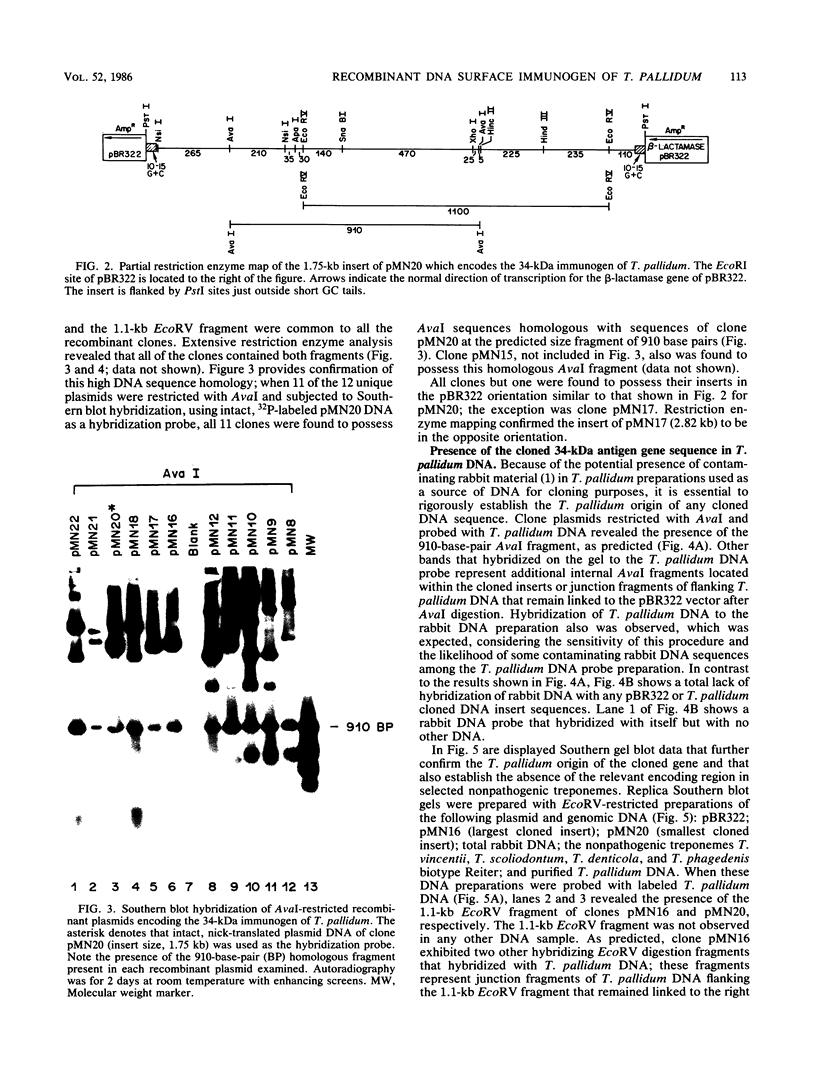
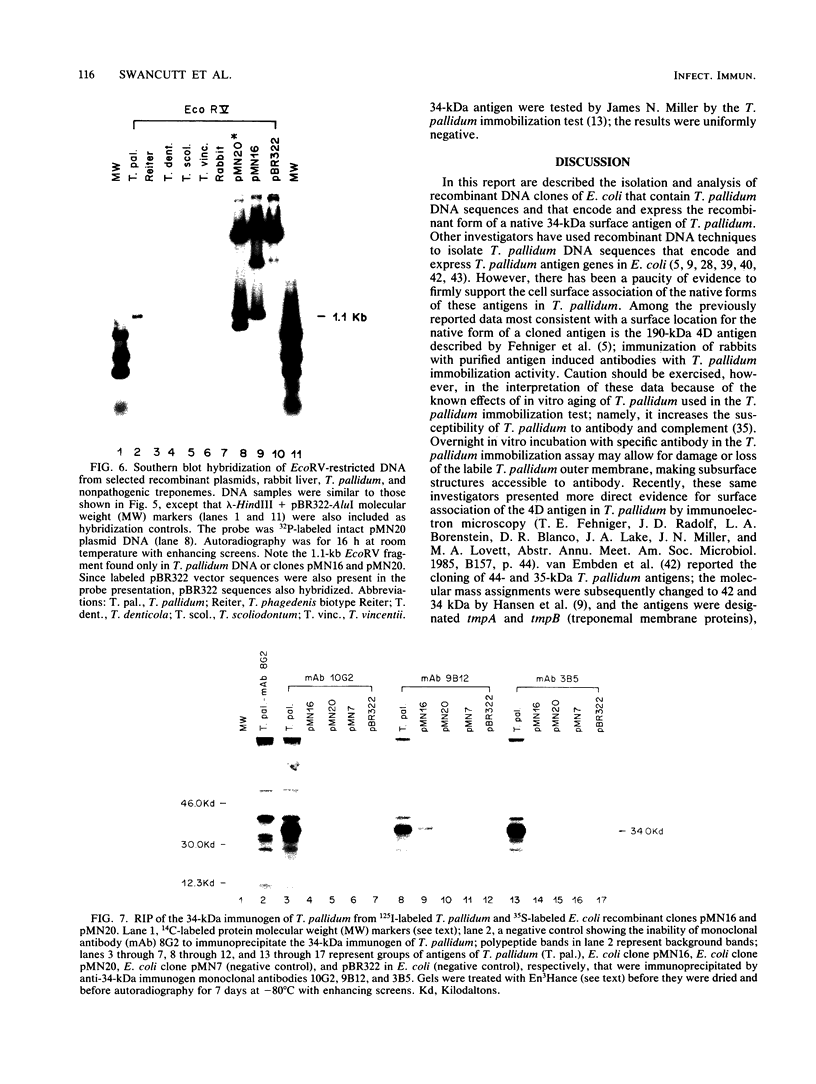
Abstract
Monoclonal antibodies directed against a 34-kilodalton (kDa) surface immunogen of Treponema pallidum were used to select 12 unique T. pallidum DNA-containing Escherichia coli recombinant clones expressing the recombinant form of the 34-kDa immunogen. The phenotype of the clones was dependent on the presence of recombinant plasmids in the host cell. Restriction enzyme analyses and Southern hybridization of plasmid DNA demonstrated that all recombinant clones contained common DNA sequences of T. pallidum origin. Further hybridization analyses revealed that the cloned T. pallidum DNA sequences were an accurate representation of the T. pallidum genomic DNA arrangement. Purified immunoglobulin G (IgG) from pooled immune rabbit serum reacted with the clones, while IgG from pooled normal rabbit serum did not. Results of immunological experiments and Southern hybridization indicated that a similar 34-kDa immunogen was present in T. pallidum subsp. pertenue, but it was absent from four species of nonpathogenic treponemes tested, as well as from homogenates of normal rabbit testicular tissue. Metabolic labeling of the E. coli clones with [35S]methionine followed by radioimmunoprecipitation with monoclonal antibodies revealed that the 35S-labeled recombinant and 125I-labeled native (T. pallidum) forms of the antigen had identical electrophoretic mobilities. The production of a complete antigen by E. coli was independent of the orientation of the foreign gene sequence with respect to vector DNA. T. pallidum also produced an apparently identical immunoprecipitable 34-kDa antigen after metabolic labeling with [35S]methionine in the presence of cycloheximide. The apparent specificity of the 34-kDa immunogen for pathogenic treponemes and its native cell surface association on T. pallidum justifies a more intense study of this antigen and its corresponding gene.
Full text
PDF






Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Alderete J. F., Baseman J. B. Surface characterization of virulent Treponema pallidum. Infect Immun. 1980 Dec;30(3):814–823. doi: 10.1128/iai.30.3.814-823.1980. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Alderete J. F., Baseman J. B. Surface-associated host proteins on virulent Treponema pallidum. Infect Immun. 1979 Dec;26(3):1048–1056. doi: 10.1128/iai.26.3.1048-1056.1979. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bishop N. H., Miller J. N. Humoral immunity in experimental syphilis. II. The relationship of neutralizing factors in immune serum to acquired resistance. J Immunol. 1976 Jul;117(1):197–207. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ey P. L., Prowse S. J., Jenkin C. R. Isolation of pure IgG1, IgG2a and IgG2b immunoglobulins from mouse serum using protein A-sepharose. Immunochemistry. 1978 Jul;15(7):429–436. doi: 10.1016/0161-5890(78)90070-6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Fehniger T. E., Walfield A. M., Cunningham T. M., Radolf J. D., Miller J. N., Lovett M. A. Purification and characterization of a cloned protease-resistant Treponema pallidum-specific antigen. Infect Immun. 