Abstract
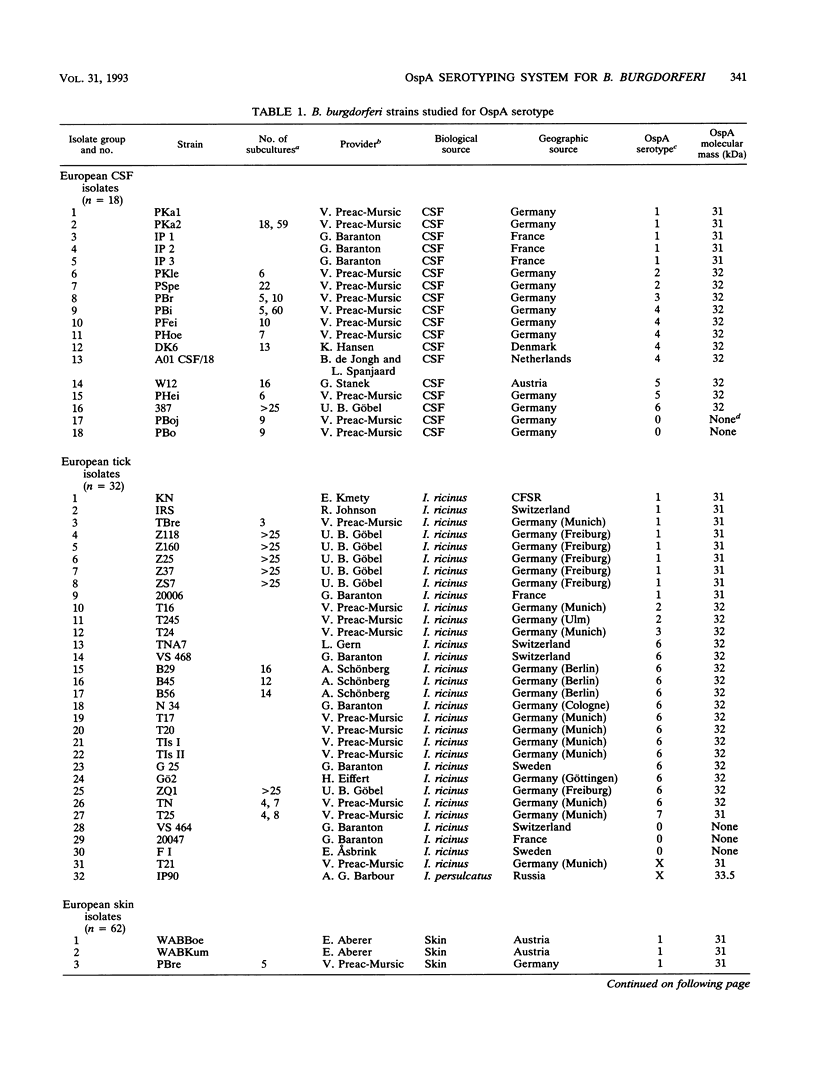
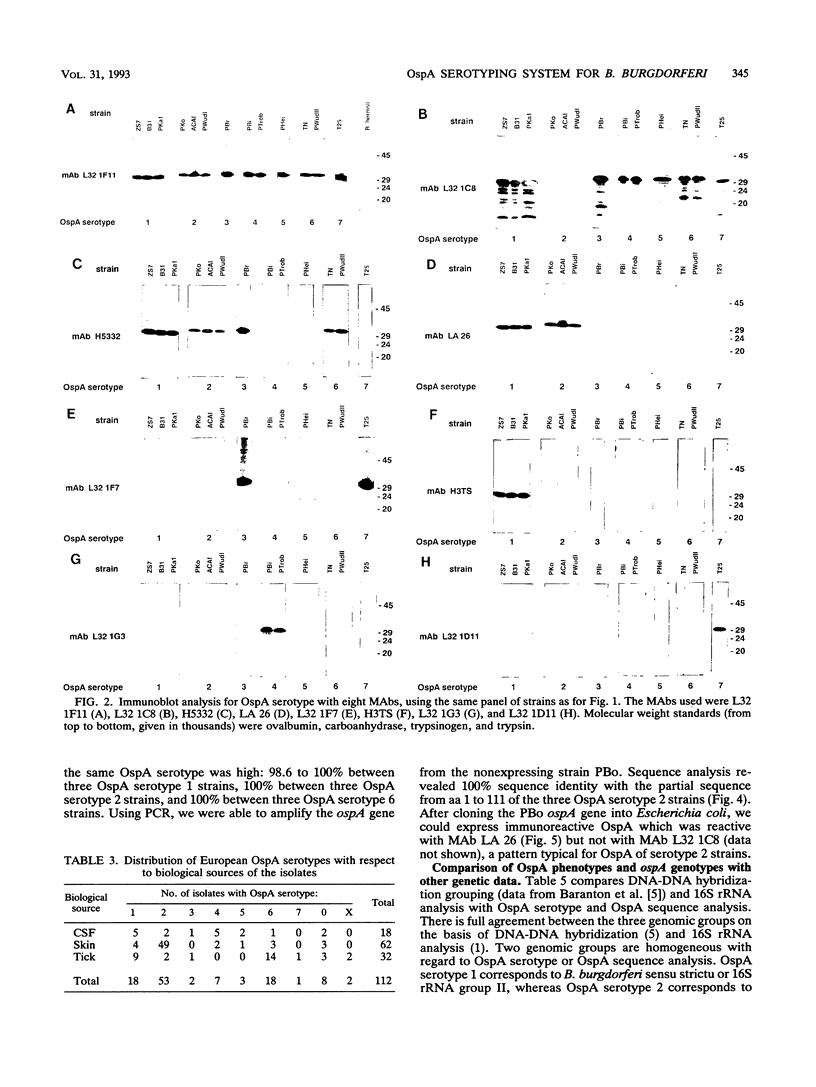
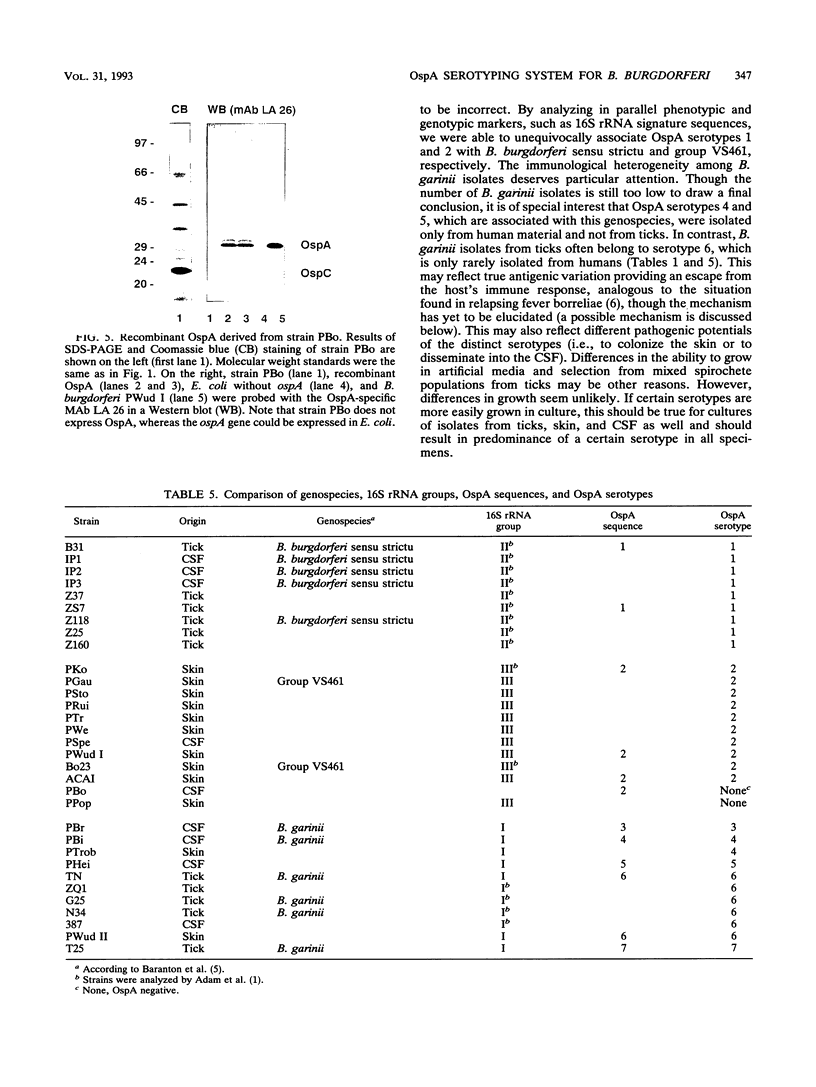
A total of 136 Borrelia burgdorferi sensu latu strains from various biological sources (ticks, human skin, and cerebrospinal fluid) and geographical sources (Europe and North America) were investigated by Western blot (immunoblot) with eight monoclonal antibodies against different epitopes of the outer surface protein A (OspA). On the basis of the differential reactivities of these monoclonal antibodies, seven OspA serotypes were defined. As determined by 16S rRNA sequence analysis, these serotypes correlated well with recently delineated genospecies: serotype 1 corresponds to B. burgdorferi sensu strictu, serotype 2 corresponds to group VS461, and serotypes 3 to 7 correspond to Borrelia garinii sp. nov. (G. Baranton, D. Postic, I. Saint Girons, P. Boerlin, J.-C. Piffaretti, M. Assous, and P. A. D. Grimont, Int. J. Syst. Bacteriol. 42:378-383, 1992). Antigenic differences were confirmed by partial sequence analysis of OspA of representatives of each serotype. Comparative sequence analysis suggested that serotype 5 OspA resulted from genetic recombination of serotype 4 and 6 ospA genes. Serotype 2 (group VS461) was most prevalent among European skin isolates (49 of 62 isolates). Among all B. garinii strains included in this study, serotype 6 was most frequently found in ticks and only rarely in human skin and cerebrospinal fluid, whereas serotypes 4 and 5 were isolated from patients but never from ticks. Our data suggest different pathogenic potentials and organotropisms of distinct OspA serotypes and raise the question of true antigenic variation among B. garinii strains.
Full text
PDF







Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Adam T., Gassmann G. S., Rasiah C., Göbel U. B. Phenotypic and genotypic analysis of Borrelia burgdorferi isolates from various sources. Infect Immun. 1991 Aug;59(8):2579–2585. doi: 10.1128/iai.59.8.2579-2585.1991. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Anderson J. F., Magnarelli L. A., LeFebvre R. B., Andreadis T. G., McAninch J. B., Perng G. C., Johnson R. C. Antigenically variable Borrelia burgdorferi isolated from cottontail rabbits and Ixodes dentatus in rural and urban areas. J Clin Microbiol. 1989 Jan;27(1):13–20. doi: 10.1128/jcm.27.1.13-20.1989. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Asbrink E., Hovmark A., Olsson I. Clinical manifestations of acrodermatitis chronica atrophicans in 50 Swedish patients. Zentralbl Bakteriol Mikrobiol Hyg A. 1986 Dec;263(1-2):253–261. doi: 10.1016/s0176-6724(86)80128-6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Baranton G., Postic D., Saint Girons I., Boerlin P., Piffaretti J. C., Assous M., Grimont P. A. Delineation of Borrelia burgdorferi sensu stricto, Borrelia garinii sp. nov., and group VS461 associated with Lyme borreliosis. Int J Syst Bacteriol. 1992 Jul;42(3):378–383. doi: 10.1099/00207713-42-3-378. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Barbour A. G., Garon C. F. Linear plasmids of the bacterium Borrelia burgdorferi have covalently closed ends. Science. 1987 Jul 24;237(4813):409–411. doi: 10.1126/science.3603026. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Barbour A. G., Heiland R. A., Howe T. R. Heterogeneity of major proteins in Lyme disease borreliae: a molecular analysis of North American and European isolates. J Infect Dis. 1985 Sep;152(3):478–484. doi: 10.1093/infdis/152.3.478. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Barbour A. G., Schrumpf M. E. Polymorphisms of major surface proteins of Borrelia burgdorferi. Zentralbl Bakteriol Mikrobiol Hyg A. 1986 Dec;263(1-2):83–91. doi: 10.1016/s0176-6724(86)80107-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Barbour A. G., Tessier S. L., Hayes S. F. Variation in a major surface protein of Lyme disease spirochetes. Infect Immun. 1984 Jul;45(1):94–100. doi: 10.1128/iai.45.1.94-100.1984. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Benach J. L., Coleman J. L., Garcia-Monco J. C., Deponte P. C. Biological activity of Borrelia burgdorferi antigens. Ann N Y Acad Sci. 1988;539:115–125. doi: 10.1111/j.1749-6632.1988.tb31845.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bergström S., Bundoc V. G., Barbour A. G. Molecular analysis of linear plasmid-encoded major surface proteins, OspA and OspB, of the Lyme disease spirochaete Borrelia burgdorferi. Mol Microbiol. 1989 Apr;3(4):479–486. doi: 10.1111/j.1365-2958.1989.tb00194.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Boerlin P., Peter O., Bretz A. G., Postic D., Baranton G., Piffaretti J. C. Population genetic analysis of Borrelia burgdorferi isolates by multilocus enzyme electrophoresis. Infect Immun. 1992 Apr;60(4):1677–1683. doi: 10.1128/iai.60.4.1677-1683.1992. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Brown R. N., Lane R. S. Lyme disease in California: a novel enzootic transmission cycle of Borrelia burgdorferi. Science. 1992 Jun 5;256(5062):1439–1442. doi: 10.1126/science.1604318. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bundoc V. G., Barbour A. G. Clonal polymorphisms of outer membrane protein OspB of Borrelia burgdorferi. Infect Immun. 1989 Sep;57(9):2733–2741. doi: 10.1128/iai.57.9.2733-2741.1989. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Burgdorfer W., Barbour A. G., Hayes S. F., Benach J. L., Grunwaldt E., Davis J. P. Lyme disease-a tick-borne spirochetosis? Science. 1982 Jun 18;216(4552):1317–1319. doi: 10.1126/science.7043737. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Coleman J. L., Benach J. L. Characterization of antigenic determinants of Borrelia burgdorferi shared by other bacteria. J Infect Dis. 1992 Apr;165(4):658–666. doi: 10.1093/infdis/165.4.658. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Daschner F. Emergence of resistance during selective decontamination of the digestive tract. Eur J Clin Microbiol Infect Dis. 1992 Jan;11(1):1–3. doi: 10.1007/BF01971262. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Eiffert H., Ohlenbusch A., Fehling W., Lotter H., Thomssen R. Nucleotide sequence of the ospAB operon of a Borrelia burgdorferi strain expressing OspA but not OspB. Infect Immun. 1992 May;60(5):1864–1868. doi: 10.1128/iai.60.5.1864-1868.1992. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Fikrig E., Barthold S. W., Kantor F. S., Flavell R. A. Protection of mice against the Lyme disease agent by immunizing with recombinant OspA. Science. 1990 Oct 26;250(4980):553–556. doi: 10.1126/science.2237407. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Fikrig E., Barthold S. W., Persing D. H., Sun X., Kantor F. S., Flavell R. A. Borrelia burgdorferi strain 25015: characterization of outer surface protein A and vaccination against infection. J Immunol. 1992 Apr 1;148(7):2256–2260. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hinnebusch J., Barbour A. G. Linear- and circular-plasmid copy numbers in Borrelia burgdorferi. J Bacteriol. 1992 Aug;174(16):5251–5257. doi: 10.1128/jb.174.16.5251-5257.1992. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Jonsson M., Noppa L., Barbour A. G., Bergström S. Heterogeneity of outer membrane proteins in Borrelia burgdorferi: comparison of osp operons of three isolates of different geographic origins. Infect Immun. 1992 May;60(5):1845–1853. doi: 10.1128/iai.60.5.1845-1853.1992. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- LeFebvre R. B., Perng G. C., Johnson R. C. Characterization of Borrelia burgdorferi isolates by restriction endonuclease analysis and DNA hybridization. J Clin Microbiol. 1989 Apr;27(4):636–639. doi: 10.1128/jcm.27.4.636-639.1989. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Marconi R. T., Garon C. F. Identification of a third genomic group of Borrelia burgdorferi through signature nucleotide analysis and 16S rRNA sequence determination. J Gen Microbiol. 1992 Mar;138(3):533–536. doi: 10.1099/00221287-138-3-533. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Marconi R. T., Garon C. F. Phylogenetic analysis of the genus Borrelia: a comparison of North American and European isolates of Borrelia burgdorferi. J Bacteriol. 1992 Jan;174(1):241–244. doi: 10.1128/jb.174.1.241-244.1992. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Marconi R. T., Lubke L., Hauglum W., Garon C. F. Species-specific identification of and distinction between Borrelia burgdorferi genomic groups by using 16S rRNA-directed oligonucleotide probes. J Clin Microbiol. 1992 Mar;30(3):628–632. doi: 10.1128/jcm.30.3.628-632.1992. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Masuzawa T., Okada Y., Yanagihara Y., Sato N. Antigenic properties of Borrelia burgdorferi isolated from Ixodes ovatus and Ixodes persulcatus in Hokkaido, Japan. J Clin Microbiol. 1991 Aug;29(8):1568–1573. doi: 10.1128/jcm.29.8.1568-1573.1991. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mursic V. P., Wilske B., Schierz G., Holmburger M., Süss E. In vitro and in vivo susceptibility of Borrelia burgdorferi. Eur J Clin Microbiol. 1987 Aug;6(4):424–426. doi: 10.1007/BF02013102. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Pfister H. W., Preac-Mursic V., Wilske B., Einhäupl K. M., Weinberger K. Latent Lyme neuroborreliosis: presence of Borrelia burgdorferi in the cerebrospinal fluid without concurrent inflammatory signs. Neurology. 1989 Aug;39(8):1118–1120. doi: 10.1212/wnl.39.8.1118. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Picken R. N. Polymerase chain reaction primers and probes derived from flagellin gene sequences for specific detection of the agents of Lyme disease and North American relapsing fever. J Clin Microbiol. 1992 Jan;30(1):99–114. doi: 10.1128/jcm.30.1.99-114.1992. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Postic D., Edlinger C., Richaud C., Grimont F., Dufresne Y., Perolat P., Baranton G., Grimont P. A. Two genomic species in Borrelia burgdorferi. Res Microbiol. 1990 May;141(4):465–475. doi: 10.1016/0923-2508(90)90072-x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Péter O., Bretz A. G. Polymorphism of outer surface proteins of Borrelia burgdorferi as a tool for classification. Zentralbl Bakteriol. 