Abstract
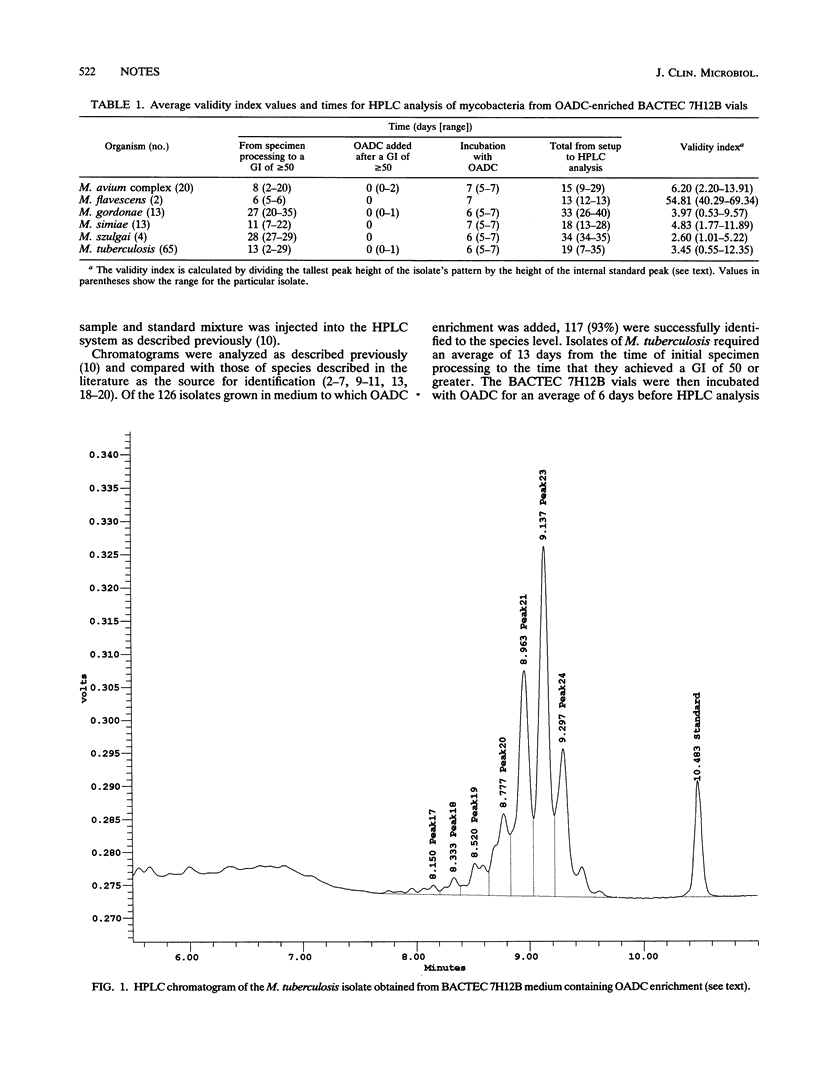
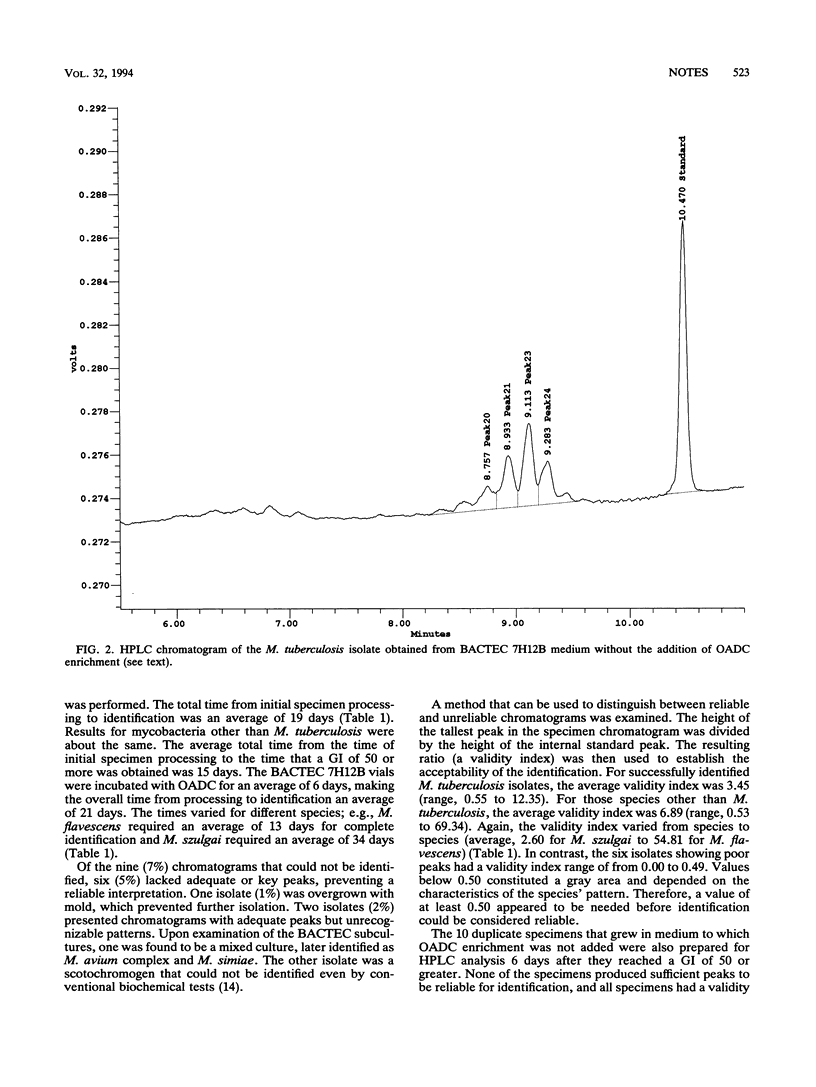
Primary cultures of mycobacteria grown in BACTEC 7H12B medium (Becton Dickinson and Co., Paramus, N.J.), with and without the addition of oleic acid-albumin-dextrose-catalase (OADC) enrichment (Becton Dickinson and Co., Cockeysville, Md.), were analyzed for their mycolic acid patterns by high-performance liquid chromatography. Of the 126 isolates grown in medium to which OADC was added, 117 (93%) were successfully identified to the species level. The time to identification of Mycobacterium tuberculosis (n = 65) averaged 19 days, and the average time was 21 days for nontuberculosis mycobacteria (n = 52) from initial specimen processing. None of the 10 isolates cultured without OADC were identified. The mycolic acid patterns were considered reliable for identification if the height of the tallest peak in the chromatogram was at least 50% of the internal standard peak height.
