Abstract
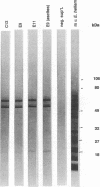
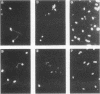
During a screening for monoclonal antibodies (MAbs) to the microsporidian Encephalitozoon hellem, three murine hybridoma cell lines producing strong enzyme-linked immunosorbent assay (ELISA) reactivities were cloned twice, were designated C12, E9, and E11, and were found to secrete MAbs to the immunoglobulin M isotype. On subsequent ELISAs, the three MAbs reacted most strongly to E. hellem, and they reacted somewhat less to Encephalitozoon cuniculi and least to Nosema corneum, two other microsporidian species. The MAbs produced values of absorbance against microsporidia that were at least three times greater than reactivities obtained with control hybridoma supernatants or with uninfected host cell proteins used as antigens. By Western blot immunodetection, the three MAbs detected three E. hellem antigens with relative molecular weights (M(r)s) of 62, 60, and 52 when assayed at the highest supernatant dilutions producing reactivity. At lower dilutions, the MAbs detected additional proteins with M(r)s of 55 and 53. By using indirect immunofluorescence antibody staining, the MAbs, as well as hyperimmune polyclonal murine antisera raised against E. cuniculi and E. hellem, were able to detect formalin-fixed, tissue culture-derived E. cuniculi and E. hellem and two other human microsporidia, Enterocytozoon bieneusi and Septata intestinalis, in formalin-fixed stool and urine, respectively. E. bieneusi, however, stained more intensely with the polyclonal antisera than with the MAbs. Neither the MAbs nor the hyperimmune murine polyclonal antibodies detected Cryptosporidium, Giardia, Trichomonas, or Isospora spp. At higher concentrations, the polyclonal antisera did stain N. corneum and yeast cells. The background staining could be absorbed with Candida albicans. These results demonstrate that polyclonal antisera to E. cuniculi and E. hellem, as well as MAbs raised against E. hellem, can be used for indirect immunofluorescence antibody staining to detect several species of microsporidia known to cause opportunistic infections in AIDS patients.
Full text
PDF



Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Blake M. S., Johnston K. H., Russell-Jones G. J., Gotschlich E. C. A rapid, sensitive method for detection of alkaline phosphatase-conjugated anti-antibody on Western blots. Anal Biochem. 1984 Jan;136(1):175–179. doi: 10.1016/0003-2697(84)90320-8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bryan R. T., Cali A., Owen R. L., Spencer H. C. Microsporidia: opportunistic pathogens in patients with AIDS. Prog Clin Parasitol. 1991;2:1–26. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Cali A., Kotler D. P., Orenstein J. M. Septata intestinalis N. G., N. Sp., an intestinal microsporidian associated with chronic diarrhea and dissemination in AIDS patients. J Eukaryot Microbiol. 1993 Jan-Feb;40(1):101–112. doi: 10.1111/j.1550-7408.1993.tb04889.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Cali A., Owen R. L. Intracellular development of Enterocytozoon, a unique microsporidian found in the intestine of AIDS patients. J Protozool. 1990 Mar-Apr;37(2):145–155. doi: 10.1111/j.1550-7408.1990.tb05885.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Canning E. U., Hollister W. S. Enterocytozoon bieneusi (Microspora): prevalence and pathogenicity in AIDS patients. Trans R Soc Trop Med Hyg. 1990 Mar-Apr;84(2):181–186. doi: 10.1016/0035-9203(90)90247-c. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Canning E. U., Hollister W. S. In vitro and in vivo investigations of human microsporidia. J Protozool. 1991 Nov-Dec;38(6):631–635. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Davis R. M., Font R. L., Keisler M. S., Shadduck J. A. Corneal microsporidiosis. A case report including ultrastructural observations. Ophthalmology. 1990 Jul;97(7):953–957. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Desportes I., Le Charpentier Y., Galian A., Bernard F., Cochand-Priollet B., Lavergne A., Ravisse P., Modigliani R. Occurrence of a new microsporidan: Enterocytozoon bieneusi n.g., n. sp., in the enterocytes of a human patient with AIDS. J Protozool. 1985 May;32(2):250–254. doi: 10.1111/j.1550-7408.1985.tb03046.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Didier E. S., Didier P. J., Friedberg D. N., Stenson S. M., Orenstein J. M., Yee R. W., Tio F. O., Davis R. M., Vossbrinck C., Millichamp N. Isolation and characterization of a new human microsporidian, Encephalitozoon hellem (n. sp.), from three AIDS patients with keratoconjunctivitis. J Infect Dis. 1991 Mar;163(3):617–621. doi: 10.1093/infdis/163.3.617. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Didier E. S., Shadduck J. A., Didier P. J., Millichamp N., Vossbrinck C. R. Studies on ocular microsporidia. J Protozool. 1991 Nov-Dec;38(6):635–638. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Didier P. J., Didier E. S., Orenstein J. M., Shadduck J. A. Fine structure of a new human microsporidian, Encephalitozoon hellem, in culture. J Protozool. 1991 Sep-Oct;38(5):502–507. doi: 10.1111/j.1550-7408.1991.tb04824.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Friedberg D. N., Stenson S. M., Orenstein J. M., Tierno P. M., Charles N. C. Microsporidial keratoconjunctivitis in acquired immunodeficiency syndrome. Arch Ophthalmol. 1990 Apr;108(4):504–508. doi: 10.1001/archopht.1990.01070060052047. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hollister W. S., Canning E. U. An enzyme-linked immunosorbent assay (ELISA) for detection of antibodies to Encephalitozoon cuniculi and its use in determination of infections in man. Parasitology. 