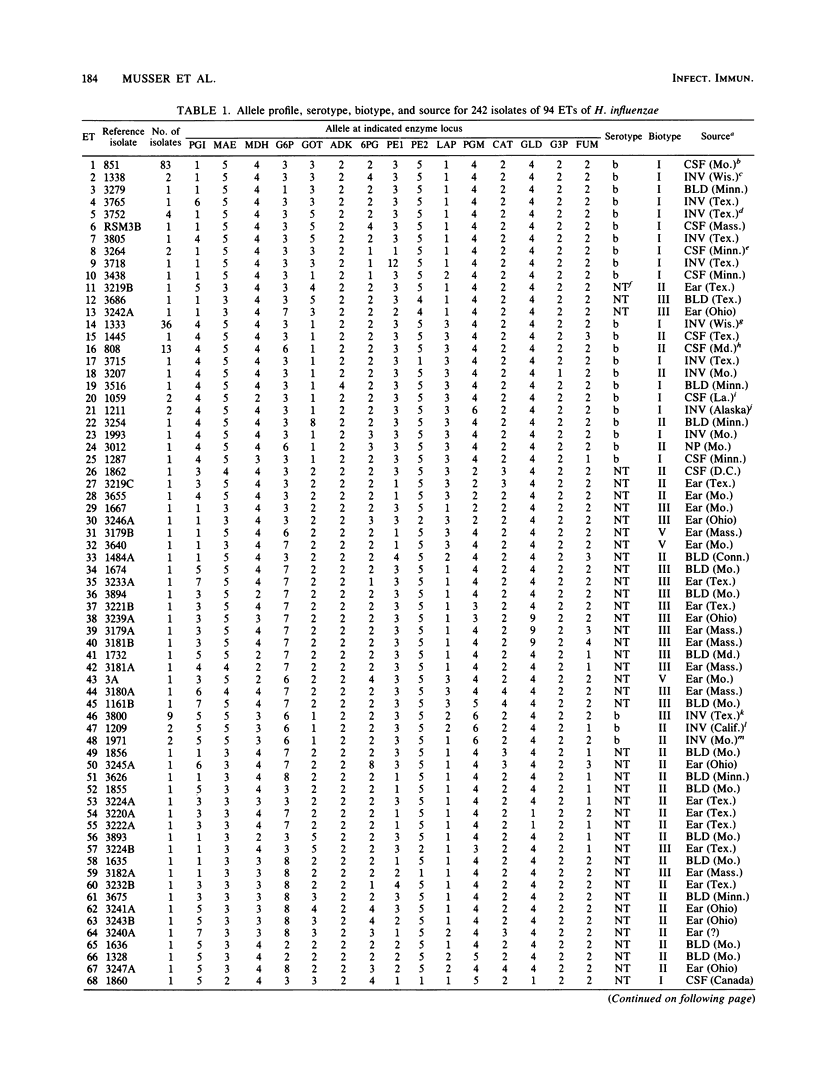
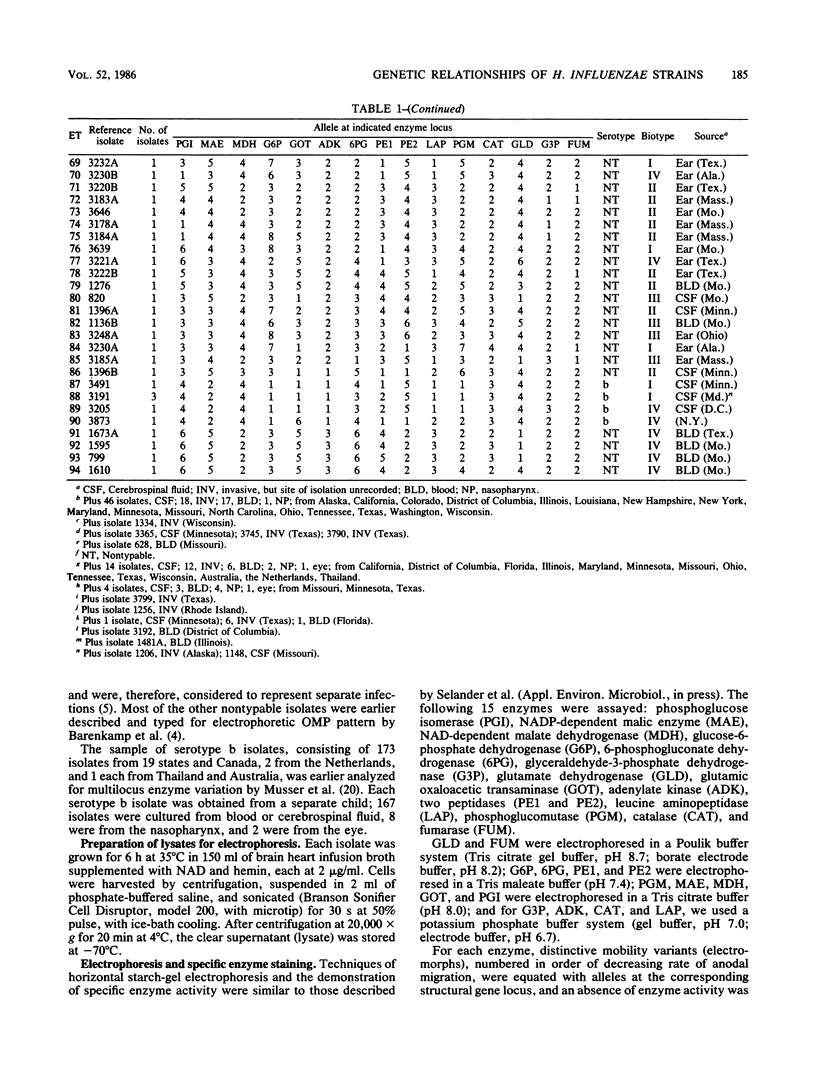
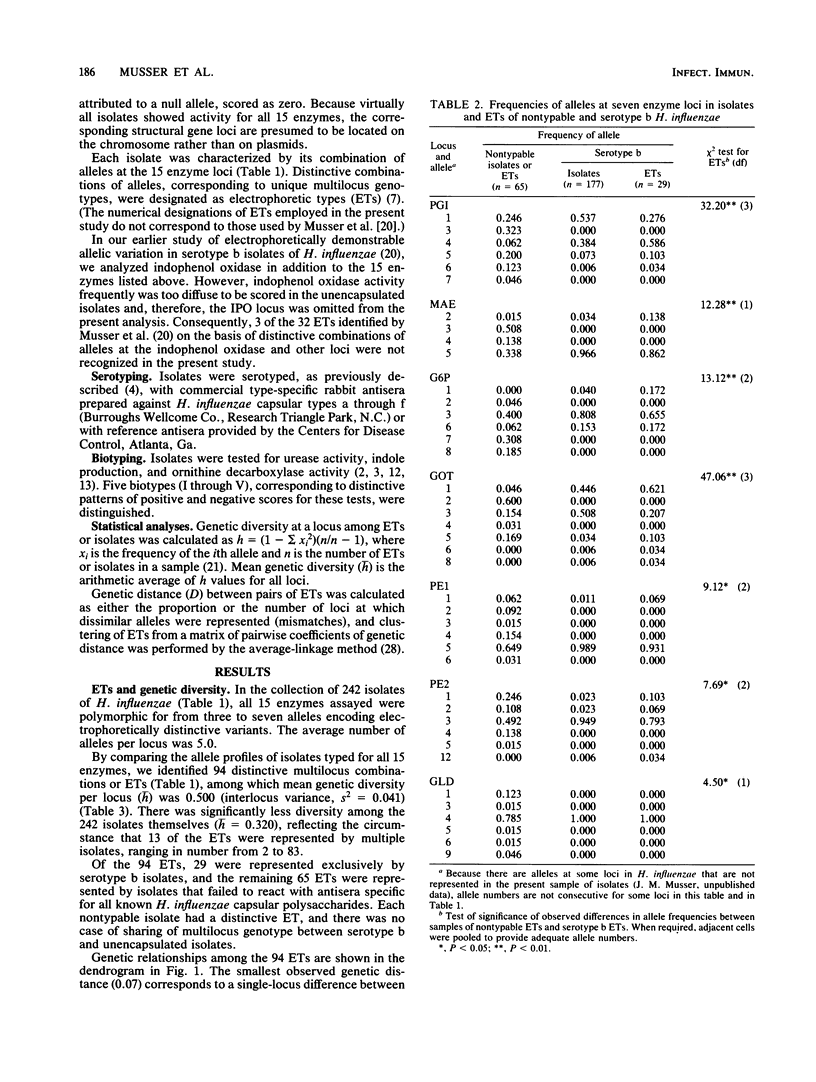
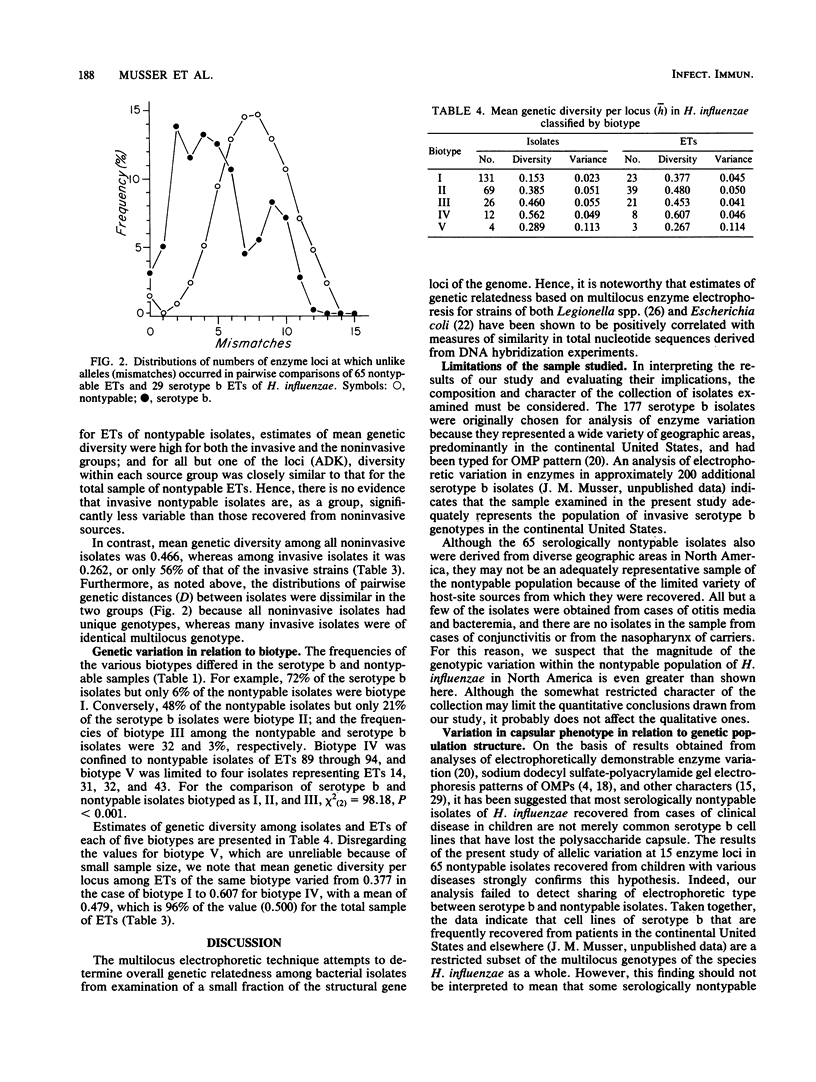
Abstract
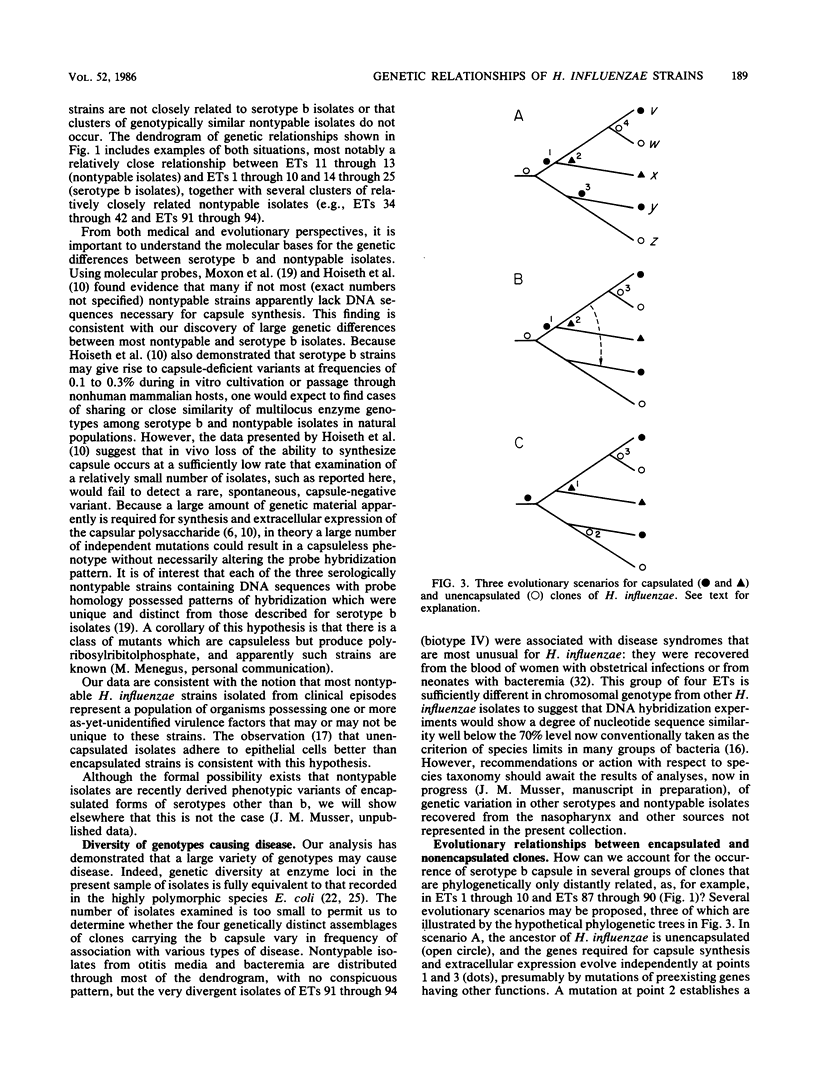
A collection of 242 strains of Haemophilus influenzae, including 65 nontypable (unencapsulated) isolates and 177 encapsulated serotype b isolates recovered largely from children with invasive and noninvasive diseases in the United States, was characterized by the electrophoretic mobilities of 15 metabolic enzymes presumably encoded by chromosomal genes. All enzymes were polymorphic for three to seven electromorphs, and 94 distinctive multilocus genotypes (electrophoretic types [ETs]) were distinguished, among which mean genetic (allelic) diversity was 0.500. Isolates recovered from cases of invasive or noninvasive diseases did not differ significantly in level of genetic variation. The observation that 29 ETs were represented exclusively by serotype b isolates and that each of the 65 nontypable isolates was of a unique ET strongly confirmed the hypothesis that unencapsulated clinical isolates are not merely phenotypic variants of the common serotype b cell lines. Rather, the two types of isolates are distinctive subsets of the multilocus chromosomal genotypes of the species as a whole. Serotype b capsule occurred in three groups of isolates that are distantly related in multilocus enzyme genotype. Isolates of four closely related nontypable biotype IV ETs associated with obstetrical infections or neonatal bacteremia were highly divergent from all others examined and may be