Abstract
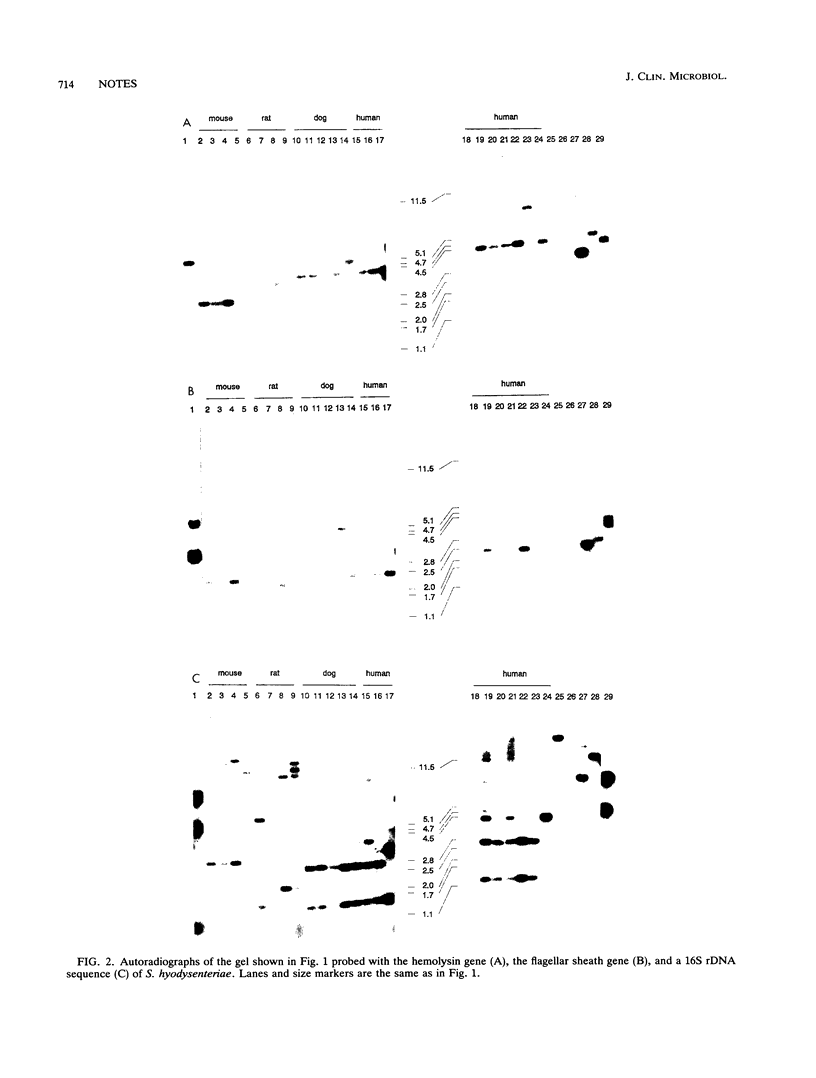
The chromosomal DNA of spirochetes isolated from human, swine, dog, mouse, rat, and chicken intestine or feces was subjected to restriction enzyme analysis and hybridization with three different DNA probes, derived from a flagellin gene, a hemolysin gene, and the 16S rDNA sequence of the pathogenic swine intestinal spirochete Serpulina hyodysenteriae. This genetic analysis showed that intestinal spirochetes represent a heterogeneous but related population of bacteria. In general, unique genotypes were distinguished among isolates from the same host species; they were not present among isolates from other host species. This suggests the host specificity of some strains. An exception to this are isolates from humans and dogs suffering from gastrointestinal disorders; these isolates showed highly similar or even identical genotypes. None of them resembled any of the genotypes of isolates found in other host species without apparent disease.
