Abstract
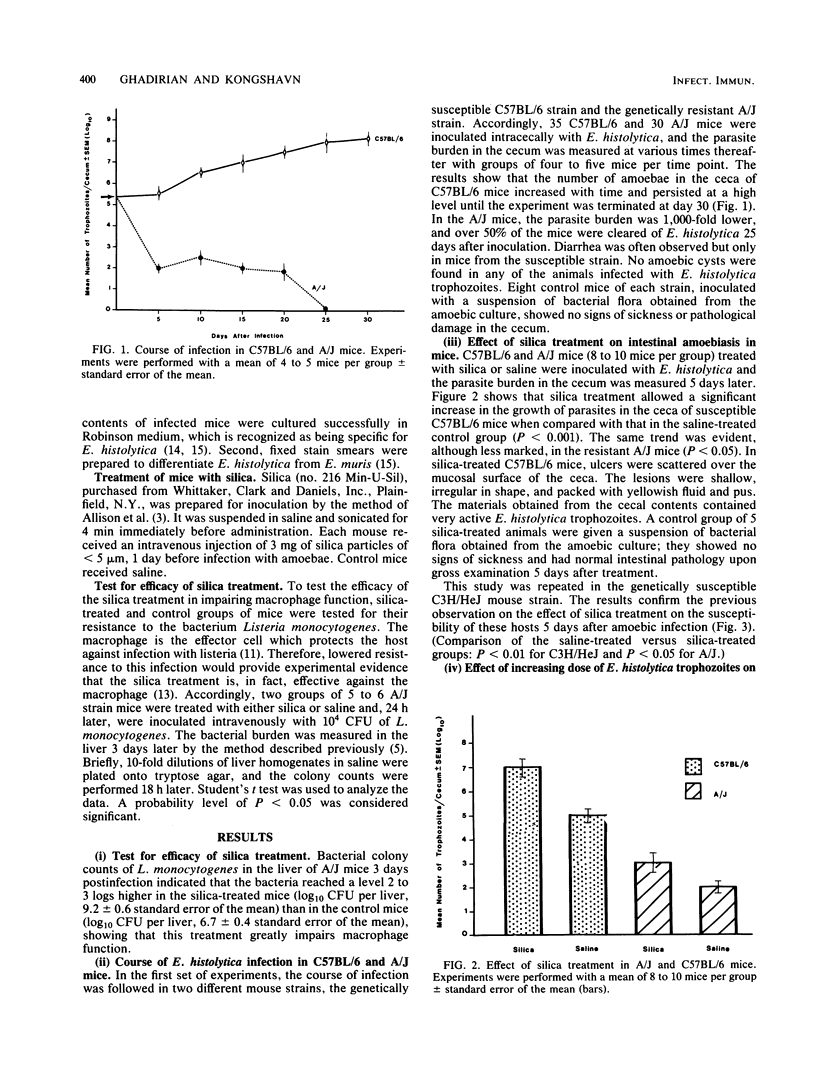
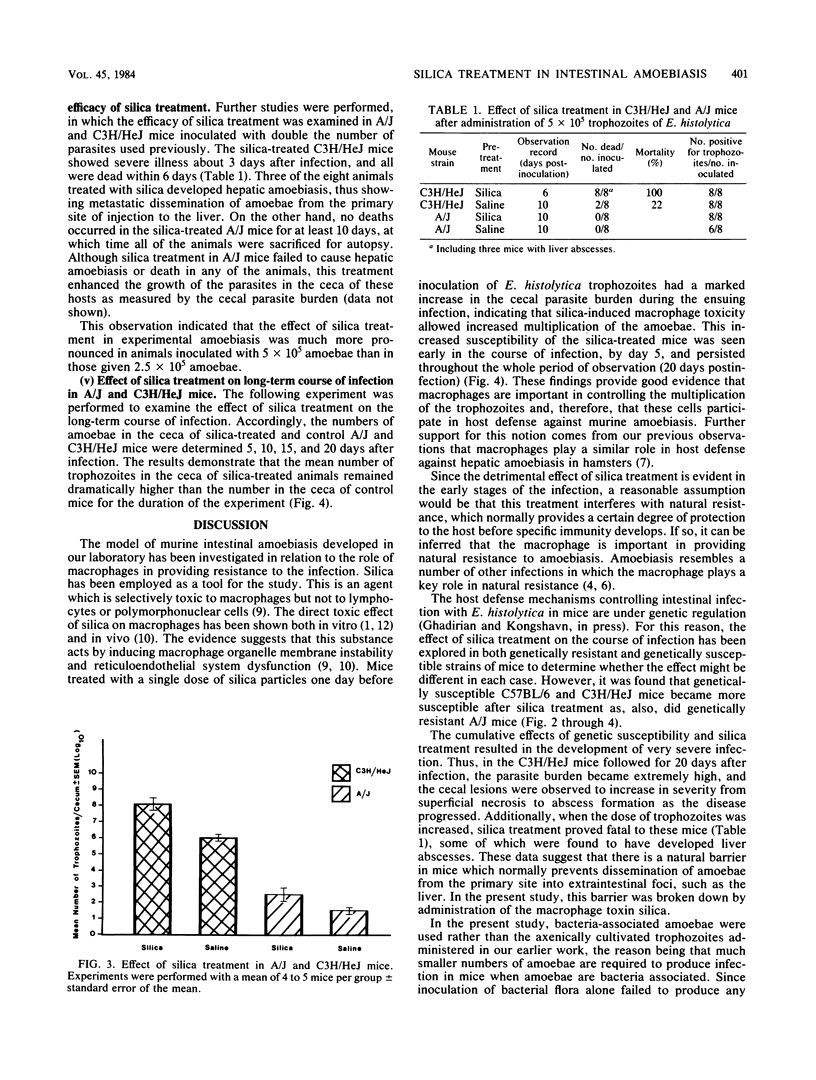
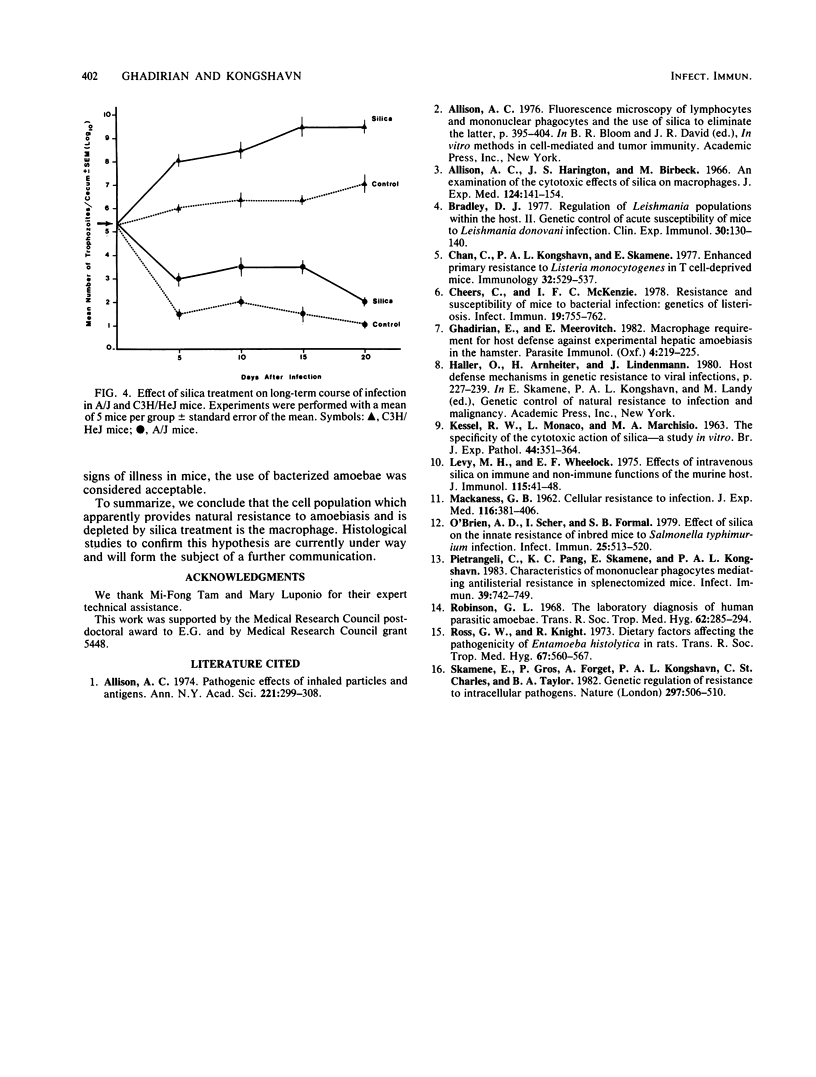
The role of macrophages in intestinal amoebiasis in mice has been investigated. The effect of injuring host macrophages on the course of infection was examined by using strains selected as being either genetically susceptible (C3H/HeJ, C57BL/6) or genetically resistant (A/J) to amoebiasis. Mice were treated with an intravenous injection of silica particles 1 day before infection with 2.5 X 10(5) or 5 X 10(5) polyxenic trophozoites of Entamoeba histolytica. The animals were killed at various times after infection, and the parasite burden in the cecum was measured. Silica treatment dramatically increased the growth of parasites in the susceptible mice. The same trend was evident, although less marked, in the resistant mice. The effect of silica treatment in experimental amoebiasis was much more pronounced in animals inoculated with 5 X 10(5) amoebae than in those with 2.5 X 10(5) amoebae. These data suggest that macrophages play an important role in host defense against amoebiasis in mice.