specifically distinct. A phylogenetic scenario was proposed in which the ancestor of H. influenzae was encapsulated and the nontypable clones arose by convergent evolutionary loss of the ability to synthesize or extracellularly express a polysaccharide capsule.
Full text
PDF



Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Albritton W. L., Setlow J. K., Slaney L. Transfer of Haemophilus influenzae chromosomal genes by cell-to-cell contact. J Bacteriol. 1982 Dec;152(3):1066–1070. doi: 10.1128/jb.152.3.1066-1070.1982. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Barenkamp S. J., Munson R. S., Jr, Granoff D. M. Comparison of outer-membrane protein subtypes and biotypes of isolates of Haemophilus influenzae type b. J Infect Dis. 1981 Nov;144(5):480–480. doi: 10.1093/infdis/144.5.480. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Barenkamp S. J., Munson R. S., Jr, Granoff D. M. Outer membrane protein and biotype analysis of pathogenic nontypable Haemophilus influenzae. Infect Immun. 1982 May;36(2):535–540. doi: 10.1128/iai.36.2.535-540.1982. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Barenkamp S. J., Munson R. S., Jr, Granoff D. M. Subtyping isolates of Haemophilus influenzae type b by outer-membrane protein profiles. J Infect Dis. 1981 May;143(5):668–676. doi: 10.1093/infdis/143.5.668. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Barenkamp S. J., Shurin P. A., Marchant C. D., Karasic R. B., Pelton S. I., Howie V. M., Granoff D. M. Do children with recurrent Haemophilus influenzae otitis media become infected with a new organism or reacquire the original strain? J Pediatr. 