1992 Jun;277(1):28–33. doi: 10.1016/s0934-8840(11)80867-4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rosa P. A., Hogan D., Schwan T. G. Polymerase chain reaction analyses identify two distinct classes of Borrelia burgdorferi. J Clin Microbiol. 1991 Mar;29(3):524–532. doi: 10.1128/jcm.29.3.524-532.1991. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Schaible U. E., Kramer M. D., Eichmann K., Modolell M., Museteanu C., Simon M. M. Monoclonal antibodies specific for the outer surface protein A (OspA) of Borrelia burgdorferi prevent Lyme borreliosis in severe combined immunodeficiency (scid) mice. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1990 May;87(10):3768–3772. doi: 10.1073/pnas.87.10.3768. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Schmid G. P. The global distribution of Lyme disease. Rev Infect Dis. 1985 Jan-Feb;7(1):41–50. doi: 10.1093/clinids/7.1.41. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Stanek G., Jurkowitsch B., Köchl C., Burger I., Khanakha G. Reactivity of European and American isolates of Borrelia burgdorferi with different monoclonal antibodies by means of a microimmunoblot technique. Zentralbl Bakteriol. 1990 Apr;272(4):426–436. doi: 10.1016/s0934-8840(11)80043-5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Steere A. C. Lyme disease. N Engl J Med. 1989 Aug 31;321(9):586–596. doi: 10.1056/NEJM198908313210906. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Stålhammar-Carlemalm M., Jenny E., Gern L., Aeschlimann A., Meyer J. Plasmid analysis and restriction fragment length polymorphisms of chromosomal DNA allow a distinction between Borrelia burgdorferi strains. Zentralbl Bakteriol. 1990 Oct;274(1):28–39. doi: 10.1016/s0934-8840(11)80972-2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Szczepanski A., Benach J. L. Lyme borreliosis: host responses to Borrelia burgdorferi. Microbiol Rev. 1991 Mar;55(1):21–34. doi: 10.1128/mr.55.1.21-34.1991. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sădziene A., Rosa P. A., Thompson P. A., Hogan D. M., Barbour A. G. Antibody-resistant mutants of Borrelia burgdorferi: in vitro selection and characterization. J Exp Med. 1992 Sep 1;176(3):799–809. doi: 10.1084/jem.176.3.799. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Temin H. M. Mechanisms of cell killing/cytopathic effects by nonhuman retroviruses. Rev Infect Dis. 1988 Mar-Apr;10(2):399–405. doi: 10.1093/clinids/10.2.399. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Thomas D. D., Comstock L. E. Interaction of Lyme disease spirochetes with cultured eucaryotic cells. Infect Immun. 