Abstract
Oligonucleotide probes specific for 16S rRNA and capable of differentiating Streptococcus uberis and S. parauberis from each other and other esculin-hydrolyzing streptococci were developed. Use of a mini-RNA extraction technique for gram-positive cocci associated with bovine mastitis has allowed the probes to be used for identification of esculin-hydrolyzing streptococci from two dairy herds at the Institute for Animal Health, Compton, United Kingdom. One hundred seventy-nine of 206 isolates were identified as S. uberis, 3 were identified as S. parauberis, and 24 were not identified. Isolates not identified by the probes were tested biochemically and found to be mainly Enterococcus faecium, E. faecalis, or S. bovis.
Full text
PDF

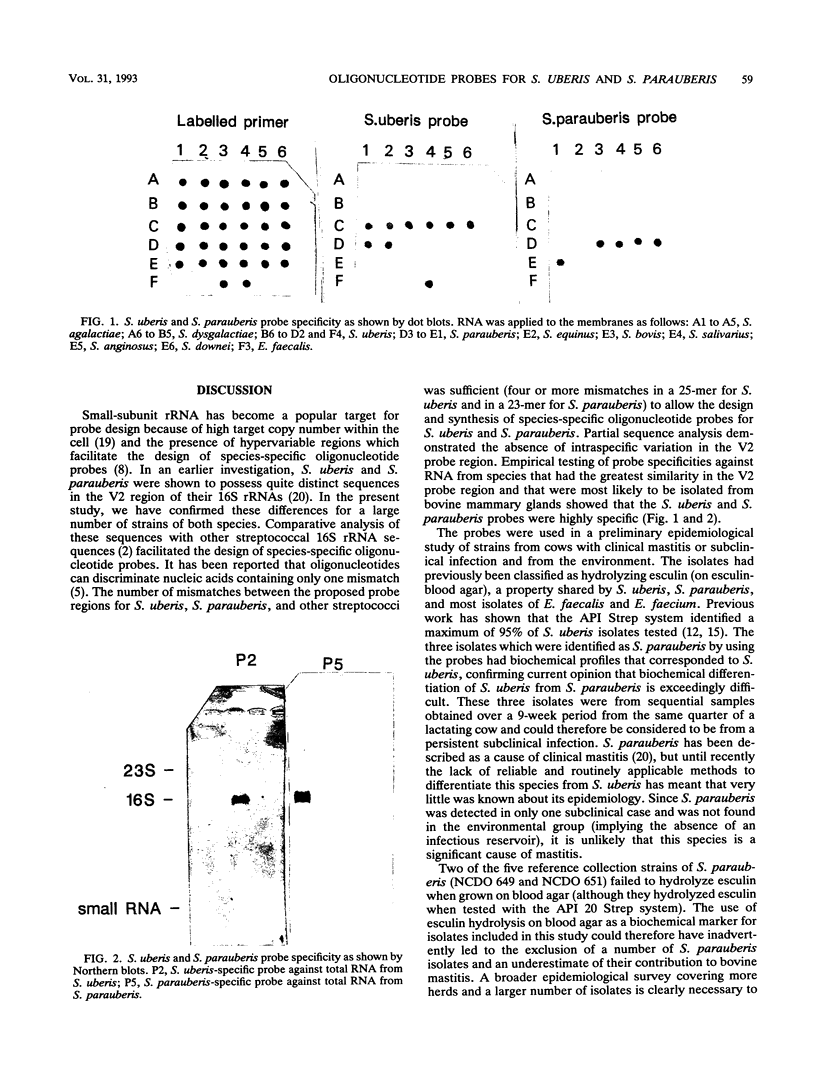
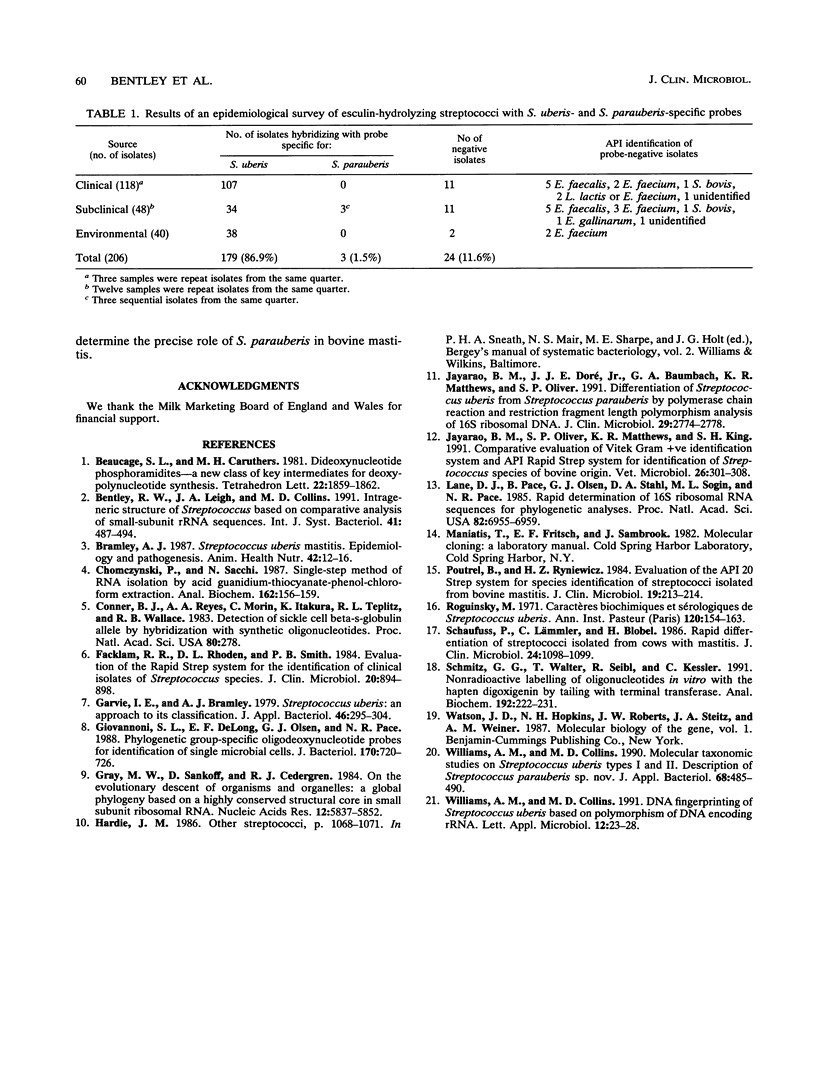
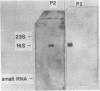
Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Bentley R. W., Leigh J. A., Collins M. D. Intrageneric structure of Streptococcus based on comparative analysis of small-subunit rRNA sequences. Int J Syst Bacteriol. 1991 Oct;41(4):487–494. doi: 10.1099/00207713-41-4-487. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Chomczynski P., Sacchi N. Single-step method of RNA isolation by acid guanidinium thiocyanate-phenol-chloroform extraction. Anal Biochem. 1987 Apr;162(1):156–159. doi: 10.1006/abio.1987.9999. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Conner B. J., Reyes A. A., Morin C., Itakura K., Teplitz R. L., Wallace R. B. Detection of sickle cell beta S-globin allele by hybridization with synthetic oligonucleotides. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1983 Jan;80(1):278–282. doi: 10.1073/pnas.80.1.278. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Facklam R. R., Rhoden D. L., Smith P. B. Evaluation of the Rapid Strep system for the identification of clinical isolates of Streptococcus species. J Clin Microbiol. 1984 Nov;20(5):894–898. doi: 10.1128/jcm.20.5.894-898.1984. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Giovannoni S. J., DeLong E. F., Olsen G. J., Pace N. R. Phylogenetic group-specific oligodeoxynucleotide probes for identification of single microbial cells. J Bacteriol. 1988 Feb;170(2):720–726. doi: 10.1128/jb.170.2.720-726.1988. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gray M. W., Sankoff D., Cedergren R. J. On the evolutionary descent of organisms and organelles: a global phylogeny based on a highly conserved structural core in small subunit ribosomal RNA. Nucleic Acids Res. 1984 Jul 25;12(14):5837–5852. doi: 10.1093/nar/12.14.5837. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Jayarao B. M., Doré J. J., Jr, Baumbach G. A., Matthews K. R., Oliver S. P. Differentiation of Streptococcus uberis from Streptococcus parauberis by polymerase chain reaction and restriction fragment length polymorphism analysis of 16S ribosomal DNA. J Clin Microbiol. 1991 Dec;29(12):2774–2778. doi: 10.1128/jcm.29.12.2774-2778.1991. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Jayarao B. M., Oliver S. P., Matthews K. R., King S. H. Comparative evaluation of Vitek gram-positive identification system and API Rapid Strep system for identification of Streptococcus species of bovine origin. Vet Microbiol. 1991 Feb 1;26(3):301–308. doi: 10.1016/0378-1135(91)90023-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lane D. J., Pace B., Olsen G. J., Stahl D. A., Sogin M. L., Pace N. R. Rapid determination of 16S ribosomal RNA sequences for phylogenetic analyses. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1985 Oct;82(20):6955–6959. doi: 10.1073/pnas.82.20.6955. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Poutrel B., Ryniewicz H. Z. Evaluation of the API 20 Strep system for species identification of streptococci isolated from bovine mastitis. J Clin Microbiol. 1984 Feb;19(2):213–214. doi: 10.1128/jcm.19.2.213-214.1984. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Roguinsky M. Caractères biochimiques et sérologiques de Streptococcus uberis. Ann Inst Pasteur (Paris) 1971 Feb;120(2):154–163. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Schaufuss P., Lämmler C., Blobel H. Rapid differentiation of streptococci isolated from cows with mastitis. J Clin Microbiol. 1986 Dec;24(6):1098–1099. doi: 10.1128/jcm.24.6.1098-1099.1986. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Schmitz G. G., Walter T., Seibl R., Kessler C. Nonradioactive labeling of oligonucleotides in vitro with the hapten digoxigenin by tailing with terminal transferase. Anal Biochem. 1991 Jan;192(1):222–231. doi: 10.1016/0003-2697(91)90212-c. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Williams A. M., Collins M. D. DNA fingerprinting of Streptococcus uberis based on polymorphism of DNA encoding rRNA. Lett Appl Microbiol. 1991 Jan;12(1):23–28. doi: 10.1111/j.1472-765x.1991.tb00493.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Williams A. M., Collins M. D. Molecular taxonomic studies on Streptococcus uberis types I and II. Description of Streptococcus parauberis sp. nov. J Appl Bacteriol. 1990 May;68(5):485–490. doi: 10.1111/j.1365-2672.1990.tb02900.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]