1984 Nov;46(2):598–607. doi: 10.1128/iai.46.2.598-607.1984. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Fitzgerald T. J., Repesh L. A., Blanco D. R., Miller J. N. Attachment of Treponema pallidum to fibronectin, laminin, collagen IV, and collagen I, and blockage of attachment by immune rabbit IgG. Br J Vener Dis. 1984 Dec;60(6):357–363. doi: 10.1136/sti.60.6.357. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- HUNTER W. M., GREENWOOD F. C. Preparation of iodine-131 labelled human growth hormone of high specific activity. Nature. 1962 May 5;194:495–496. doi: 10.1038/194495a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hanff P. A., Norris S. J., Lovett M. A., Miller J. N. Purification of Treponema pallidum, Nichols strain, by Percoll density gradient centrifugation. Sex Transm Dis. 1984 Oct-Dec;11(4):275–286. doi: 10.1097/00007435-198410000-00003. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hansen E. B., Pedersen P. E., Schouls L. M., Severin E., van Embden J. D. Genetic characterization and partial sequence determination of a Treponema pallidum operon expressing two immunogenic membrane proteins in Escherichia coli. J Bacteriol. 1985 Jun;162(3):1227–1237. doi: 10.1128/jb.162.3.1227-1237.1985. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hindersson P., Petersen C. S., Axelsen N. H. Purified flagella from Treponema phagedenis biotype Reiter does not induce protective immunity against experimental syphilis in rabbits. Sex Transm Dis. 1985 Jul-Sep;12(3):124–127. doi: 10.1097/00007435-198507000-00006. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Holt S. C. Anatomy and chemistry of spirochetes. Microbiol Rev. 1978 Mar;42(1):114–160. doi: 10.1128/mr.42.1.114-160.1978. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Jones S. A., Marchitto K. S., Miller J. N., Norgard M. V. Monoclonal antibody with hemagglutination, immobilization, and neutralization activities defines an immunodominant, 47,000 mol wt, surface-exposed immunogen of Treponema pallidum (Nichols). J Exp Med. 1984 Nov 1;160(5):1404–1420. doi: 10.1084/jem.160.5.1404. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Laemmli U. K. Cleavage of structural proteins during the assembly of the head of bacteriophage T4. Nature. 1970 Aug 15;227(5259):680–685. doi: 10.1038/227680a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Laskey R. A., Mills A. D. Enhanced autoradiographic detection of 32P and 125I using intensifying screens and hypersensitized film. FEBS Lett. 1977 Oct 15;82(2):314–316. doi: 10.1016/0014-5793(77)80609-1. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Loeb M. R., Smith D. H. Lactoperoxidase and Iodo-Gen-catalyzed iodination labels inner and outer membrane proteins of Haemophilus influenzae. J Bacteriol. 1983 Jul;155(1):443–446. doi: 10.1128/jb.155.1.443-446.1983. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lukehart S. A., Baker-Zander S. A., Gubish E. R., Jr Identification of Treponema pallidum antigens: comparison with a nonpathogenic treponeme. J Immunol. 1982 Aug;129(2):833–838. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lukehart S. A. Prospects for development of a treponemal vaccine. Rev Infect Dis. 1985 May-Jun;7 (Suppl 2):S305–S313. doi: 10.1093/clinids/7-supplement_2.s305. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Macrina F. L. Molecular cloning of bacterial antigens and virulence determinants. Annu Rev Microbiol. 1984;38:193–219. doi: 10.1146/annurev.mi.38.100184.001205. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Marchitto K. S., Jones S. A., Schell R. F., Holmans P. L., Norgard M. V. Monoclonal antibody analysis of specific antigenic similarities among pathogenic Treponema pallidum subspecies. Infect Immun. 1984 Sep;45(3):660–666. doi: 10.1128/iai.45.3.660-666.1984. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Miao R., Fieldsteel A. H. Genetics of Treponema: relationship between Treponema pallidum and five cultivable treponemes. J Bacteriol. 1978 Jan;133(1):101–107. doi: 10.1128/jb.133.1.101-107.1978. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Miller J. N. Value and limitations of nontreponemal and treponemal tests in the laboratory diagnosis of syphilis. Clin Obstet Gynecol. 1975 Mar;18(1):191–203. doi: 10.1097/00003081-197503000-00017. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Moskophidis M., Müller F. Molecular analysis of immunoglobulins M and G immune response to protein antigens of Treponema pallidum in human syphilis. Infect Immun. 1984 Jan;43(1):127–132. doi: 10.1128/iai.43.1.127-132.1984. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Norgard M. V., Miller J. N. Cloning and expression of Treponema pallidum (Nichols) antigen genes in Escherichia coli. Infect Immun. 1983 Nov;42(2):435–445. doi: 10.1128/iai.42.2.435-445.1983. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Norgard M. V., Miller J. N. Plasmid DNA in Treponema pallidum (Nichols): potential for antibiotic resistance by syphilis bacteria. Science. 1981 Jul 31;213(4507):553–555. doi: 10.1126/science.6264606. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Norgard M. V. Molecular assessment of S1 endonuclease-resistant snapback hairpin loops generated by DNA polymerase I during the in-vitro nick translation reaction. Appl Biochem Biotechnol. 1985 Feb;11(1):1–15. doi: 10.1007/BF02824307. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Norgard M. V. Rapid and simple removal of contaminating RNA from plasmid DNA without the use of RNase. Anal Biochem. 1981 May 1;113(1):34–42. doi: 10.1016/0003-2697(81)90040-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Norris S. J., Sell S. Antigenic complexity of Treponema pallidum: antigenicity and surface localization of major polypeptides. J Immunol. 1984 Nov;133(5):2686–2692. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Pedersen N. S., Axelsen N. H., Jørgensen B. B., Petersen C. S. Antibodies in secondary syphilis against five of forty Reiter treponeme antigens. Scand J Immunol. 1980;11(6):629–633. doi: 10.1111/j.1365-3083.1980.tb00031.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Pedersen N. S., Axelsen N. H., Petersen C. S. Antigenic analysis of Treponema pallidum: cross-reactions between individual antigens of T. pallidum and T. Reiter. Scand J Immunol. 