Abstract
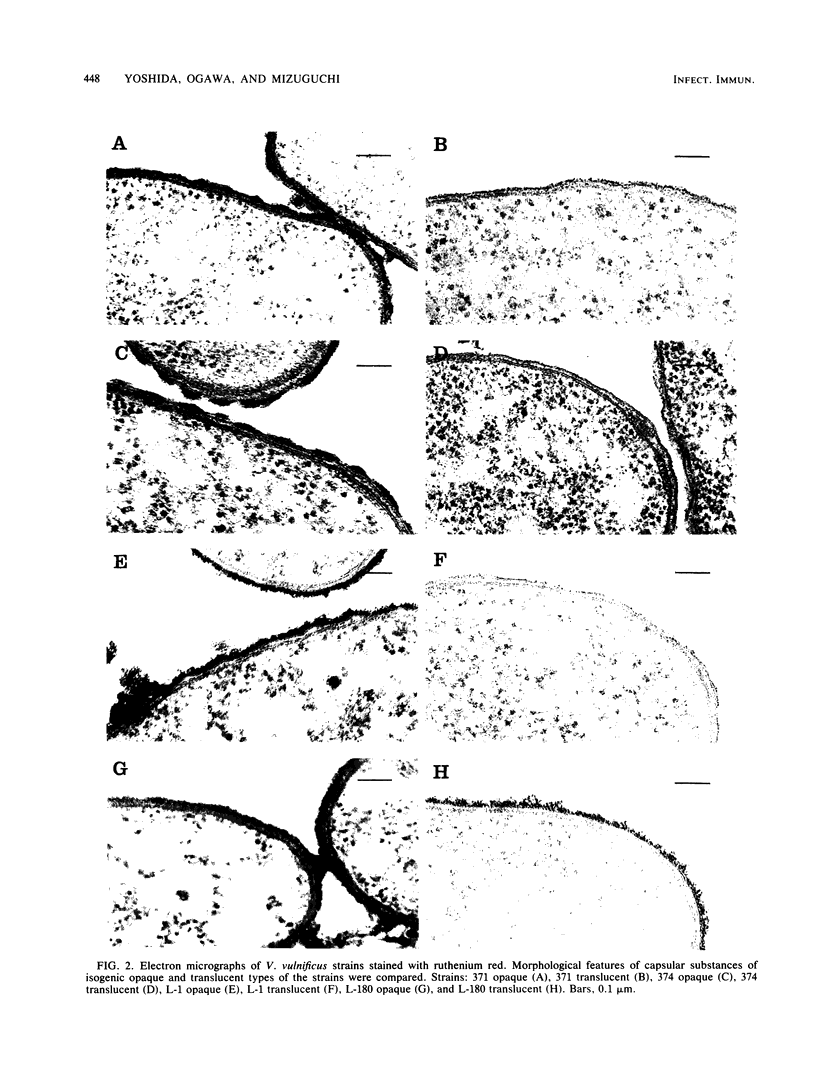
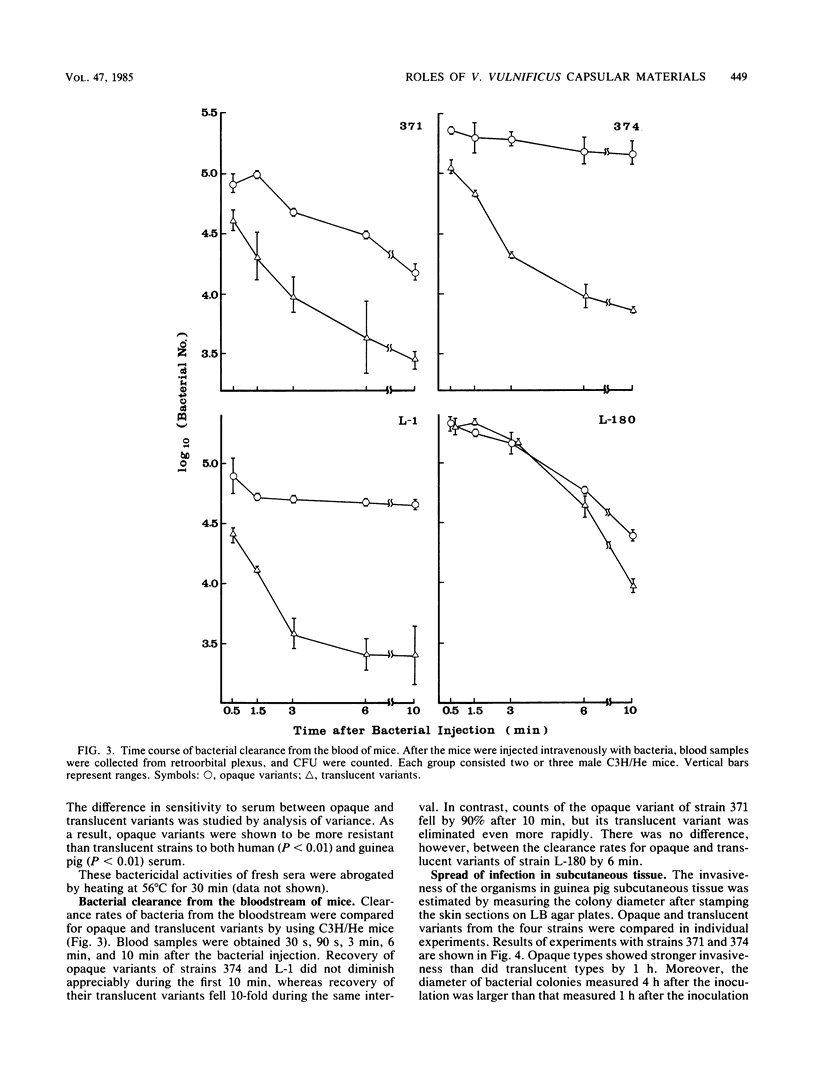
Colonies which varied in opacity were isolated from the four strains of Vibrio vulnificus. Opaque and translucent colonial types of the strains were distinguished from the corresponding parent strains. Variation in the opacity of colonies formed by each strain was accompanied by variation of capsular material formation, which was clarified by electron microscopy of the organisms stained with ruthenium red. The opaque-type colonies of the strains had capsular materials. On the other hand, three translucent-type colonies had no observable capsular materials, and one had incomplete capsular materials, in contrast to the corresponding opaque type. The corresponding opaque and translucent types of the strains were compared for points of virulence in mice and guinea pigs. By having capsular materials, the bacterial strains acquired resistance to serum bactericidal action, antiphagocytic activity, high lethality for mice, and strong invasiveness in the subcutaneous tissue of guinea pigs. Capsular materials of V. vulnificus were considered to be important for the expression of virulence.
