Abstract
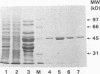
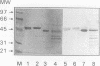
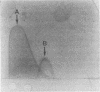
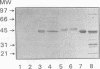
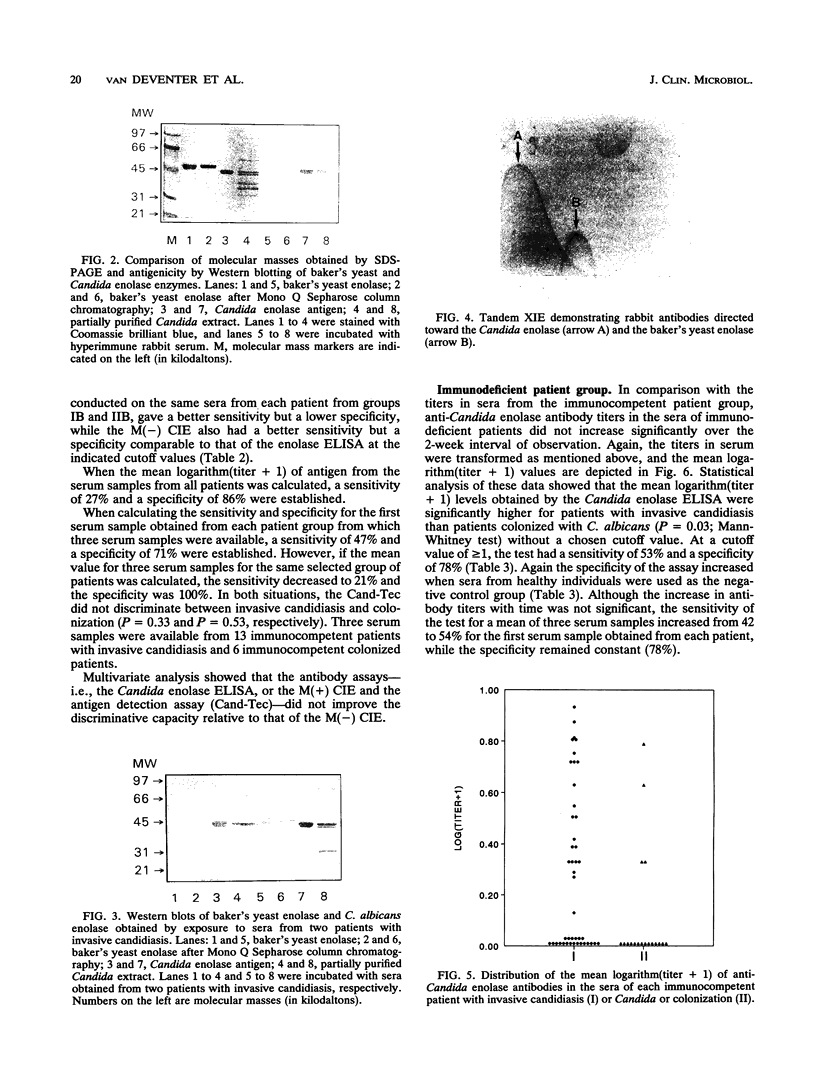
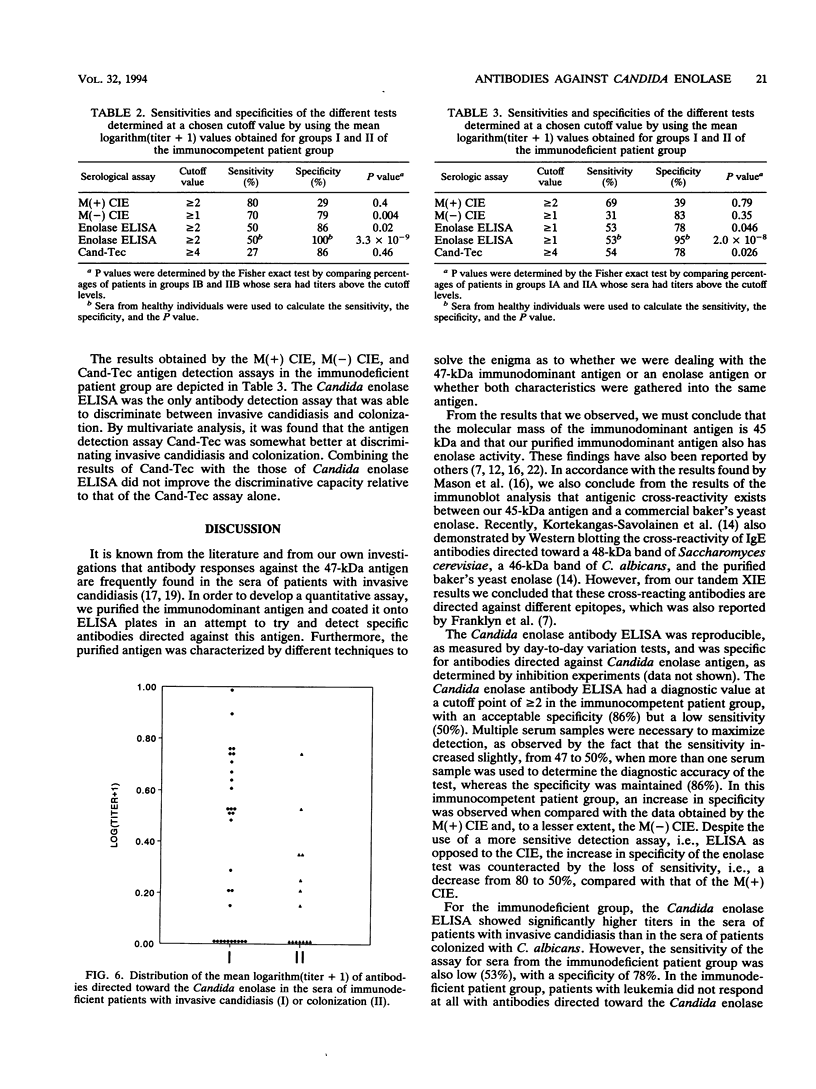
An immunodominant antigen with enolase enzyme activity was purified and used for the development of an assay to detect antibodies directed against this antigen in sera from patients with either invasive candidiasis or Candida colonization. The Au enzyme-linked immunosorbent assay established with the Candida enolase antigen was able to discriminate significantly between invasive candidiasis and colonization in both immunocompetent and immunodeficient groups of patients. The test had a sensitivity of 50% and a specificity of 86% in the immunocompetent patient group. In the immunodeficient patient group, a sensitivity of 53% and a specificity of 78% were established. Antibody levels determined by a counterimmunoelectrophoresis assay with the same set of sera resulted in a better sensitivity for sera from the immunocompetent patient group but a lower specificity, i.e., 80 and 29%, respectively. The counterimmunoelectrophoresis assay of sera from the immunodeficient patient group was not able to discriminate significantly between invasive candidiasis and colonization. With the use of more serum from each patient, the sensitivity of the antibody detection assays increased, while the specificity was maintained. The increase, however, was not statistically significant. Combining the results of the antibody assays with antigen titers obtained by the Cand-Tec assay did not improve the predictive value with respect to invasive candidiasis, as determined by multivariance regression analysis. Furthermore, it was demonstrated by performance of Western blots (immunoblots) that sera from patients as well as a rabbit antiserum cross-reacted with the Candida enolase and baker's yeast enolase enzyme. However, by tandem crossed immunoelectrophoresis it was demonstrated that the antibodies were directed toward different epitopes of the antigen.
Full text
PDF




Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Axelsen N. H., Kirkpatrick C. H., Buckley R. H. Precipitins to Candida albicans in chronic mucocutaneous candidiasis studied by crossed immunoelectrophoresis with intermediate gel. Correlation with clinical and immunological findings. Clin Exp Immunol. 1974 Jul;17(3):385–394. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bailey J. W., Sada E., Brass C., Bennett J. E. Diagnosis of systemic candidiasis by latex agglutination for serum antigen. J Clin Microbiol. 1985 May;21(5):749–752. doi: 10.1128/jcm.21.5.749-752.1985. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bodey G. P., Anaissie E. J. Chronic systemic candidiasis. Eur J Clin Microbiol Infect Dis. 1989 Oct;8(10):855–857. doi: 10.1007/BF01963770. