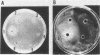
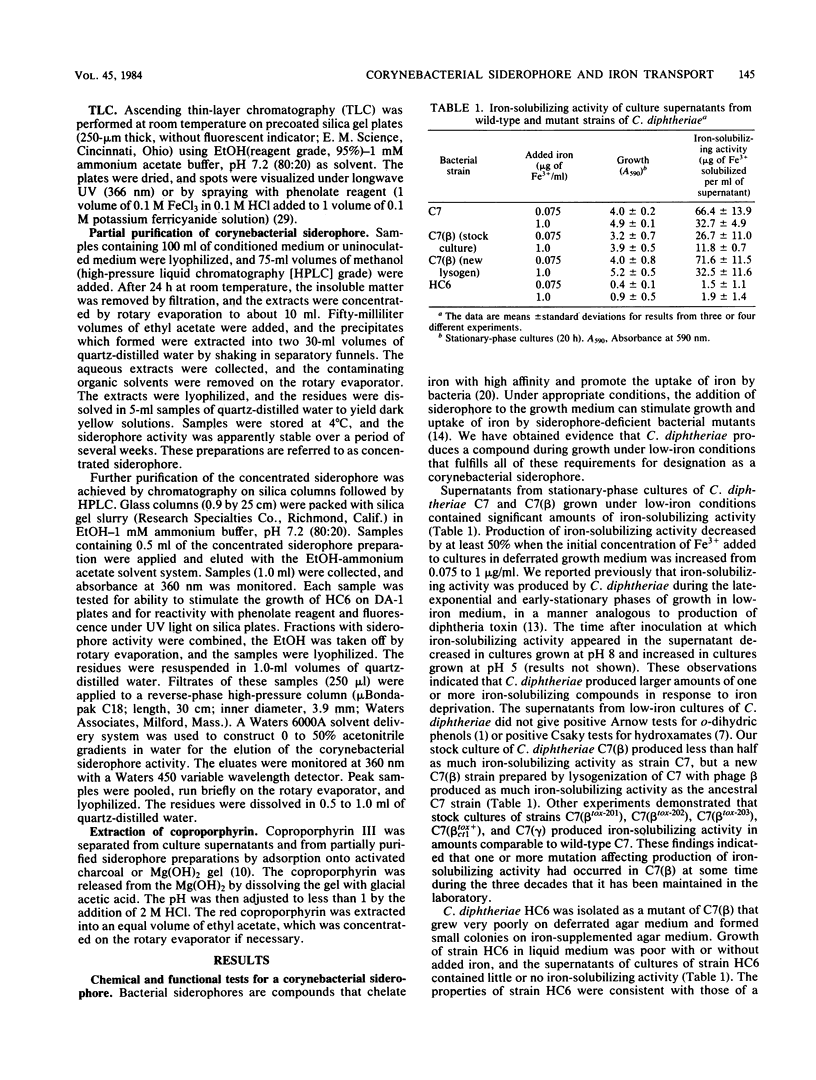
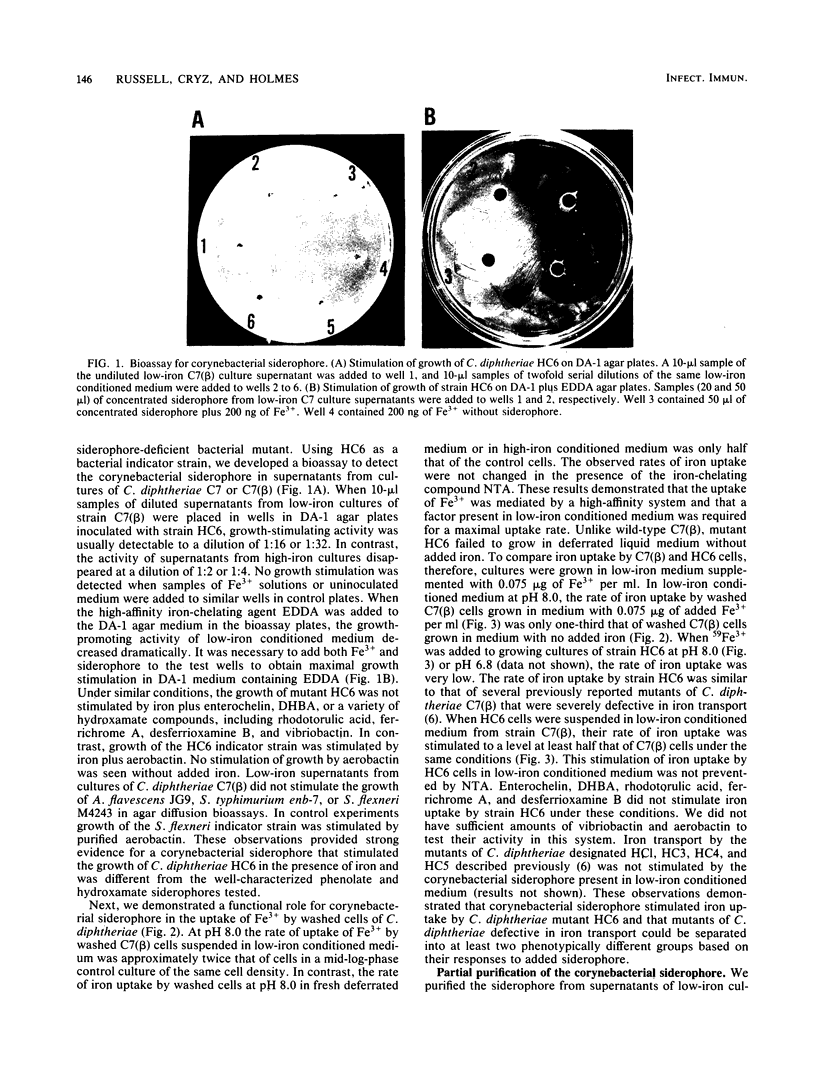
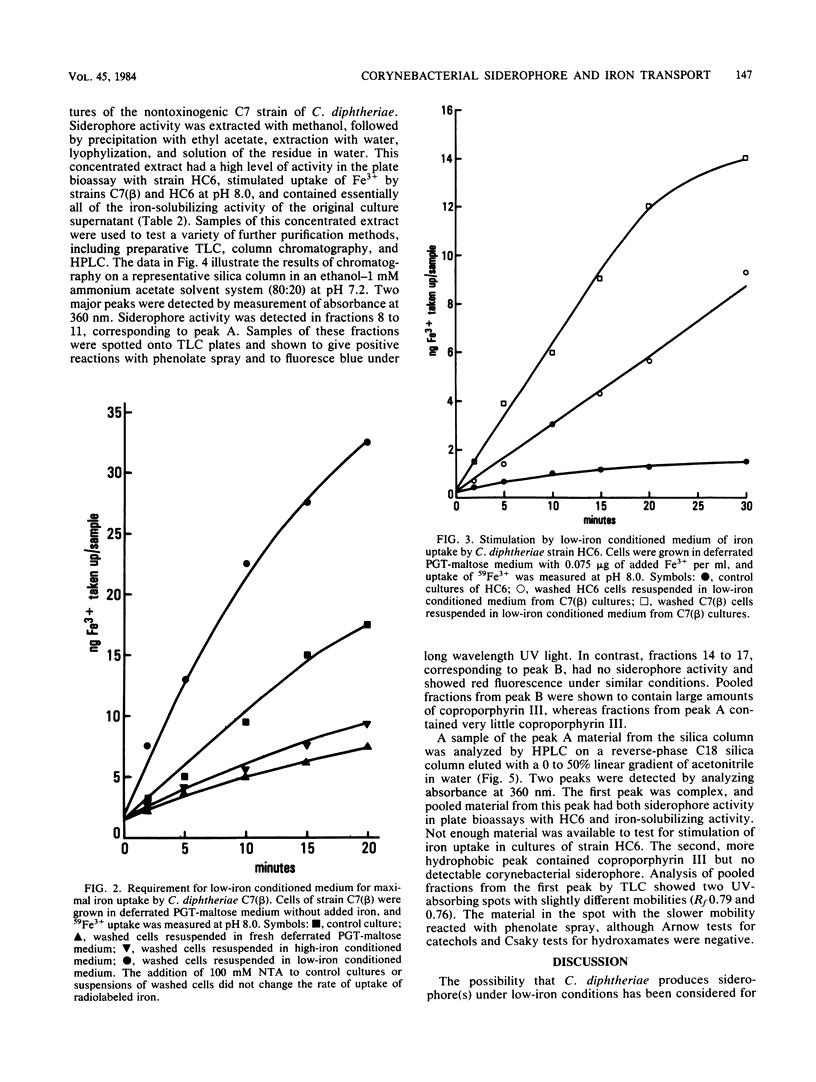
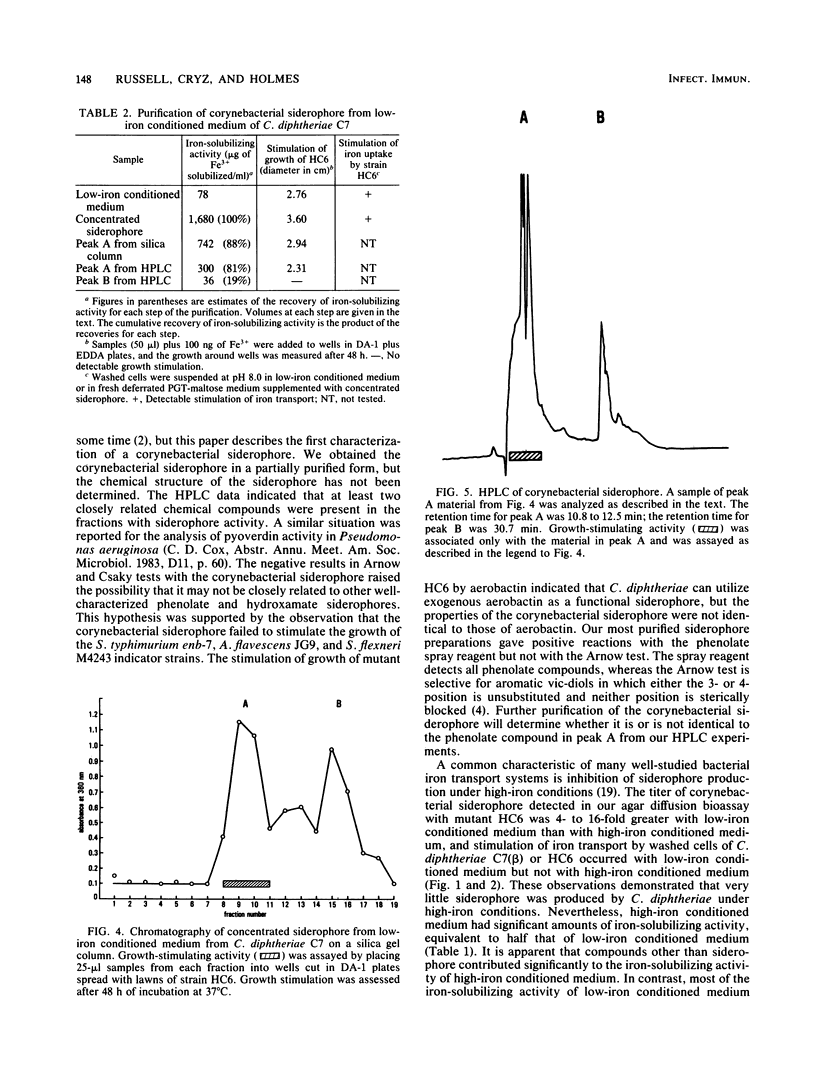
Abstract
During growth under conditions of iron deprivation, Corynebacterium diphtheriae secreted a siderophore into the culture medium. This extracellular siderophore was necessary for rates of iron uptake at pH 8.0 by C. diphtheriae C7 and related strains. We isolated a mutant of C. diphtheriae C7(beta), strain HC6, which did not make the corynebacterial siderophore. Strain HC6 grew very poorly, even under high-iron conditions, and had a severe defect in iron transport. Both growth and iron uptake by strain HC6 were greatly stimulated by the corynebacterial siderophore. We used strain HC6 to develop a bioassay for the corynebacterial siderophore and to look for other potential siderophores for C. diphtheriae. Among the purified phenolate and hydroxamate siderophores tested, only aerobactin was able to stimulate the growth of strain HC6. Partial purification of the corynebacterial siderophore was achieved. The siderophore did not give positive reactions in the Arnow test for phenolates or the Csaky test for hydroxamates and may have a novel chemical structure.
