Abstract
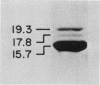
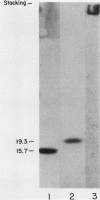
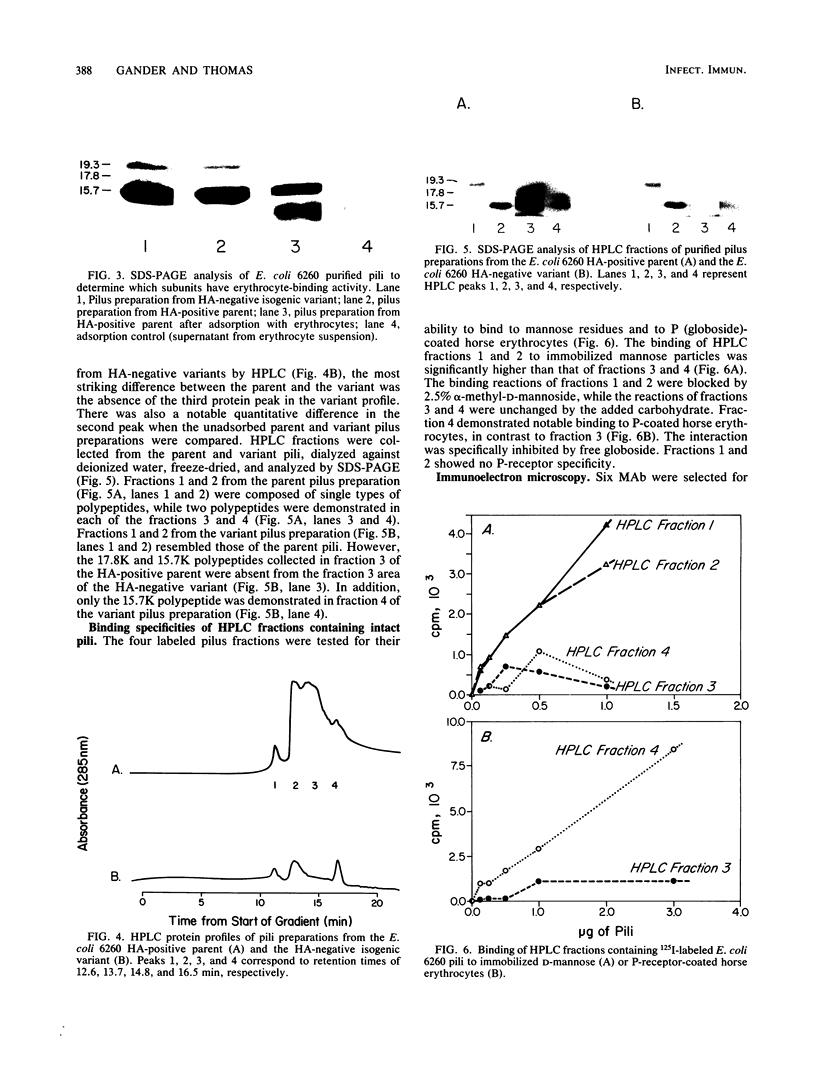
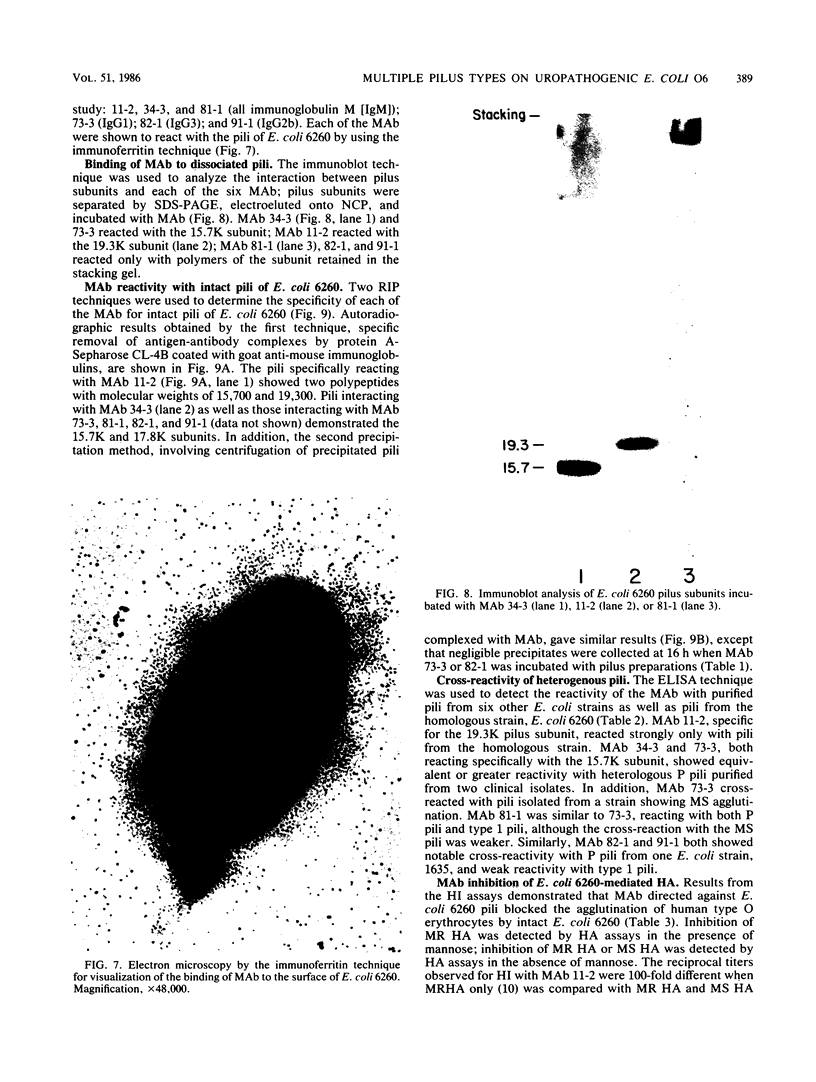
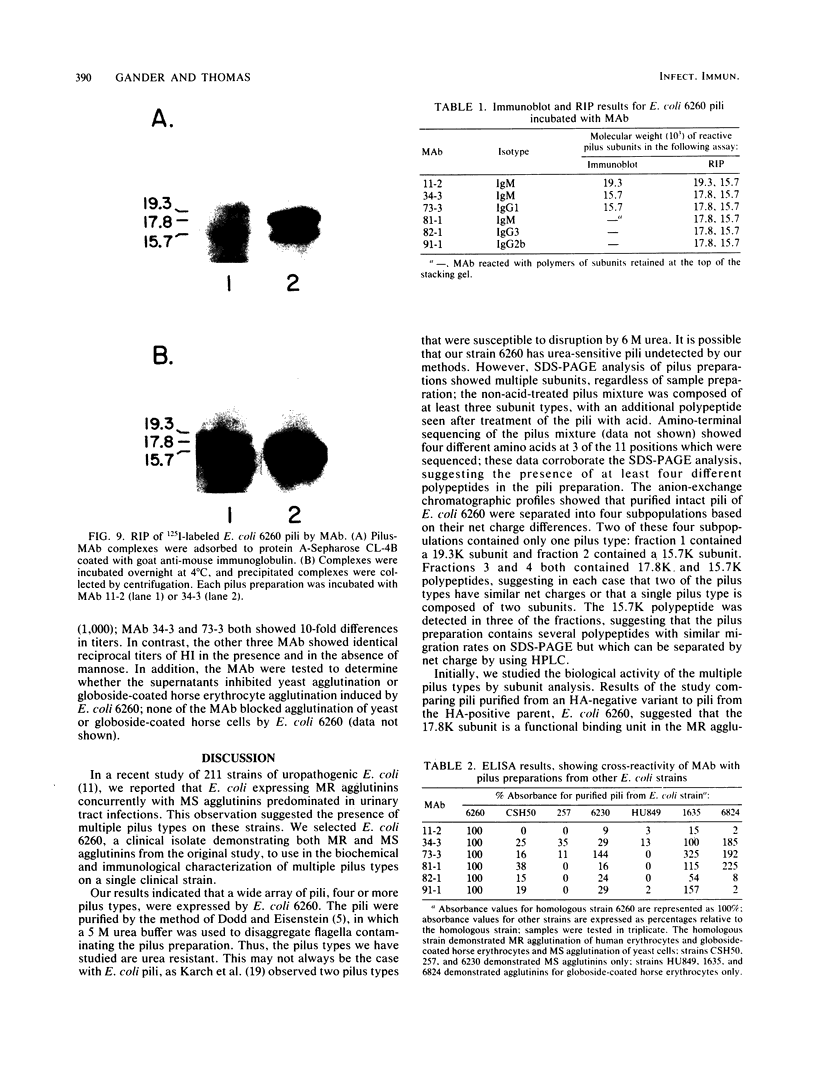
Multiple pilus types from a uropathogenic strain of Escherichia coli O6, strain 6260, were characterized by sodium dodecyl sulfate-polyacrylamide gel electrophoresis (SDS-PAGE), high-pressure liquid chromatography, binding assays, and erythrocyte adsorption. In addition, monoclonal antibodies were raised against purified pili of E. coli 6260 and used for immunological characterization. SDS-PAGE analysis of the purified pili showed at least three different subunits with molecular weights of 15,700, 17,800, and 19,300. SDS-PAGE analysis of four protein peaks from anion-exchange chromatography of intact pili showed polypeptides with molecular weights of 19,300 (fraction 1), 15,700 (fraction 2), and 17,800 and 15,700 (both fractions 3 and 4). Erythrocyte adsorption of the whole-pilus preparation removed the 17,800-molecular-weight subunit (17.8K subunit) and reduced the 15.7K subunit. Pili from an isogenic hemagglutination-negative variant of E. coli 6260, showing only the 15.7K and 19.3K subunits by SDS-PAGE, lacked the 17.8K subunit of fractions 3 and 4 present in the parent high-pressure liquid chromatography profile. Our data suggest that two of the pilus subunits, the 15.7K and 17.8K subunits, mediate mannose-resistant agglutination of human erythrocytes. Pili in fractions 1 and 2 from the parent strain bound specifically to mannose residues, while pili in fraction 4 bound to P-coated horse erythrocytes; no receptor specificity was identified for pili in fraction 3. Immunological analysis by the immunoblot technique showed that monoclonal antibody 11-2 reacted with the 19.3K subunit, monoclonal antibodies 34-3 and 73-3 reacted with the 15.7K subunit, and monoclonal antibodies 81-1, 82-1, and 91-1 reacted with polymers of subunits retained in the stacking gel. Intact pili precipitated by any of the six monoclonal antibodies showed two polypeptides by SDS-PAGE: 15.7K and 19.3K polypeptides for