Abstract
An hypothesis is proposed that there exists a subgroup of African-American hypertensive patients whose hypertension could have been prevented by the early detection and treatment of easily recognizable symptoms that signal the initiation of the pathophysiologic processes that lead to essential hypertension.
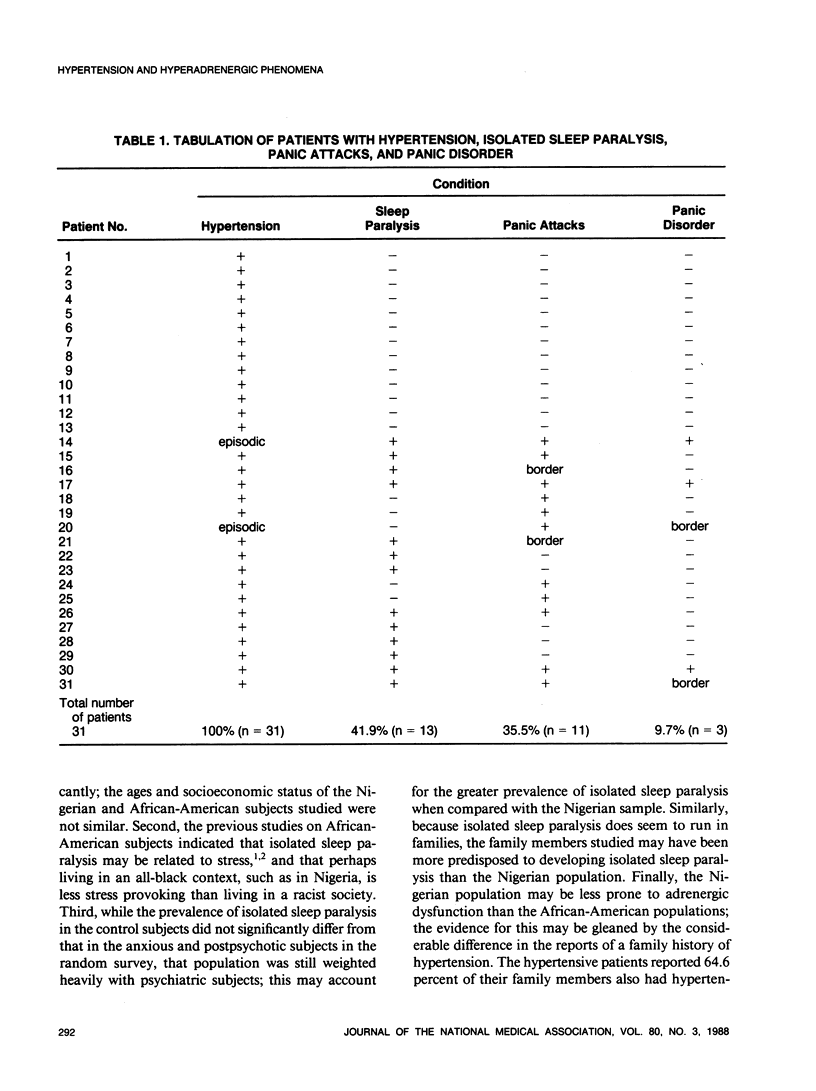
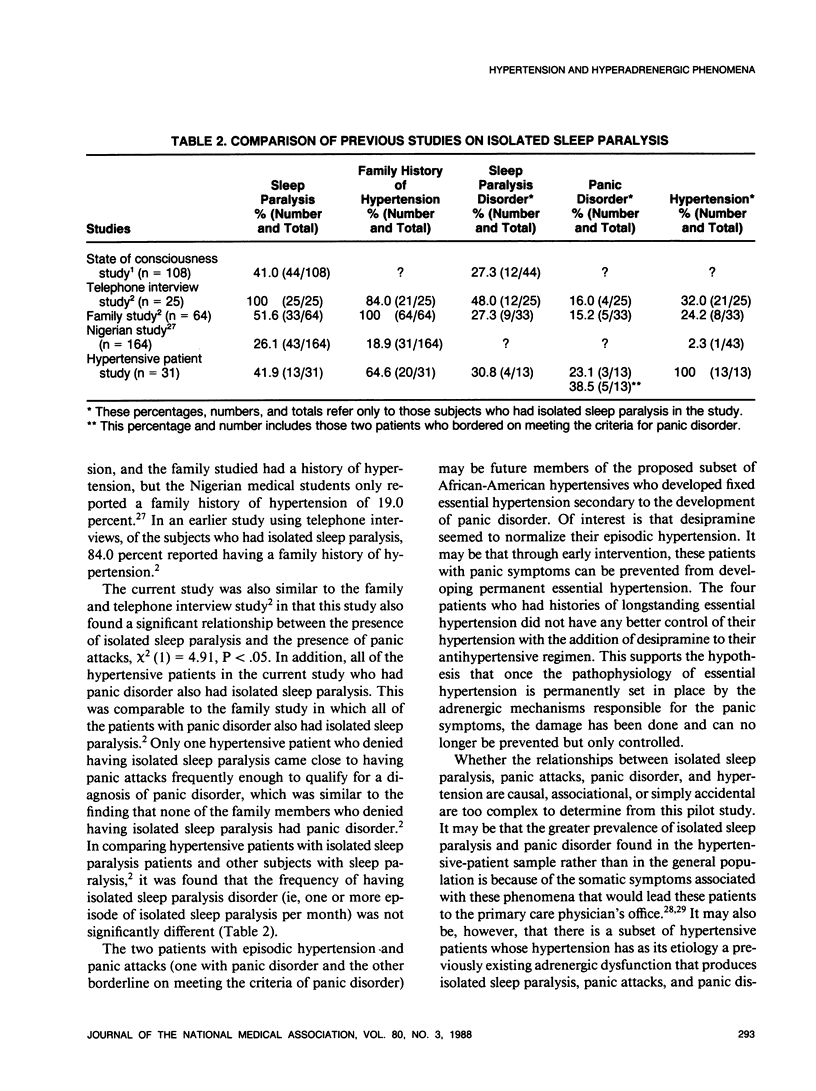
A pilot study of 31 patients with elevated blood pressure revealed that 41.9 percent had isolated sleep paralysis, 35.5 percent had panic attacks, and 9.7 percent had panic disorder. These proposed hyperadrenergic phenomena may be related to the development of hypertension in certain individuals.
Full text
PDF



Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Bell C. C. Black intrapsychic survival skills: alteration of states of consciousness. J Natl Med Assoc. 1982 Oct;74(10):1017–1020. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bell C. C., Dixie-Bell D. D., Thompson B. Further studies on the prevalence of isolated sleep paralysis in black subjects. J Natl Med Assoc. 1986 Jul;78(7):649–659. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bell C. C., Shakoor B., Thompson B., Dew D., Hughley E., Mays R., Shorter-Gooden K. Prevalence of isolated sleep paralysis in black subjects. J Natl Med Assoc. 1984 May;76(5):501–508. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bell C. C. Simultaneous treatment of hypertension and opiate withdrawal using an alpha 2-adrenergic agonist. J Natl Med Assoc. 1983 Jan;75(1):89–93. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bell C. C. States of consciousness. J Natl Med Assoc. 1980 Apr;72(4):331–334. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Charney D. S., Heninger G. R., Breier A. Noradrenergic function in panic anxiety. Effects of yohimbine in healthy subjects and patients with agoraphobia and panic disorder. Arch Gen Psychiatry. 1984 Aug;41(8):751–763. doi: 10.1001/archpsyc.1984.01790190025003. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Charney D. S., Heninger G. R., Redmond D. E., Jr Yohimbine induced anxiety and increased noradrenergic function in humans: effects of diazepam and clonidine. Life Sci. 1983 Jul 4;33(1):19–29. doi: 10.1016/0024-3205(83)90707-5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Charney D. S., Redmond D. E., Jr Neurobiological mechanisms in human anxiety. Evidence supporting central noradrenergic hyperactivity. Neuropharmacology. 