Full text
PDF



Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Blake P. A., Merson M. H., Weaver R. E., Hollis D. G., Heublein P. C. Disease caused by a marine Vibrio. Clinical characteristics and epidemiology. N Engl J Med. 1979 Jan 4;300(1):1–5. doi: 10.1056/NEJM197901043000101. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bowdre J. H., Poole M. D., Oliver J. D. Edema and hemoconcentration in mice experimentally infected with Vibrio vulnificus. Infect Immun. 1981 Jun;32(3):1193–1199. doi: 10.1128/iai.32.3.1193-1199.1981. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- COOPER M. L., KELLER H. M., WALTERS E. W. Microscopic characteristics of colonies of Shigella flexneri 2a and 2b and their relation to antigenic composition, mouse virulence and immunogenicity. J Immunol. 1957 Mar;78(3):160–171. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Glynn A. A., Howard C. J. The sensitivity to complement of strains of Escherichia coli related to their K antigens. Immunology. 1970 Mar;18(3):331–346. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hollis D. G., Weaver R. E., Baker C. N., Thornsberry C. Halophilic Vibrio species isolated from blood cultures. J Clin Microbiol. 1976 Apr;3(4):425–431. doi: 10.1128/jcm.3.4.425-431.1976. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- James J. F., Zurlinden E., Lammel C. J., Brooks G. F. Relation of protein I and colony opacity to serum killing of Neisseria gonorrhoeae. J Infect Dis. 1982 Jan;145(1):37–44. doi: 10.1093/infdis/145.1.37. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Johnson D. E., Calia F. M. Hemolytic reaction of clinical and environmental strains of Vibrio vulnificus. J Clin Microbiol. 1981 Oct;14(4):457–459. doi: 10.1128/jcm.14.4.457-459.1981. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kreger A., DeChatelet L., Shirley P. Interaction of Vibrio vulnificus with human polymorphonuclear leukocytes: association of virulence with resistance to phagocytosis. J Infect Dis. 1981 Sep;144(3):244–248. doi: 10.1093/infdis/144.3.244. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kreger A., Lockwood D. Detection of extracellular toxin(s) produced by Vibrio vulnificus. Infect Immun. 1981 Aug;33(2):583–590. doi: 10.1128/iai.33.2.583-590.1981. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Labrec E. H., Schneider H., Magnani T. J., Formal S. B. EPITHELIAL CELL PENETRATION AS AN ESSENTIAL STEP IN THE PATHOGENESIS OF BACILLARY DYSENTERY. J Bacteriol. 1964 Nov;88(5):1503–1518. doi: 10.1128/jb.88.5.1503-1518.1964. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Luft J. H. Ruthenium red and violet. I. Chemistry, purification, methods of use for electron microscopy and mechanism of action. Anat Rec. 1971 Nov;171(3):347–368. doi: 10.1002/ar.1091710302. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Salit I. E., Gotschlich E. C. Gonococcal color and opacity variants: virulence for chicken embryos. Infect Immun. 1978 Nov;22(2):359–364. doi: 10.1128/iai.22.2.359-364.1978. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Smith G. C., Merkel J. R. Collagenolytic activity of Vibrio vulnificus: potential contribution to its invasiveness. Infect Immun. 1982 Mar;35(3):1155–1156. doi: 10.1128/iai.35.3.1155-1156.1982. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Tamplin M. L., Specter S., Rodrick G. E., Friedman H. Differential complement activation and susceptibility to human serum bactericidal action by Vibrio species. Infect Immun. 1983 Dec;42(3):1187–1190. doi: 10.1128/iai.42.3.1187-1190.1983. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Taylor P. W. Bactericidal and bacteriolytic activity of serum against gram-negative bacteria. Microbiol Rev. 1983 Mar;47(1):46–83. doi: 10.1128/mr.47.1.46-83.1983. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wright A. C., Simpson L. M., Oliver J. D. Role of iron in the pathogenesis of Vibrio vulnificus infections. Infect Immun. 1981 Nov;34(2):503–507. doi: 10.1128/iai.34.2.503-507.1981. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]