monoclonal antibody 11-2, and 15.7K and 17.8K polypeptides for monoclonal antibodies 34-3, 73-3, 81-1, 82-1, and 91-1. The cross-reactivity of the monoclonal antibodies with purified pili from other E. coli strains was determined by enzyme-linked immunosorbent assay. Monoclonal antibody 11-2 showed no significant cross-reactivity with heterogeneous pili. In contrast, the other monoclonal antibodies showed equivalent or greater reactivity with P pili from heterologous strains as compared with reactivity with E. coli 6260 pili.(ABSTRACT TRUNCATED AT 400 WORDS)
Full text
PDF





Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Abraham S. N., Hasty D. L., Simpson W. A., Beachey E. H. Antiadhesive properties of a quaternary structure-specific hybridoma antibody against type 1 fimbriae of Escherichia coli. J Exp Med. 1983 Oct 1;158(4):1114–1128. doi: 10.1084/jem.158.4.1114. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Clegg S. Serological heterogeneity among fimbrial antigens causing mannose-resistant hemagglutination by uropathogenic Escherichia coli. Infect Immun. 1982 Feb;35(2):745–748. doi: 10.1128/iai.35.2.745-748.1982. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Cohen M. L., Falkow S. Protein antigens from Staphylococcus aureus strains associated with toxic-shock syndrome. Science. 1981 Feb 20;211(4484):842–844. doi: 10.1126/science.7466361. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Daugharty H., Warfield D. T., Davis M. L. Solid-phase radioimmunoassay of total and influenza-specific immunoglobulin G. Appl Microbiol. 1972 Feb;23(2):360–367. doi: 10.1128/am.23.2.360-367.1972. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Dodd D. C., Eisenstein B. I. Antigenic quantitation of type 1 fimbriae on the surface of Escherichia coli cells by an enzyme-linked immunosorbent inhibition assay. Infect Immun. 1982 Nov;38(2):764–773. doi: 10.1128/iai.38.2.764-773.1982. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Duguid J. P., Clegg S., Wilson M. I. The fimbrial and non-fimbrial haemagglutinins of Escherichia coli. J Med Microbiol. 1979 May;12(2):213–227. doi: 10.1099/00222615-12-2-213. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Edén C. S., Hansson H. A. Escherichia coli pili as possible mediators of attachment to human urinary tract epithelial cells. Infect Immun. 1978 Jul;21(1):229–237. doi: 10.1128/iai.21.1.229-237.1978. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Eisenstein B. I., Clements J. R., Dodd D. C. Isolation and characterization of a monoclonal antibody directed against type 1 fimbriae organelles from Escherichia coli. Infect Immun. 1983 Oct;42(1):333–340. doi: 10.1128/iai.42.1.333-340.1983. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Eisenstein B. I. Phase variation of type 1 fimbriae in Escherichia coli is under transcriptional control. Science. 1981 Oct 16;214(4518):337–339. doi: 10.1126/science.6116279. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Engvall E., Perlmann P. Enzyme-linked immunosorbent assay, Elisa. 3. Quantitation of specific antibodies by enzyme-labeled anti-immunoglobulin in antigen-coated tubes. J Immunol. 1972 Jul;109(1):129–135. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Eshdat Y., Silverblatt F. J., Sharon N. Dissociation and reassembly of Escherichia coli type 1 pili. J Bacteriol. 1981 Oct;148(1):308–314. doi: 10.1128/jb.148.1.308-314.1981. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gander R. M., Thomas V. L., Forland M. Mannose-resistant hemagglutination and P receptor recognition of uropathogenic Escherichia coli isolated from adult patients. J Infect Dis. 1985 Mar;151(3):508–513. doi: 10.1093/infdis/151.3.508. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hagberg L., Jodal U., Korhonen T. K., Lidin-Janson G., Lindberg U., Svanborg Edén C. Adhesion, hemagglutination, and virulence of Escherichia coli causing urinary tract infections. Infect Immun. 1981 Feb;31(2):564–570. doi: 10.1128/iai.31.2.564-570.1981. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hansen E. J., Frisch C. F., McDade R. L., Jr, Johnston K. H. Identification of immunogenic outer membrane proteins of Haemophilus influenzae type b in the infant rat model system. Infect Immun. 1981 Jun;32(3):1084–1092. doi: 10.1128/iai.32.3.1084-1092.1981. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hull R. A., Gill R. E., Hsu P., Minshew B. H., Falkow S. Construction and expression of recombinant plasmids encoding type 1 or D-mannose-resistant pili from a urinary tract infection Escherichia coli isolate. Infect Immun. 1981 Sep;33(3):933–938. doi: 10.1128/iai.33.3.933-938.1981. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Karch H., Leying H., Büscher K. H., Kroll H. P., Opferkuch W. Isolation and separation of physicochemically distinct fimbrial types expressed on a single culture of Escherichia coli O7:K1:H6. Infect Immun. 1985 Feb;47(2):549–554. doi: 10.1128/iai.47.2.549-554.1985. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Klemm P., Orskov I., Orskov F. F7 and type 1-like fimbriae from three Escherichia coli strains isolated from urinary tract infections: protein chemical and immunological aspects. Infect Immun. 1982 May;36(2):462–468. doi: 10.1128/iai.36.2.462-468.1982. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Källenius G., Möllby R., Svenson S. B., Helin I., Hultberg H., Cedergren B., Winberg J. Occurrence of P-fimbriated Escherichia coli in urinary tract infections. Lancet. 1981 Dec 19;2(8260-61):1369–1372. doi: 10.1016/s0140-6736(81)92797-5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Laemmli U. K. Cleavage of structural proteins during the assembly of the head of bacteriophage T4. Nature. 1970 Aug 15;227(5259):680–685. doi: 10.1038/227680a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lomberg H., Hanson L. A., Jacobsson B., Jodal U., Leffler H., Edén C. S. Correlation of P blood group, vesicoureteral reflux, and bacterial attachment in patients with recurrent pyelonephritis. N Engl J Med. 1983 May 19;308(20):1189–1192. doi: 10.1056/NEJM198305193082003. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Normark S., Lark D., Hull R., Norgren M., Båga M., O'Hanley P., Schoolnik G., Falkow S. Genetics of digalactoside-binding adhesin from a uropathogenic Escherichia coli strain. Infect Immun. 1983 Sep;41(3):942–949. doi: 10.1128/iai.41.3.942-949.1983. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Nowicki B., Rhen M., Väisänen-Rhen V., Pere A., Korhonen T. K. Immunofluorescence study of fimbrial phase variation in Escherichia coli KS71. J Bacteriol. 1984 Nov;160(2):691–695. doi: 10.1128/jb.160.2.691-695.1984. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Parkkinen J., Finne J., Achtman M., Väisänen V., Korhonen T. K. Escherichia coli strains binding neuraminyl alpha 2-3 galactosides. Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 1983 Mar 16;111(2):456–461. doi: 10.1016/0006-291x(83)90328-5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Shulman M., Wilde C. D., Köhler G. A better cell line for making hybridomas secreting specific antibodies. Nature. 1978 Nov 16;276(5685):269–270. doi: 10.1038/276269a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Silverblatt F. J., Cohen L. S. Antipili antibody affords protection against experimental ascending pyelonephritis. J Clin Invest. 1979 Jul;64(1):333–336. doi: 10.1172/JCI109458. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Stamey T. A., Sexton C. C. The role of vaginal colonization with enterobacteriaceae in recurrent urinary infections. J Urol. 1975 Feb;113(2):214–217. doi: 10.1016/s0022-5347(17)59447-1. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Towbin H., Staehelin T., Gordon J. Electrophoretic transfer of proteins from polyacrylamide gels to nitrocellulose sheets: procedure and some applications. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1979 Sep;76(9):4350–4354. doi: 10.1073/pnas.76.9.4350. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Väisänen V., Korhonen T. K., Jokinen M., Gahmberg C. G., Ehnholm C. Blood group M specific haemagglutinin in pyelonephritogenic Escherichia coli. Lancet. 1982 May 22;1(8282):1192–1192. doi: 10.1016/s0140-6736(82)92264-4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Watts T. H., Scraba D. G., Paranchych W. Formation of 9-nm filaments from pilin monomers obtained by octyl-glucoside dissociation of Pseudomonas aeruginosa pili. J Bacteriol. 1982 Sep;151(3):1508–1513. doi: 10.1128/jb.151.3.1508-1513.1982. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]