Abstract
Human rotaviruses were isolated from asymptomatic neonates at various hospitals and clinics in the city of Bangalore, India, and were found to be subgroup I specific and possess long RNA patterns (M. Sukumaran, K. Gowda, P. P. Maiya, T. P. Srinivas, M. S. Kumar, S. Aijaz, R. R. Reddy, L. Padilla, H. B. Greenberg, and C. D. Rao, Arch. Virol. 126:239-251, 1992). Three of these strains were adapted to tissue culture and found by serotype analysis and neutralization assays to be of serotype 10, a serotype commonly found in cattle but infrequently found in humans and not previously identified in neonates. By RNA-RNA hybridization, a high level of relatedness to a serotype 10 bovine rotavirus strain and a low-to-medium level of relatedness to a human rotavirus strain were observed. Since this human isolate shares a genogroup with bovine rotavirus, it is likely that it originated by interspecies transmission. A human rotavirus strain isolated from asymptomatic neonates and similar to bovine rotavirus might represent a good vaccine candidate.
Full text
PDF



Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Aboudy Y., Shif I., Zilberstein I., Gotlieb-Stematsky T. Use of polyclonal and monoclonal antibodies and analysis of viral RNA in the detection of unusual group A human rotaviruses. J Med Virol. 1988 Jul;25(3):351–359. doi: 10.1002/jmv.1890250312. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Beards G. M., Desselberger U., Flewett T. H. Temporal and geographical distributions of human rotavirus serotypes, 1983 to 1988. J Clin Microbiol. 1989 Dec;27(12):2827–2833. doi: 10.1128/jcm.27.12.2827-2833.1989. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Beards G., Xu L., Ballard A., Desselberger U., McCrae M. A. A serotype 10 human rotavirus. J Clin Microbiol. 1992 Jun;30(6):1432–1435. doi: 10.1128/jcm.30.6.1432-1435.1992. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
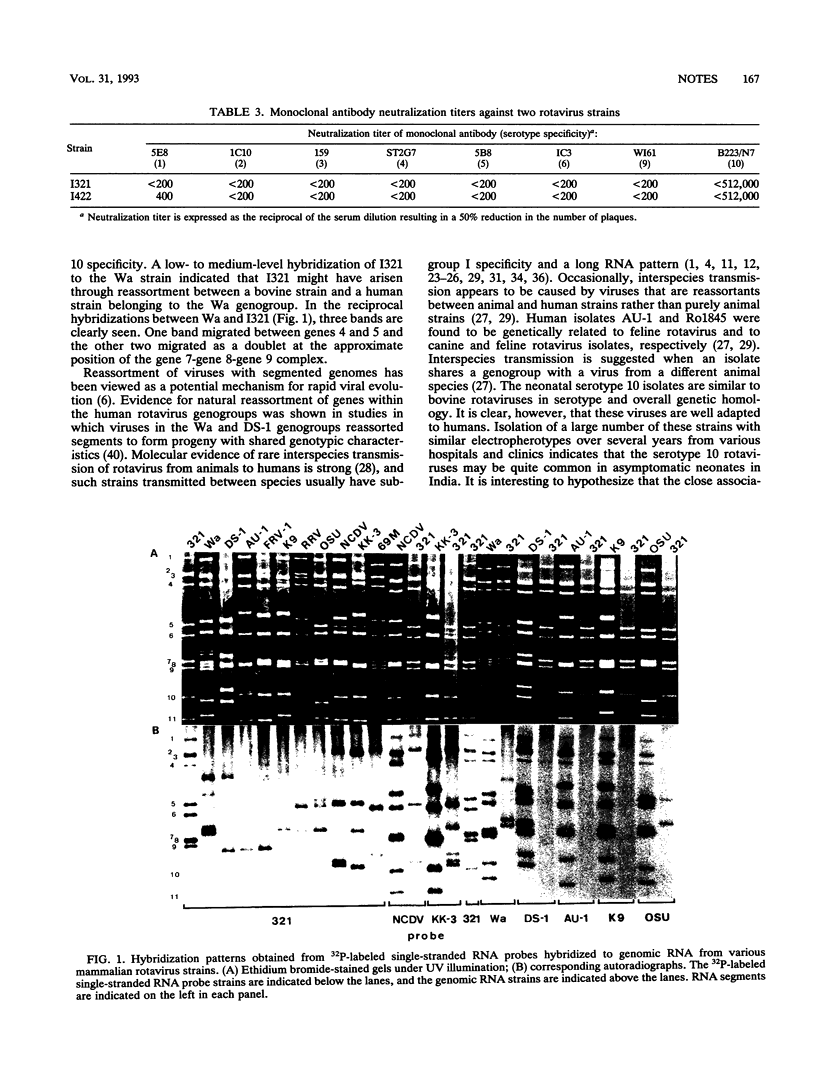
- Brown D. W., Mathan M. M., Mathew M., Martin R., Beards G. M., Mathan V. I. Rotavirus epidemiology in Vellore, south India: group, subgroup, serotype, and electrophoretype. J Clin Microbiol. 1988 Nov;26(11):2410–2414. doi: 10.1128/jcm.26.11.2410-2414.1988. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Browning G. F., Fitzgerald T. A., Chalmers R. M., Snodgrass D. R. A novel group A rotavirus G serotype: serological and genomic characterization of equine isolate FI23. J Clin Microbiol. 1991 Sep;29(9):2043–2046. doi: 10.1128/jcm.29.9.2043-2046.1991. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Chanock S. J., Wenske E. A., Fields B. N. Human rotaviruses and genome RNA. J Infect Dis. 1983 Jul;148(1):49–50. doi: 10.1093/infdis/148.1.49. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Estes M. K., Cohen J. Rotavirus gene structure and function. Microbiol Rev. 1989 Dec;53(4):410–449. doi: 10.1128/mr.53.4.410-449.1989. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Flores J., Greenberg H. B., Myslinski J., Kalica A. R., Wyatt R. G., Kapikian A. Z., Chanock R. M. Use of transcription probes for genotyping rotavirus reassortants. Virology. 