1981;13(2):143–150. doi: 10.1111/j.1365-3083.1981.tb00120.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Penn C. W., Bailey M. J., Cockayne A. The axial filament antigen of Treponema pallidum. Immunology. 1985 Apr;54(4):635–641. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Petersen C. S., Pedersen N. S., Axelsen N. H. A simple method for the isolation of flagella from Treponema Reiter. Acta Pathol Microbiol Scand C. 1981 Dec;89(6):379–385. doi: 10.1111/j.1699-0463.1981.tb02716.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Peterson K. M., Baseman J. B., Alderete J. F. Treponema pallidum receptor binding proteins interact with fibronectin. J Exp Med. 1983 Jun 1;157(6):1958–1970. doi: 10.1084/jem.157.6.1958. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Robertson S. M., Kettman J. R., Miller J. N., Norgard M. V. Murine monoclonal antibodies specific for virulent Treponema pallidum (Nichols). Infect Immun. 1982 Jun;36(3):1076–1085. doi: 10.1128/iai.36.3.1076-1085.1982. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sell S., Norris S. J. The biology, pathology, and immunology of syphilis. Int Rev Exp Pathol. 1983;24:203–276. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Southern E. M. Detection of specific sequences among DNA fragments separated by gel electrophoresis. J Mol Biol. 1975 Nov 5;98(3):503–517. doi: 10.1016/s0022-2836(75)80083-0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Stamm L. V., Bassford P. J., Jr Cellular and extracellular protein antigens of Treponema pallidum synthesized during in vitro incubation of freshly extracted organisms. Infect Immun. 1985 Mar;47(3):799–807. doi: 10.1128/iai.47.3.799-807.1985. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Stamm L. V., Folds J. D., Bassford P. J., Jr Expression of Treponema pallidum antigens in Escherichia coli K-12. Infect Immun. 1982 Jun;36(3):1238–1241. doi: 10.1128/iai.36.3.1238-1241.1982. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Stamm L. V., Kerner T. C., Jr, Bankaitis V. A., Bassford P. J., Jr Identification and preliminary characterization of Treponema pallidum protein antigens expressed in Escherichia coli. Infect Immun. 1983 Aug;41(2):709–721. doi: 10.1128/iai.41.2.709-721.1983. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Thomas D. D., Baseman J. B., Alderete J. F. Fibronectin mediates Treponema pallidum cytadherence through recognition of fibronectin cell-binding domain. J Exp Med. 1985 Mar 1;161(3):514–525. doi: 10.1084/jem.161.3.514. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Walfield A. M., Hanff P. A., Lovett M. A. Expression of Treponema pallidum antigens in Escherichia coli. Science. 1982 Apr 30;216(4545):522–523. doi: 10.1126/science.7041257. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- van Embden J. D., van der Donk H. J., van Eijk R. V., van der Heide H. G., de Jong J. A., van Olderen M. F., Osterhaus A. B., Schouls L. M. Molecular cloning and expression of Treponema pallidum DNA in Escherichia coli K-12. Infect Immun. 1983 Oct;42(1):187–196. doi: 10.1128/iai.42.1.187-196.1983. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]