1987 Apr;94(Pt 2):209–219. doi: 10.1017/s0031182000053890. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kotler D. P., Francisco A., Clayton F., Scholes J. V., Orenstein J. M. Small intestinal injury and parasitic diseases in AIDS. Ann Intern Med. 1990 Sep 15;113(6):444–449. doi: 10.7326/0003-4819-113-6-444. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Laemmli U. K. Cleavage of structural proteins during the assembly of the head of bacteriophage T4. Nature. 1970 Aug 15;227(5259):680–685. doi: 10.1038/227680a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Niederkorn J. Y., Shadduck J. A., Weidner E. Antigenic cross-reactivity among different microsporidan spores as determined by immunofluorescence. J Parasitol. 1980 Aug;66(4):675–677. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Orenstein J. M., Chiang J., Steinberg W., Smith P. D., Rotterdam H., Kotler D. P. Intestinal microsporidiosis as a cause of diarrhea in human immunodeficiency virus-infected patients: a report of 20 cases. Hum Pathol. 1990 May;21(5):475–481. doi: 10.1016/0046-8177(90)90003-n. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Orenstein J. M. Microsporidiosis in the acquired immunodeficiency syndrome. J Parasitol. 1991 Dec;77(6):843–864. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Orenstein J. M., Tenner M., Cali A., Kotler D. P. A microsporidian previously undescribed in humans, infecting enterocytes and macrophages, and associated with diarrhea in an acquired immunodeficiency syndrome patient. Hum Pathol. 1992 Jul;23(7):722–728. doi: 10.1016/0046-8177(92)90339-5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Orenstein J. M., Zierdt W., Zierdt C., Kotler D. P. Identification of spores of Enterocytozoon bieneusi in stool and duodenal fluid from AIDS patients. Lancet. 1990 Nov 3;336(8723):1127–1128. doi: 10.1016/0140-6736(90)92600-m. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Schwartz D. A., Bryan R. T., Hewan-Lowe K. O., Visvesvara G. S., Weber R., Cali A., Angritt P. Disseminated microsporidiosis (Encephalitozoon hellem) and acquired immunodeficiency syndrome. Autopsy evidence for respiratory acquisition. Arch Pathol Lab Med. 1992 Jun;116(6):660–668. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Schwartz D. A., Visvesvara G. S., Diesenhouse M. C., Weber R., Font R. L., Wilson L. A., Corrent G., Serdarevic O. N., Rosberger D. F., Keenen P. C. Pathologic features and immunofluorescent antibody demonstration of ocular microsporidiosis (Encephalitozoon hellem) in seven patients with acquired immunodeficiency syndrome. Am J Ophthalmol. 1993 Mar 15;115(3):285–292. doi: 10.1016/s0002-9394(14)73577-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Shadduck J. A., Greeley E. Microsporidia and human infections. Clin Microbiol Rev. 1989 Apr;2(2):158–165. doi: 10.1128/cmr.2.2.158. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Shadduck J. A. Human microsporidiosis and AIDS. Rev Infect Dis. 1989 Mar-Apr;11(2):203–207. doi: 10.1093/clinids/11.2.203. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Shadduck J. A., Meccoli R. A., Davis R., Font R. L. Isolation of a microsporidian from a human patient. J Infect Dis. 1990 Sep;162(3):773–776. doi: 10.1093/infdis/162.3.773. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Vossbrinck C. R., Baker M. D., Didier E. S., Debrunner-Vossbrinck B. A., Shadduck J. A. Ribosomal DNA sequences of Encephalitozoon hellem and Encephalitozoon cuniculi: species identification and phylogenetic construction. J Eukaryot Microbiol. 1993 May-Jun;40(3):354–362. doi: 10.1111/j.1550-7408.1993.tb04928.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Weber R., Bryan R. T., Owen R. L., Wilcox C. M., Gorelkin L., Visvesvara G. S. Improved light-microscopical detection of microsporidia spores in stool and duodenal aspirates. The Enteric Opportunistic Infections Working Group. N Engl J Med. 1992 Jan 16;326(3):161–166. doi: 10.1056/NEJM199201163260304. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Weiss L. M., Cali A., Levee E., LaPlace D., Tanowitz H., Simon D., Wittner M. Diagnosis of Encephalitozoon cuniculi infection by western blot and the use of cross-reactive antigens for the possible detection of microsporidiosis in humans. Am J Trop Med Hyg. 1992 Oct;47(4):456–462. doi: 10.4269/ajtmh.1992.47.456. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Zierdt C. H., Gill V. J., Zierdt W. S. Detection of microsporidian spores in clinical samples by indirect fluorescent-antibody assay using whole-cell antisera to Encephalitozoon cuniculi and Encephalitozoon hellem. J Clin Microbiol. 1993 Nov;31(11):3071–3074. doi: 10.1128/jcm.31.11.3071-3074.1993. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- van Gool T., Hollister W. S., Schattenkerk W. E., Van den Bergh Weerman M. A., Terpstra W. J., van Ketel R. J., Reiss P., Canning E. U. Diagnosis of Enterocytozoon bieneusi microsporidiosis in AIDS patients by recovery of spores from faeces. Lancet. 1990 Sep 15;336(8716):697–698. doi: 10.1016/0140-6736(90)92198-q. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- van Gool T., Snijders F., Reiss P., Eeftinck Schattenkerk J. K., van den Bergh Weerman M. A., Bartelsman J. F., Bruins J. J., Canning E. U., Dankert J. Diagnosis of intestinal and disseminated microsporidial infections in patients with HIV by a new rapid fluorescence technique. J Clin Pathol. 1993 Aug;46(8):694–699. doi: 10.1136/jcp.46.8.694. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]