1982 Sep;121(2):288–295. doi: 10.1016/0042-6822(82)90168-4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Flores J., Perez-Schael I., Boeggeman E., White L., Perez M., Purcell R., Hoshino Y., Midthun K., Chanock R. M., Kapikian A. Z. Genetic relatedness among human rotaviruses. J Med Virol. 1985 Oct;17(2):135–143. doi: 10.1002/jmv.1890170206. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Flores J., Perez I., White L., Perez M., Kalica A. R., Marquina R., Wyatt R. G., Kapikian A. Z., Chanock R. M. Genetic relatedness among human rotaviruses as determined by RNA hybridization. Infect Immun. 1982 Aug;37(2):648–655. doi: 10.1128/iai.37.2.648-655.1982. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gerna G., Sarasini A., Di Matteo A., Zentilin L., Miranda P., Parea M., Baldanti F., Arista S., Milanesi G., Battaglia M. Serotype 3 human rotavirus strains with subgroup I specificity. J Clin Microbiol. 1990 Jun;28(6):1342–1347. doi: 10.1128/jcm.28.6.1342-1347.1990. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ghosh S. K., Naik T. N. Detection of a large number of subgroup 1 human rotaviruses with a "long" RNA electropherotype. Arch Virol. 1989;105(1-2):119–127. doi: 10.1007/BF01311122. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gorziglia M., Green K., Nishikawa K., Taniguchi K., Jones R., Kapikian A. Z., Chanock R. M. Sequence of the fourth gene of human rotaviruses recovered from asymptomatic or symptomatic infections. J Virol. 1988 Aug;62(8):2978–2984. doi: 10.1128/jvi.62.8.2978-2984.1988. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Greenberg H., McAuliffe V., Valdesuso J., Wyatt R., Flores J., Kalica A., Hoshino Y., Singh N. Serological analysis of the subgroup protein of rotavirus, using monoclonal antibodies. Infect Immun. 1983 Jan;39(1):91–99. doi: 10.1128/iai.39.1.91-99.1983. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hoshino Y., Wyatt R. G., Flores J., Midthun K., Kapikian A. Z. Serotypic characterization of rotaviruses derived from asymptomatic human neonatal infections. J Clin Microbiol. 1985 Mar;21(3):425–430. doi: 10.1128/jcm.21.3.425-430.1985. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kalica A. R., Greenberg H. B., Espejo R. T., Flores J., Wyatt R. G., Kapikian A. Z., Chanock R. M. Distinctive ribonucleic acid patterns of human rotavirus subgroups 1 and 2. Infect Immun. 1981 Sep;33(3):958–961. doi: 10.1128/iai.33.3.958-961.1981. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kobayashi N., Lintag I. C., Urasawa T., Taniguchi K., Saniel M. C., Urasawa S. Unusual human rotavirus strains having subgroup I specificity and "long" RNA electropherotype. Arch Virol. 1989;109(1-2):11–23. doi: 10.1007/BF01310514. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Matsuda Y., Nakagomi O. Antigenic and molecular characterization of bovine rotaviruses isolated in Japan. Res Virol. 1989 Jul-Aug;140(4):337–350. doi: 10.1016/s0923-2516(89)80114-1. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Midthun K., Valdesuso J., Kapikian A. Z., Hoshino Y., Green K. Y. Identification of serotype 9 human rotavirus by enzyme-linked immunosorbent assay with monoclonal antibodies. J Clin Microbiol. 1989 Sep;27(9):2112–2114. doi: 10.1128/jcm.27.9.2112-2114.1989. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Nakagomi O., Nakagomi T., Akatani K., Ikegami N. Identification of rotavirus genogroups by RNA-RNA hybridization. Mol Cell Probes. 1989 Sep;3(3):251–261. doi: 10.1016/0890-8508(89)90006-6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Nakagomi O., Nakagomi T., Akatani K., Ikegami N., Katsushima N. Relative frequency of rotavirus serotypes in Yamagata, Japan, over four consecutive rotavirus seasons. Res Virol. 1990 Jul-Aug;141(4):459–463. doi: 10.1016/0923-2516(90)90047-m. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Nakagomi O., Nakagomi T. Genetic diversity and similarity among mammalian rotaviruses in relation to interspecies transmission of rotavirus. Arch Virol. 1991;120(1-2):43–55. doi: 10.1007/BF01310948. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Nakagomi O., Nakagomi T., Hoshino Y., Flores J., Kapikian A. Z. Genetic analysis of a human rotavirus that belongs to subgroup I but has an RNA pattern typical of subgroup II human rotaviruses. J Clin Microbiol. 1987 Jul;25(7):1159–1164. doi: 10.1128/jcm.25.7.1159-1164.1987. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Nakagomi O., Nakagomi T. Molecular evidence for naturally occurring single VP7 gene substitution reassortant between human rotaviruses belonging to two different genogroups. Arch Virol. 1991;119(1-2):67–81. doi: 10.1007/BF01314324. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Nakagomi O., Nakagomi T., Oyamada H., Suto T. Relative frequency of human rotavirus subgroups 1 and 2 in Japanese children with acute gastroenteritis. J Med Virol. 1985 Sep;17(1):29–34. doi: 10.1002/jmv.1890170105. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Nakagomi O., Ohshima A., Aboudy Y., Shif I., Mochizuki M., Nakagomi T., Gotlieb-Stematsky T. Molecular identification by RNA-RNA hybridization of a human rotavirus that is closely related to rotaviruses of feline and canine origin. J Clin Microbiol. 1990 Jun;28(6):1198–1203. doi: 10.1128/jcm.28.6.1198-1203.1990. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Nakagomi O., Oyamada H., Kuroki S., Kobayashi Y., Ohshima A., Nakagomi T. Molecular identification of a novel human rotavirus in relation to subgroup and electropherotype of genomic RNA. J Med Virol. 1989 Jul;28(3):163–168. doi: 10.1002/jmv.1890280311. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Nakagomi T., Nakagomi O. RNA-RNA hybridization identifies a human rotavirus that is genetically related to feline rotavirus. J Virol. 1989 Mar;63(3):1431–1434. doi: 10.1128/jvi.63.3.1431-1434.1989. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Padilla-Noriega L., Arias C. F., López S., Puerto F., Snodgrass D. R., Taniguchi K., Greenberg H. B. Diversity of rotavirus serotypes in Mexican infants with gastroenteritis. J Clin Microbiol. 