Abstract
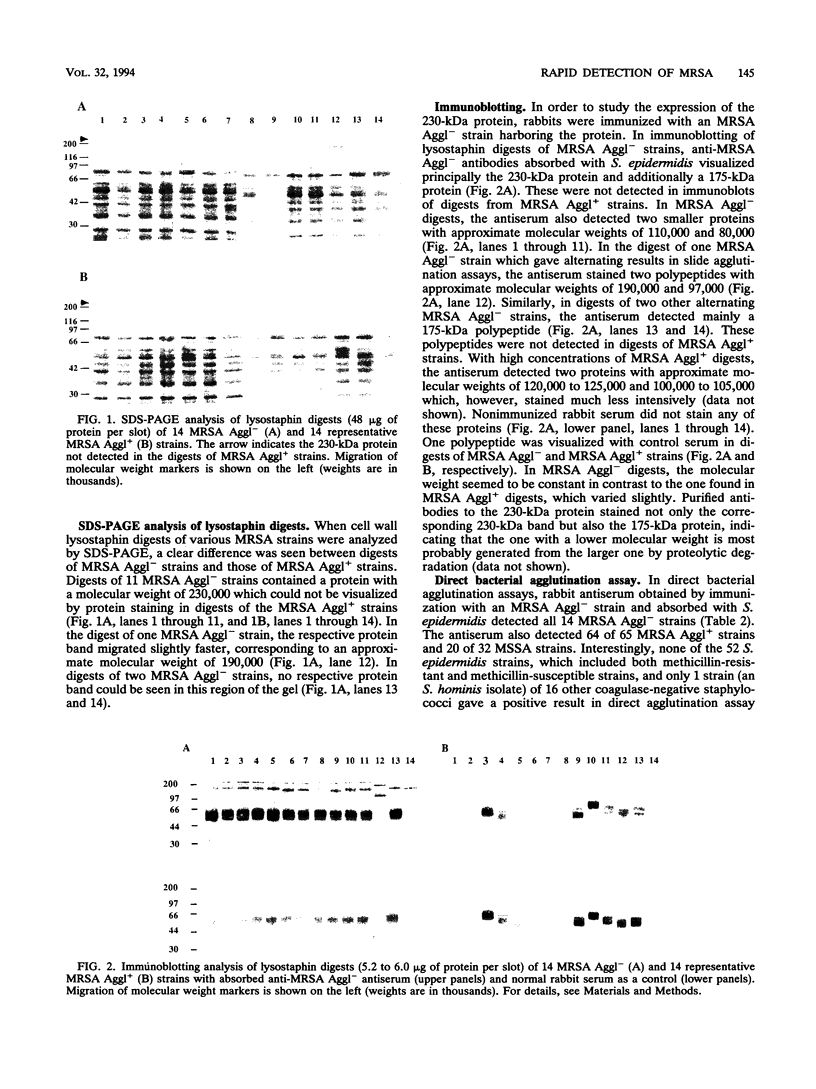
Seventy-nine methicillin-resistant Staphylococcus aureus (MRSA) strains, isolated during 1980 to 1990, were classified as MRSA Aggl- (14 strains) and MRSA Aggl+ (65 strains) strains on the basis of test results in slide agglutination assays designed to detect fibrinogen-binding protein (clumping factor) and protein A on the staphylococcal surface. Sodium dodecyl sulfate-polyacrylamide gel electrophoresis analysis revealed that lysostaphin digests of MRSA Aggl- strains contained a high-molecular-weight protein which was not detected in digests of MRSA Aggl+ strains. Immunization of rabbits with an MRSA Aggl- strain produced an antiserum which agglutinated all MRSA Aggl- strains and also 64 of 65 MRSA Aggl+ strains. Only 1 of 68 coagulase-negative staphylococci showed agglutination in this assay. The anti-MRSA Aggl- antiserum reacted mainly with a 230-kDa staphylococcal surface protein but also with a 175-kDa protein, probably formed by proteolysis of the former and a few slightly smaller proteins. These could not be immunologically detected in lysostaphin digests of MRSA Aggl+ strains. Purified antibodies reacting with the 230-kDa protein agglutinated all MRSA Aggl- strains, indicating that the protein is located on the surfaces of staphylococci. The results suggest a tentative role for the 230-kDa protein or its fragments as a novel target to develop more efficient rapid identification methods for S. aureus, including MRSA.