Full text
PDF
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Allison A. C., Harington J. S., Birbeck M. An examination of the cytotoxic effects of silica on macrophages. J Exp Med. 1966 Aug 1;124(2):141–154. doi: 10.1084/jem.124.2.141. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Allison A. C. Pathogenic effects of inhaled particles and antigens. Ann N Y Acad Sci. 1974;221:299–308. doi: 10.1111/j.1749-6632.1974.tb28229.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bradley D. J. Regulation of Leishmania populations within the host. II. genetic control of acute susceptibility of mice to Leishmania donovani infection. Clin Exp Immunol. 1977 Oct;30(1):130–140. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Chan C., Kongshavn P. A., Skamene E. Enhanced primary resistance to Listeria monocytogenes in T cell-deprived mice. Immunology. 1977 Apr;32(4):529–537. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Cheers C., McKenzie I. F. Resistance and susceptibility of mice to bacterial infection: genetics of listeriosis. Infect Immun. 1978 Mar;19(3):755–762. doi: 10.1128/iai.19.3.755-762.1978. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ghadirian E., Meerovitch E. Macrophage requirement for host defence against experimental hepatic amoebiasis in the hamster. Parasite Immunol. 1982 Jul;4(4):219–225. doi: 10.1111/j.1365-3024.1982.tb00433.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- KESSEL R. W., MONACO L., MARCHISIO M. A. THE SPECIFICITY OF THE CYTOTOXIC ACTION OF SILICA--A STUDY IN VITRO. Br J Exp Pathol. 1963 Aug;44:351–364. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Levy M. H., Wheelock E. F. Effects of intravenous silica on immune and non-immune functions of the murine host. J Immunol. 1975 Jul;115(1):41–48. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- MACKANESS G. B. Cellular resistance to infection. J Exp Med. 1962 Sep 1;116:381–406. doi: 10.1084/jem.116.3.381. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- O'Brien A. D., Scher I., Formal S. B. Effect of silica on the innate resistance of inbred mice to Salmonella typhimurium infection. Infect Immun. 1979 Aug;25(2):513–520. doi: 10.1128/iai.25.2.513-520.1979. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Pietrangeli C., Pang K. C., Skamene E., Kongshavn P. A. Characteristics of mononuclear phagocytes mediating antilisterial resistance in splenectomized mice. Infect Immun. 1983 Feb;39(2):742–749. doi: 10.1128/iai.39.2.742-749.1983. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Robinson G. L. The laboratory diagnosis of human parasitic amoebae. Trans R Soc Trop Med Hyg. 1968;62(2):285–294. doi: 10.1016/0035-9203(68)90170-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ross G. W., Knight R. Dietary factors affecting the pathogenicity of Entamoeba histolytica in rats. Trans R Soc Trop Med Hyg. 1973;67(4):560–567. doi: 10.1016/0035-9203(73)90087-4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Skamene E., Gros P., Forget A., Kongshavn P. A., St Charles C., Taylor B. A. Genetic regulation of resistance to intracellular pathogens. Nature. 1982 Jun 10;297(5866):506–509. doi: 10.1038/297506a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]