Full text
PDF

Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Body B. A., Warren N. G., Spicer A., Henderson D., Chery M. Use of Gen-Probe and Bactec for rapid isolation and identification of mycobacteria. Correlation of probe results with growth index. Am J Clin Pathol. 1990 Mar;93(3):415–420. doi: 10.1093/ajcp/93.3.415. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Butler W. R., Ahearn D. G., Kilburn J. O. High-performance liquid chromatography of mycolic acids as a tool in the identification of Corynebacterium, Nocardia, Rhodococcus, and Mycobacterium species. J Clin Microbiol. 1986 Jan;23(1):182–185. doi: 10.1128/jcm.23.1.182-185.1986. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Butler W. R., Jost K. C., Jr, Kilburn J. O. Identification of mycobacteria by high-performance liquid chromatography. J Clin Microbiol. 1991 Nov;29(11):2468–2472. doi: 10.1128/jcm.29.11.2468-2472.1991. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Butler W. R., Kilburn J. O. High-performance liquid chromatography patterns of mycolic acids as criteria for identification of Mycobacterium chelonae, Mycobacterium fortuitum, and Mycobacterium smegmatis. J Clin Microbiol. 1990 Sep;28(9):2094–2098. doi: 10.1128/jcm.28.9.2094-2098.1990. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Butler W. R., Kilburn J. O. Identification of major slowly growing pathogenic mycobacteria and Mycobacterium gordonae by high-performance liquid chromatography of their mycolic acids. J Clin Microbiol. 1988 Jan;26(1):50–53. doi: 10.1128/jcm.26.1.50-53.1988. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Butler W. R., Thibert L., Kilburn J. O. Identification of Mycobacterium avium complex strains and some similar species by high-performance liquid chromatography. J Clin Microbiol. 1992 Oct;30(10):2698–2704. doi: 10.1128/jcm.30.10.2698-2704.1992. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Butler W. R., Warren N. G., Kubica G. P., Kilburn J. O. Modified method for testing the quality of albumin-containing enrichments used in growth media for mycobacteria. J Clin Microbiol. 1990 May;28(5):1068–1070. doi: 10.1128/jcm.28.5.1068-1070.1990. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Cage G. D. High-performance liquid chromatography patterns of Mycobacterium gordonae mycolic acids. J Clin Microbiol. 1992 Sep;30(9):2402–2407. doi: 10.1128/jcm.30.9.2402-2407.1992. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Coyle M. B., Carlson L. C., Wallis C. K., Leonard R. B., Raisys V. A., Kilburn J. O., Samadpour M., Böttger E. C. Laboratory aspects of "Mycobacterium genavense," a proposed species isolated from AIDS patients. J Clin Microbiol. 1992 Dec;30(12):3206–3212. doi: 10.1128/jcm.30.12.3206-3212.1992. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ellner P. D., Kiehn T. E., Cammarata R., Hosmer M. Rapid detection and identification of pathogenic mycobacteria by combining radiometric and nucleic acid probe methods. J Clin Microbiol. 1988 Jul;26(7):1349–1352. doi: 10.1128/jcm.26.7.1349-1352.1988. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Guthertz L. S., Lim S. D., Jang Y., Duffey P. S. Curvilinear-gradient high-performance liquid chromatography for identification of mycobacteria. J Clin Microbiol. 1993 Jul;31(7):1876–1881. doi: 10.1128/jcm.31.7.1876-1881.1993. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ridderhof J. C., Wallace R. J., Jr, Kilburn J. O., Butler W. R., Warren N. G., Tsukamura M., Steele L. C., Wong E. S. Chronic tenosynovitis of the hand due to Mycobacterium nonchromogenicum: use of high-performance liquid chromatography for identification of isolates. Rev Infect Dis. 1991 Sep-Oct;13(5):857–864. doi: 10.1093/clinids/13.5.857. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Thibert L., Lapierre S. Routine application of high-performance liquid chromatography for identification of mycobacteria. J Clin Microbiol. 1993 Jul;31(7):1759–1763. doi: 10.1128/jcm.31.7.1759-1763.1993. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]