1989 Apr;57(4):1324–1326. doi: 10.1128/iai.57.4.1324-1326.1989. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wallich R., Schaible U. E., Simon M. M., Heiberger A., Kramer M. D. Cloning and sequencing of the gene encoding the outer surface protein A (OspA) of a European Borrelia burgdorferi isolate. Nucleic Acids Res. 1989 Nov 11;17(21):8864–8864. doi: 10.1093/nar/17.21.8864. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Weber K., Schierz G., Wilske B., Preac-Mursic V. Zur Klinik und Atiologie der Acrodermatitis chronica atrophicans. Hautarzt. 1984 Nov;35(11):571–577. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wilske B., Anderson J. F., Baranton G., Barbour A. G., Hovind-Hougen K., Johnson R. C., Preac-Mursic V. Taxonomy of Borrelia spp. Scand J Infect Dis Suppl. 1991;77:108–129. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wilske B., Luft B., Schubach W. H., Zumstein G., Jauris S., Preac-Mursic V., Kramer M. D. Molecular analysis of the outer surface protein A (OspA) of Borrelia burgdorferi for conserved and variable antibody binding domains. Med Microbiol Immunol. 1992;181(4):191–207. doi: 10.1007/BF00215765. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wilske B., Preac-Mursic V., Schierz G. Antigenic heterogeneity of European Borrelia burgdorferi strains isolated from patients and ticks. Lancet. 1985 May 11;1(8437):1099–1099. doi: 10.1016/s0140-6736(85)92396-7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wilske B., Preac-Mursic V., Schierz G., Busch K. V. Immunochemical and immunological analysis of European Borrelia burgdorferi strains. Zentralbl Bakteriol Mikrobiol Hyg A. 1986 Dec;263(1-2):92–102. doi: 10.1016/s0176-6724(86)80108-0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wilske B., Preac-Mursic V., Schierz G., Gueye W., Herzer P., Weber K. Immunochemische Analyse der Immunantwort bei Spätmanifestationen der Lyme Borreliose. Zentralbl Bakteriol Mikrobiol Hyg A. 1988 Mar;267(4):549–558. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wilske B., Preac-Mursic V., Schierz G., Kühbeck R., Barbour A. G., Kramer M. Antigenic variability of Borrelia burgdorferi. Ann N Y Acad Sci. 1988;539:126–143. doi: 10.1111/j.1749-6632.1988.tb31846.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Zumstein G., Fuchs R., Hofmann A., Preac-Mursic V., Soutschek E., Wilske B. Genetic polymorphism of the gene encoding the outer surface protein A (OspA) of Borrelia burgdorferi. Med Microbiol Immunol. 1992;181(2):57–70. doi: 10.1007/BF00189424. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]