Full text
PDF



Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Aldridge K. E., Kogos C., Sanders C. V., Marier R. L. Comparison of rapid identification assays for Staphylococcus aureus. J Clin Microbiol. 1984 May;19(5):703–704. doi: 10.1128/jcm.19.5.703-704.1984. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Baker J. S., Bormann M. A., Boudreau D. H. Evaluation of various rapid agglutination methods for the identification of Staphylococcus aureus. J Clin Microbiol. 1985 May;21(5):726–729. doi: 10.1128/jcm.21.5.726-729.1985. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Berger-Bächi B., Barberis-Maino L., Strässle A., Kayser F. H. FemA, a host-mediated factor essential for methicillin resistance in Staphylococcus aureus: molecular cloning and characterization. Mol Gen Genet. 1989 Oct;219(1-2):263–269. doi: 10.1007/BF00261186. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Berke A., Tilton R. C. Evaluation of rapid coagulase methods for the identification of Staphylococcus aureus. J Clin Microbiol. 1986 May;23(5):916–919. doi: 10.1128/jcm.23.5.916-919.1986. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Brown W. J. Comparison of a yellow latex reagent with other agglutination methods for the identification of Staphylococcus aureus. J Clin Microbiol. 1986 Mar;23(3):640–642. doi: 10.1128/jcm.23.3.640-642.1986. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Eskola J., Käyhty H., Takala A. K., Peltola H., Rönnberg P. R., Kela E., Pekkanen E., McVerry P. H., Mäkelä P. H. A randomized, prospective field trial of a conjugate vaccine in the protection of infants and young children against invasive Haemophilus influenzae type b disease. N Engl J Med. 1990 Nov 15;323(20):1381–1387. doi: 10.1056/NEJM199011153232004. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Essers L., Radebold K. Rapid and reliable identification of Staphylococcus aureus by a latex agglutination test. J Clin Microbiol. 1980 Nov;12(5):641–643. doi: 10.1128/jcm.12.5.641-643.1980. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Fournier J. M., Bouvet A., Mathieu D., Nato F., Boutonnier A., Gerbal R., Brunengo P., Saulnier C., Sagot N., Slizewicz B. New latex reagent using monoclonal antibodies to capsular polysaccharide for reliable identification of both oxacillin-susceptible and oxacillin-resistant Staphylococcus aureus. J Clin Microbiol. 1993 May;31(5):1342–1344. doi: 10.1128/jcm.31.5.1342-1344.1993. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Guzmàn C. A., Guardati M. C., Fenoglio D., Coratza G., Pruzzo C., Satta G. Novel immunoenzymatic assay for identification of coagulase- and protein A-negative Staphylococcus aureus strains. J Clin Microbiol. 1992 May;30(5):1194–1197. doi: 10.1128/jcm.30.5.1194-1197.1992. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Holderbaum D., Spech R. A., Ehrhart L. A. Specific binding of collagen to Staphylococcus aureus. Coll Relat Res. 1985 Jun;5(3):261–271. doi: 10.1016/s0174-173x(85)80016-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kuusela P. Fibronectin binds to Staphylococcus aureus. Nature. 1978 Dec 14;276(5689):718–720. doi: 10.1038/276718a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- LOWRY O. H., ROSEBROUGH N. J., FARR A. L., RANDALL R. J. Protein measurement with the Folin phenol reagent. J Biol Chem. 1951 Nov;193(1):265–275. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Laemmli U. K. Cleavage of structural proteins during the assembly of the head of bacteriophage T4. Nature. 1970 Aug 15;227(5259):680–685. doi: 10.1038/227680a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lairscey R., Buck G. E. Performance of four slide agglutination methods for identification of Staphylococcus aureus when testing methicillin-resistant staphylococci. J Clin Microbiol. 1987 Jan;25(1):181–182. doi: 10.1128/jcm.25.1.181-182.1987. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lopes J. D., dos Reis M., Brentani R. R. Presence of laminin receptors in Staphylococcus aureus. Science. 1985 Jul 19;229(4710):275–277. doi: 10.1126/science.3160113. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Niskanen A., Korkeala H., Manninen M., Vuento M., Kuusela P. Evaluation of three slide agglutination tests for rapid identification of Staphylococcus aureus. Acta Vet Scand. 1991;32(4):543–549. doi: 10.1186/BF03546956. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Piper J., Hadfield T., McCleskey F., Evans M., Friedstrom S., Lauderdale P., Winn R. Efficacies of rapid agglutination tests for identification of methicillin-resistant staphylococcal strains as Staphylococcus aureus. J Clin Microbiol. 1988 Sep;26(9):1907–1909. doi: 10.1128/jcm.26.9.1907-1909.1988. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ruane P. J., Morgan M. A., Citron D. M., Mulligan M. E. Failure of rapid agglutination methods to detect oxacillin-resistant Staphylococcus aureus. J Clin Microbiol. 1986 Sep;24(3):490–492. doi: 10.1128/jcm.24.3.490-492.1986. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Speziale P., Raucci G., Visai L., Switalski L. M., Timpl R., Hök M. Binding of collagen to Staphylococcus aureus Cowan 1. J Bacteriol. 1986 Jul;167(1):77–81. doi: 10.1128/jb.167.1.77-81.1986. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Towbin H., Staehelin T., Gordon J. Electrophoretic transfer of proteins from polyacrylamide gels to nitrocellulose sheets: procedure and some applications. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1979 Sep;76(9):4350–4354. doi: 10.1073/pnas.76.9.4350. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ubukata K., Yamashita N., Konno M. Occurrence of a beta-lactam-inducible penicillin-binding protein in methicillin-resistant staphylococci. Antimicrob Agents Chemother. 1985 May;27(5):851–857. doi: 10.1128/aac.27.5.851. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wanger A. R., Morris S. L., Ericsson C., Singh K. V., LaRocco M. T. Latex agglutination-negative methicillin-resistant Staphylococcus aureus recovered from neonates: epidemiologic features and comparison of typing methods. J Clin Microbiol. 1992 Oct;30(10):2583–2588. doi: 10.1128/jcm.30.10.2583-2588.1992. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Woolfrey B. F., Lally R. T., Ederer M. N. An evaluation of three rapid coagglutination tests: Sero-STAT, Accu-Staph, and Staphyloslide, for differentiating Staphylococcus aureus from other species of staphylococci. Am J Clin Pathol. 1984 Mar;81(3):345–348. doi: 10.1093/ajcp/81.3.345. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]