1984 Oct;105(4):533–537. doi: 10.1016/s0022-3476(84)80415-1. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Catlin B. W., Bendler J. W., 3rd, Goodgal S. H. The type b capsulation locus of Haemophilus influenzae: map location and size. J Gen Microbiol. 1972 May;70(3):411–422. doi: 10.1099/00221287-70-3-411. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Caugant D. A., Levin B. R., Selander R. K. Genetic diversity and temporal variation in the E. coli population of a human host. Genetics. 1981 Jul;98(3):467–490. doi: 10.1093/genetics/98.3.467. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gyorkey F., Musher D., Gyorkey P., Goree A., Baughn R. Nontypable Haemophilus influenzae are unencapsulated both in vivo and in vitro. J Infect Dis. 1984 Apr;149(4):518–522. doi: 10.1093/infdis/149.4.518. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hoiseth S. K., Connelly C. J., Moxon E. R. Genetics of spontaneous, high-frequency loss of b capsule expression in Haemophilus influenzae. Infect Immun. 1985 Aug;49(2):389–395. doi: 10.1128/iai.49.2.389-395.1985. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Huber P. S., Egwu I. N. Capsular variation in experimental strains of Haemophilus influenzae. Med Microbiol Immunol. 1985;173(6):345–353. doi: 10.1007/BF02125038. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kilian M., Thomsen B. Antigenic heterogeneity of immunoglobulin A1 proteases from encapsulated and non-encapsulated Haemophilus influenzae. Infect Immun. 1983 Oct;42(1):126–132. doi: 10.1128/iai.42.1.126-132.1983. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lampe R. M., Mason E. O., Jr, Kaplan S. L., Umstead C. L., Yow M. D., Feigin R. D. Adherence of Haemophilus influenzae to buccal epithelial cells. Infect Immun. 1982 Jan;35(1):166–172. doi: 10.1128/iai.35.1.166-172.1982. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Loeb M. R., Smith D. H. Outer membrane protein composition in disease isolates of Haemophilus influenzae: pathogenic and epidemiological implications. Infect Immun. 1980 Dec;30(3):709–717. doi: 10.1128/iai.30.3.709-717.1980. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Moxon E. R., Deich R. A., Connelly C. Cloning of chromosomal DNA from Haemophilus influenzae. Its use for studying the expression of type b capsule and virulence. J Clin Invest. 1984 Feb;73(2):298–306. doi: 10.1172/JCI111214. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Musser J. M., Granoff D. M., Pattison P. E., Selander R. K. A population genetic framework for the study of invasive diseases caused by serotype b strains of Haemophilus influenzae. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1985 Aug;82(15):5078–5082. doi: 10.1073/pnas.82.15.5078. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Nei M. Estimation of average heterozygosity and genetic distance from a small number of individuals. Genetics. 1978 Jul;89(3):583–590. doi: 10.1093/genetics/89.3.583. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ochman H., Whittam T. S., Caugant D. A., Selander R. K. Enzyme polymorphism and genetic population structure in Escherichia coli and Shigella. J Gen Microbiol. 1983 Sep;129(9):2715–2726. doi: 10.1099/00221287-129-9-2715. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Riley H. D., Jr Hemophilus influenzae infections: part I. Crit Rev Clin Lab Sci. 1981;15(3):231–275. doi: 10.3109/10408368109105872. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Selander R. K., Levin B. R. Genetic diversity and structure in Escherichia coli populations. Science. 1980 Oct 31;210(4469):545–547. doi: 10.1126/science.6999623. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Selander R. K., McKinney R. M., Whittam T. S., Bibb W. F., Brenner D. J., Nolte F. S., Pattison P. E. Genetic structure of populations of Legionella pneumophila. J Bacteriol. 1985 Sep;163(3):1021–1037. doi: 10.1128/jb.163.3.1021-1037.1985. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Stuy J. H. On the nature of nontypable Haemophilus influenzae. Antonie Van Leeuwenhoek. 1978;44(3-4):367–376. doi: 10.1007/BF00394313. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Stuy J. H. Transfer of genetic information within a colony of Haemophilus influenzae. J Bacteriol. 1985 Apr;162(1):1–4. doi: 10.1128/jb.162.1.1-4.1985. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Turk D. C. The pathogenicity of Haemophilus influenzae. J Med Microbiol. 1984 Aug;18(1):1–16. doi: 10.1099/00222615-18-1-1. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wallace R. J., Jr, Baker C. J., Quinones F. J., Hollis D. G., Weaver R. E., Wiss K. Nontypable Haemophilus influenzae (biotype 4) as a neonatal, maternal, and genital pathogen. Rev Infect Dis. 1983 Jan-Feb;5(1):123–136. doi: 10.1093/clinids/5.1.123. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]