1983 Dec;22(12B):1531–1536. doi: 10.1016/0028-3908(83)90122-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Coryell W., Noyes R., Clancy J. Excess mortality in panic disorder. A comparison with primary unipolar depression. Arch Gen Psychiatry. 1982 Jun;39(6):701–703. doi: 10.1001/archpsyc.1982.04290060051010. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Faravelli C., Webb T., Ambonetti A., Fonnesu F., Sessarego A. Prevalence of traumatic early life events in 31 agoraphobic patients with panic attacks. Am J Psychiatry. 1985 Dec;142(12):1493–1494. doi: 10.1176/ajp.142.12.1493. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Finlay-Jones R., Brown G. W. types of stressful life event and the onset of anxiety and depressive disorders. Psychol Med. 1981 Nov;11(4):803–815. doi: 10.1017/s0033291700041301. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Grant S. J., Huang Y. H., Redmond D. E., Jr Benzodiazepines attenuate single unit activity in the locus coeruleus. Life Sci. 1980 Dec 8;27(23):2231–2236. doi: 10.1016/0024-3205(80)90389-6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hoehn-Saric R., Merchant A. F., Keyser M. L., Smith V. K. Effects of clonidine on anxiety disorders. Arch Gen Psychiatry. 1981 Nov;38(11):1278–1282. doi: 10.1001/archpsyc.1981.01780360094011. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Katon W. Panic disorder and somatization. Review of 55 cases. Am J Med. 1984 Jul;77(1):101–106. doi: 10.1016/0002-9343(84)90443-1. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Katon W., Vitaliano P. P., Russo J., Cormier L., Anderson K., Jones M. Panic disorder: epidemiology in primary care. J Fam Pract. 1986 Sep;23(3):233–239. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ko G. N., Elsworth J. D., Roth R. H., Rifkin B. G., Leigh H., Redmond D. E., Jr Panic-induced elevation of plasma MHPG levels in phobic-anxious patients. Effects of clonidine and imipramine. Arch Gen Psychiatry. 1983 Apr;40(4):425–430. doi: 10.1001/archpsyc.1983.01790040079011. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Nesse R. M., Cameron O. G., Curtis G. C., McCann D. S., Huber-Smith M. J. Adrenergic function in patients with panic anxiety. Arch Gen Psychiatry. 1984 Aug;41(8):771–776. doi: 10.1001/archpsyc.1984.01790190045005. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Noyes R., Clancy J., Hoenk P. R., Slymen D. J. Anxiety neurosis and physical illness. Compr Psychiatry. 1978 Sep-Oct;19(5):407–413. doi: 10.1016/0010-440x(78)90069-x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Noyes R., Jr, Clancy J., Hoenk P. R., Slymen D. J. The prognosis of anxiety neurosis. Arch Gen Psychiatry. 1980 Feb;37(2):173–178. doi: 10.1001/archpsyc.1980.01780150063006. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Pollack M. H., Rosenbaum J. F. Management of antidepressant-induced side effects: a practical guide for the clinician. J Clin Psychiatry. 1987 Jan;48(1):3–8. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Shear M. K., Kligfield P., Harshfield G., Devereux R. B., Polan J. J., Mann J. J., Pickering T., Frances A. J. Cardiac rate and rhythm in panic patients. Am J Psychiatry. 1987 May;144(5):633–637. doi: 10.1176/ajp.144.5.633. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Uhde T. W., Boulenger J. P., Roy-Byrne P. P., Geraci M. F., Vittone B. J., Post R. M. Longitudinal course of panic disorder: clinical and biological considerations. Prog Neuropsychopharmacol Biol Psychiatry. 1985;9(1):39–51. doi: 10.1016/0278-5846(85)90178-2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Von Korff M., Shapiro S., Burke J. D., Teitlebaum M., Skinner E. A., German P., Turner R. W., Klein L., Burns B. Anxiety and depression in a primary care clinic. Comparison of Diagnostic Interview Schedule, General Health Questionnaire, and practitioner assessments. Arch Gen Psychiatry. 1987 Feb;44(2):152–156. doi: 10.1001/archpsyc.1987.01800140058008. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ward D. G., Gunn C. G. Locus coeruleus complex: differential modulation of depressor mechanisms. Brain Res. 1976 May 7;107(2):407–411. doi: 10.1016/0006-8993(76)90237-7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Warheit G. J., Holzer C. E., 3rd, Arey S. A. Race and mental illness: an epidemiologic update. J Health Soc Behav. 1975 Sep;16(3):243–256. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]