1990 Jun;28(6):1114–1119. doi: 10.1128/jcm.28.6.1114-1119.1990. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Shaw R. D., Stoner-Ma D. L., Estes M. K., Greenberg H. B. Specific enzyme-linked immunoassay for rotavirus serotypes 1 and 3. J Clin Microbiol. 1985 Aug;22(2):286–291. doi: 10.1128/jcm.22.2.286-291.1985. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Snodgrass D. R., Fitzgerald T., Campbell I., Scott F. M., Browning G. F., Miller D. L., Herring A. J., Greenberg H. B. Rotavirus serotypes 6 and 10 predominate in cattle. J Clin Microbiol. 1990 Mar;28(3):504–507. doi: 10.1128/jcm.28.3.504-507.1990. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Steele A. D., Alexander J. J. The relative frequency of subgroup I and II rotaviruses in black infants in South Africa. J Med Virol. 1988 Mar;24(3):321–327. doi: 10.1002/jmv.1890240309. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sukumaran M., Gowda K., Maiya P. P., Srinivas T. P., Kumar M. S., Aijaz S., Reddy R. R., Padilla L., Greenberg H. B., Rao C. D. Exclusive asymptomatic neonatal infections by human rotavirus strains having subgroup I specificity and "long" RNA electropherotype. Arch Virol. 1992;126(1-4):239–251. doi: 10.1007/BF01309698. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Tam J. S., Zheng B. J., Lo S. K., Yeung C. Y., Lo M., Ng M. H. Distinct populations of rotaviruses circulating among neonates and older infants. J Clin Microbiol. 1990 May;28(5):1033–1038. doi: 10.1128/jcm.28.5.1033-1038.1990. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Taniguchi K., Urasawa T., Kobayashi N., Gorziglia M., Urasawa S. Nucleotide sequence of VP4 and VP7 genes of human rotaviruses with subgroup I specificity and long RNA pattern: implication for new G serotype specificity. J Virol. 1990 Nov;64(11):5640–5644. doi: 10.1128/jvi.64.11.5640-5644.1990. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Vesikari T., Ruuska T., Koivu H. P., Green K. Y., Flores J., Kapikian A. Z. Evaluation of the M37 human rotavirus vaccine in 2- to 6-month-old infants. Pediatr Infect Dis J. 1991 Dec;10(12):912–917. doi: 10.1097/00006454-199112000-00006. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ward R. L., Knowlton D. R., Pierce M. J. Efficiency of human rotavirus propagation in cell culture. J Clin Microbiol. 1984 Jun;19(6):748–753. doi: 10.1128/jcm.19.6.748-753.1984. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ward R. L., Nakagomi O., Knowlton D. R., McNeal M. M., Nakagomi T., Clemens J. D., Sack D. A., Schiff G. M. Evidence for natural reassortants of human rotaviruses belonging to different genogroups. J Virol. 1990 Jul;64(7):3219–3225. doi: 10.1128/jvi.64.7.3219-3225.1990. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Zheng S. L., Woode G. N., Melendy D. R., Ramig R. F. Comparative studies of the antigenic polypeptide species VP4, VP6, and VP7 of three strains of bovine rotavirus. J Clin Microbiol. 1989 Sep;27(9):1939–1945. doi: 10.1128/jcm.27.9.1939-1945.1989. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]