Full text
PDF




Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Achacha M., Messier S. Identification of Treponema hyodysenteriae and Treponema innocens using two four-hour identification systems. J Vet Diagn Invest. 1991 Jul;3(3):211–214. doi: 10.1177/104063879100300304. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Andersen J. K., Saunders N. A. Epidemiological typing of Yersinia enterocolitica by analysis of restriction fragment length polymorphisms with a cloned ribosomal RNA gene. J Med Microbiol. 1990 Jul;32(3):179–187. doi: 10.1099/00222615-32-3-179. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Baum D. H., Joens L. A. Serotypes of beta-hemolytic Treponema hyodysenteriae. Infect Immun. 1979 Sep;25(3):792–796. doi: 10.1128/iai.25.3.792-796.1979. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Blaha T. Beitrag zur Epizootiologie der Schweinedysenterie--die Ratte als das mögliche Erregerreservoir. Zentralbl Veterinarmed B. 1983 Mar;30(2):141–144. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bélanger M., Jacques M. Evaluation of the An-Ident system and an indole spot test for the rapid differentiation of porcine treponemes. J Clin Microbiol. 1991 Aug;29(8):1727–1729. doi: 10.1128/jcm.29.8.1727-1729.1991. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Coene M., Agliano A. M., Paques A. T., Cattani P., Dettori G., Sanna A., Cocito C. Comparative analysis of the genomes of intestinal spirochetes of human and animal origin. Infect Immun. 1989 Jan;57(1):138–145. doi: 10.1128/iai.57.1.138-145.1989. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Combs B. G., Hampson D. J., Harders S. J. Typing of Australian isolates of Treponema hyodysenteriae by serology and by DNA restriction endonuclease analysis. Vet Microbiol. 1992 Jun 1;31(2-3):273–285. doi: 10.1016/0378-1135(92)90085-8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Combs B., Hampson D. J., Mhoma J. R., Buddle J. R. Typing of Treponema hyodysenteriae by restriction endonuclease analysis. Vet Microbiol. 1989 Apr;19(4):351–359. doi: 10.1016/0378-1135(89)90100-4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- De Buyser M. L., Morvan A., Grimont F., el Solh N. Characterization of Staphylococcus species by ribosomal RNA gene restriction patterns. J Gen Microbiol. 1989 Apr;135(4):989–999. doi: 10.1099/00221287-135-4-989. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Dettori G., Burioni R., Grillo R., Cattani P. Molecular cloning and characterization of DNA from human intestinal spirochetes. Eur J Epidemiol. 1992 Mar;8(2):198–205. doi: 10.1007/BF00144800. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Graves L. M., Swaminathan B., Reeves M. W., Wenger J. Ribosomal DNA fingerprinting of Listeria monocytogenes using a digoxigenin-labeled DNA probe. Eur J Epidemiol. 1991 Jan;7(1):77–82. doi: 10.1007/BF00221345. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Grimont F., Grimont P. A. Ribosomal ribonucleic acid gene restriction patterns as potential taxonomic tools. Ann Inst Pasteur Microbiol. 1986 Sep-Oct;137B(2):165–175. doi: 10.1016/s0769-2609(86)80105-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hampson D. J., Mhoma J. R., Combs B., Buddle J. R. Proposed revisions to the serological typing system for Treponema hyodysenteriae. Epidemiol Infect. 1989 Feb;102(1):75–84. doi: 10.1017/s0950268800029708. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Harris D. L., Glock R. D., Christensen C. R., Kinyon J. M. Inoculation of pigs with Treponema hyodysenteriae (new species) and reproduction f the disease. Vet Med Small Anim Clin. 1972 Jan;67(1):61–64. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Harris D. L., Kinyon J. M. Significance of anaerobic spirochetes in the intestines of animals. Am J Clin Nutr. 1974 Nov;27(11):1297–1304. doi: 10.1093/ajcn/27.11.1297. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hovind-Hougen K., Birch-Andersen A., Henrik-Nielsen R., Orholm M., Pedersen J. O., Teglbjaerg P. S., Thaysen E. H. Intestinal spirochetosis: morphological characterization and cultivation of the spirochete Brachyspira aalborgi gen. nov., sp. nov. J Clin Microbiol. 1982 Dec;16(6):1127–1136. doi: 10.1128/jcm.16.6.1127-1136.1982. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hunter D., Wood T. An evaluation of the API ZYM system as a means of classifying spirochaetes associated with swine dysentery. Vet Rec. 1979 Apr 28;104(17):383–384. doi: 10.1136/vr.104.17.383. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Joens L. A., Kinyon J. M. Isolation of Treponema hyodysenteriae from wild rodents. J Clin Microbiol. 1982 Jun;15(6):994–997. doi: 10.1128/jcm.15.6.994-997.1982. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Johnson R. C., Hyde F. W., Rumpel C. M. Taxonomy of the Lyme disease spirochetes. Yale J Biol Med. 1984 Jul-Aug;57(4):529–537. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Koopman M. B., de Leeuw O. S., van der Zeijst B. M., Kusters J. G. Cloning and DNA sequence analysis of a Serpulina (Treponema) hyodysenteriae gene encoding a periplasmic flagellar sheath protein. Infect Immun. 1992 Jul;60(7):2920–2925. doi: 10.1128/iai.60.7.2920-2925.1992. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Käsbohrer A., Gelderblom H. R., Arasteh K., Heise W., Grosse G., L'age M., Schönberg A., Koch M. A., Pauli G. Intestinale Spirochätose bei HIV-Infektion. Vorkommen, Isolierung und Morphologie der Spirochäten. Dtsch Med Wochenschr. 1990 Oct 5;115(40):1499–1506. doi: 10.1055/s-2008-1065183. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lemcke R. M., Burrows M. R. A disc growth-inhibition test for differentiating Treponema hyodysenteriae from other intestinal spirochaetes. Vet Rec. 1979 Jun 16;104(24):548–551. doi: 10.1136/vr.104.24.548. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lymbery A. J., Hampson D. J., Hopkins R. M., Combs B., Mhoma J. R. Multilocus enzyme electrophoresis for identification and typing of Treponema hyodysenteriae and related spirochaetes. Vet Microbiol. 1990 Mar;22(1):89–99. doi: 10.1016/0378-1135(90)90127-h. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mapother M. E., Joens L. A. New serotypes of Treponema hyodysenteriae. J Clin Microbiol. 1985 Aug;22(2):161–164. doi: 10.1128/jcm.22.2.161-164.1985. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Meier C., Srisopar B., Amtsberg G. Untersuchungen zum Vorkommen von Treponemen bei Hunden mit Darmerkrankungen. Berl Munch Tierarztl Wochenschr. 1982 May 15;95(10):185–188. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Moureau P., Derclaye I., Gregoire D., Janssen M., Cornelis G. R. Campylobacter species identification based on polymorphism of DNA encoding rRNA. J Clin Microbiol. 1989 Jul;27(7):1514–1517. doi: 10.1128/jcm.27.7.1514-1517.1989. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Muir S., Koopman M. B., Libby S. J., Joens L. A., Heffron F., Kusters J. G. Cloning and expression of a Serpula (Treponema) hyodysenteriae hemolysin gene. Infect Immun. 1992 Feb;60(2):529–535. doi: 10.1128/iai.60.2.529-535.1992. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Paster B. J., Dewhirst F. E., Weisburg W. G., Tordoff L. A., Fraser G. J., Hespell R. B., Stanton T. B., Zablen L., Mandelco L., Woese C. R. Phylogenetic analysis of the spirochetes. J Bacteriol. 1991 Oct;173(19):6101–6109. doi: 10.1128/jb.173.19.6101-6109.1991. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Schönberg A., Camey C., Kahl O., Wilske B., Preac-Mursic V., Hovind-Hougen K. First isolation of Borrelia burgdorferi, the agent of Lyme borreliosis, from Ixodes ricinus (Acari: Ixodidae) in Berlin (West). Zentralbl Bakteriol Mikrobiol Hyg A. 1988 Jun;268(4):487–494. doi: 10.1016/s0176-6724(88)80128-7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Songer J. G., Glock R. D., Schwartz K. J., Harris D. L. Isolation of Treponema hyodysenteriae from sources other than swine. J Am Vet Med Assoc. 1978 Feb 15;172(4):464–466. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Stanton T. B. Proposal to change the genus designation Serpula to Serpulina gen. nov. containing the species Serpulina hyodysenteriae comb. nov. and Serpulina innocens comb. nov. Int J Syst Bacteriol. 1992 Jan;42(1):189–190. doi: 10.1099/00207713-42-1-189. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Taylor D. J., Alexander T. J. The production of dysentery in swine by feeding cultures containing a spirochaete. Br Vet J. 1971 Nov;127(11):58–61. doi: 10.1016/s0007-1935(17)37282-2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Turek J. J., Meyer R. C. Studies on a canine intestinal spirochete. I. Its isolation, cultivation and ultrastructure. Can J Comp Med. 1977 Jul;41(3):332–337. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Weisburg W. G., Barns S. M., Pelletier D. A., Lane D. J. 16S ribosomal DNA amplification for phylogenetic study. J Bacteriol. 1991 Jan;173(2):697–703. doi: 10.1128/jb.173.2.697-703.1991. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- de Wergifosse P., Coene M. M. Comparison of the genomes of pathogenic treponemes of human and animal origin. Infect Immun. 1989 May;57(5):1629–1631. doi: 10.1128/iai.57.5.1629-1631.1989. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- ter Huurne A. A., van Houten M., Koopman M. B., van der Zeijst B. A., Gaastra W. Characterization of Dutch porcine Serpulina (Treponema) isolates by restriction endonuclease analysis and DNA hybridization. J Gen Microbiol. 1992 Sep;138(9):1929–1934. doi: 10.1099/00221287-138-9-1929. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- ter Huurne A. A., van Houten M., Muir S., Kusters J. G., van der Zeijst B. A., Gaastra W. Inactivation of a Serpula (Treponema) hyodysenteriae hemolysin gene by homologous recombination: importance of this hemolysin in pathogenesis in mice. FEMS Microbiol Lett. 1992 Apr 1;71(1):109–113. doi: 10.1016/0378-1097(92)90550-8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]