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Burnie J. P., Williams J. D. Evaluation of the Ramco latex agglutination test in the early diagnosis of systemic candidiasis. Eur J Clin Microbiol. 1985 Apr;4(2):98–101. doi: 10.1007/BF02013571. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Eisinger M., Lee J. S., Hefton J. M., Darzynkiewicz Z., Chiao J. W., de Harven E. Human epidermal cell cultures: growth and differentiation in the absence of differentiation in the absence of dermal components or medium supplements. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1979 Oct;76(10):5340–5344. doi: 10.1073/pnas.76.10.5340. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ellsworth J. H., Reiss E., Bradley R. L., Chmel H., Armstrong D. Comparative serological and cutaneous reactivity of candidal cytoplasmic proteins and mannan separated by affinity for concanavalin A. J Clin Microbiol. 1977 Jan;5(1):91–99. doi: 10.1128/jcm.5.1.91-99.1977. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Faux J. A., Agbarakwe A. E., Misbah S. A., Chapel H. M. A comparison of specific IgG antibody levels to the cell wall mannan of Candida albicans in normal individuals and in patients with primary antibody deficiency. J Immunol Methods. 1992 Aug 30;153(1-2):167–172. doi: 10.1016/0022-1759(92)90319-o. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Franklyn K. M., Warmington J. R., Ott A. K., Ashman R. B. An immunodominant antigen of Candida albicans shows homology to the enzyme enolase. Immunol Cell Biol. 1990 Jun;68(Pt 3):173–178. doi: 10.1038/icb.1990.24. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Fung J. C., Donta S. T., Tilton R. C. Candida detection system (CAND-TEC) to differentiate between Candida albicans colonization and disease. J Clin Microbiol. 1986 Oct;24(4):542–547. doi: 10.1128/jcm.24.4.542-547.1986. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Greenfield R. A., Bussey M. J., Stephens J. L., Jones J. M. Serial enzyme-linked immunosorbent assays for antibody to Candida antigens during induction chemotherapy for acute leukemia. J Infect Dis. 1983 Aug;148(2):275–283. doi: 10.1093/infdis/148.2.275. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Herent P., Stynen D., Hernando F., Fruit J., Poulain D. Retrospective evaluation of two latex agglutination tests for detection of circulating antigens during invasive candidosis. J Clin Microbiol. 1992 Aug;30(8):2158–2164. doi: 10.1128/jcm.30.8.2158-2164.1992. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Jones J. M. Laboratory diagnosis of invasive candidiasis. Clin Microbiol Rev. 1990 Jan;3(1):32–45. doi: 10.1128/cmr.3.1.32. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Karwowska W., Lisowska-Grospierre B. Diagnostic significance of the human antibody response to a major cytoplasmic antigen of C. albicans. Immunol Lett. 1984;8(3):127–129. doi: 10.1016/0165-2478(84)90064-6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Komshian S. V., Uwaydah A. K., Sobel J. D., Crane L. R. Fungemia caused by Candida species and Torulopsis glabrata in the hospitalized patient: frequency, characteristics, and evaluation of factors influencing outcome. Rev Infect Dis. 1989 May-Jun;11(3):379–390. doi: 10.1093/clinids/11.3.379. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kortekangas-Savolainen O., Kalimo K., Lammintausta K., Savolainen J. IgE-binding components of baker's yeast (Saccharomyces cerevisiae) recognized by immunoblotting analysis. Simultaneous IgE binding to mannan and 46-48 kD allergens of Saccharomyces cerevisiae and Candida albicans. Clin Exp Allergy. 1993 Mar;23(3):179–184. doi: 10.1111/j.1365-2222.1993.tb00879.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Laemmli U. K. Cleavage of structural proteins during the assembly of the head of bacteriophage T4. Nature. 1970 Aug 15;227(5259):680–685. doi: 10.1038/227680a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mason A. B., Brandt M. E., Buckley H. R. Enolase activity associated with a C. albicans cytoplasmic antigen. Yeast. 1989 Apr;5(Spec No):S231–S239. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Matthews R. C., Burnie J. P., Tabaqchali S. Immunoblot analysis of the serological response in systemic candidosis. Lancet. 1984 Dec 22;2(8417-8418):1415–1418. doi: 10.1016/s0140-6736(84)91618-0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- McAlister L., Holland M. J. Targeted deletion of a yeast enolase structural gene. Identification and isolation of yeast enolase isozymes. J Biol Chem. 1982 Jun 25;257(12):7181–7188. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Porsius J. C., van Vliet H. J., van Zeijl J. H., Goessens W. H., Michel M. F. Detection of an antibody response in immunocompetent patients with systemic candidiasis or Candida albicans colonisation. Eur J Clin Microbiol Infect Dis. 1990 May;9(5):352–355. doi: 10.1007/BF01973744. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Walsh T. J., Hathorn J. W., Sobel J. D., Merz W. G., Sanchez V., Maret S. M., Buckley H. R., Pfaller M. A., Schaufele R., Sliva C. Detection of circulating candida enolase by immunoassay in patients with cancer and invasive candidiasis. N Engl J Med. 1991 Apr 11;324(15):1026–1031. doi: 10.1056/NEJM199104113241504. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Zöller L., Krämer I., Kappe R., Sonntag H. G. Enzyme immunoassays for invasive Candida infections: reactivity of somatic antigens of Candida albicans. J Clin Microbiol. 1991 Sep;29(9):1860–1867. doi: 10.1128/jcm.29.9.1860-1867.1991. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- van Deventer A. J., van Vliet H. J., Voogd L., Hop W. C., Goessens W. H. Increased specificity of antibody detection in surgical patients with invasive candidiasis with cytoplasmic antigens depleted of mannan residues. J Clin Microbiol. 1993 Apr;31(4):994–997. doi: 10.1128/jcm.31.4.994-997.1993. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]