Full text
PDF


Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- BARDSDALE W. L., PAPPENHEIMER A. M., Jr Phage-host relationships in nontoxigenic and toxigenic diphtheria bacilli. J Bacteriol. 1954 Feb;67(2):220–232. doi: 10.1128/jb.67.2.220-232.1954. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Barksdale L. Corynebacterium diphtheriae and its relatives. Bacteriol Rev. 1970 Dec;34(4):378–422. doi: 10.1128/br.34.4.378-422.1970. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Barnum D. W. Spectrophotometric determination of catechol, epinephrine, dopa, dopamine and other aromatic vic-diols. Anal Chim Acta. 1977 Mar;89(1):157–166. doi: 10.1016/S0003-2670(01)83081-6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- CLARKE G. D. The effect of ferrous ions on the formation of toxin and porphyrin by a strain of Corynebacterium diphtheriae. J Gen Microbiol. 1958 Jun;18(3):698–707. doi: 10.1099/00221287-18-3-698. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Cryz S. J., Jr, Russell L. M., Holmes R. K. Regulation of toxinogenesis in Corynebacterium diphtheriae: mutations in the bacterial genome that alter the effects of iron on toxin production. J Bacteriol. 1983 Apr;154(1):245–252. doi: 10.1128/jb.154.1.245-252.1983. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Finkelstein R. A., Sciortino C. V., McIntosh M. A. Role of iron in microbe-host interactions. Rev Infect Dis. 1983 Sep-Oct;5 (Suppl 4):S759–S777. doi: 10.1093/clinids/5.supplement_4.s759. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- GROMAN N. B., EATON M. Genetic factors in Corynebacterium diphtheriae conversion. J Bacteriol. 1955 Dec;70(6):637–640. doi: 10.1128/jb.70.6.637-640.1955. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gibson F., Magrath D. I. The isolation and characterization of a hydroxamic acid (aerobactin) formed by Aerobacter aerogenes 62-I. Biochim Biophys Acta. 1969 Nov 18;192(2):175–184. doi: 10.1016/0304-4165(69)90353-5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gray C. H. The isolation of coproporphyrin III from Corynebacterium diphtheriae culture filtrates. Biochem J. 1948;43(2):191–193. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Holmes R. K., Barksdale L. Genetic analysis of tox+ and tox- bacteriophages of Corynebacterium diphtheriae. J Virol. 1969 Jun;3(6):586–598. doi: 10.1128/jvi.3.6.586-598.1969. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Macham L. P., Ratledge C. A new group of water-soluble iron-binding compounds from Mycobacteria: the exochelins. J Gen Microbiol. 1975 Aug;89(2):379–382. doi: 10.1099/00221287-89-2-379. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Miles A. A., Khimji P. L. Enterobacterial chelators of iron: their occurrence, detection, and relation to pathogenicity. J Med Microbiol. 1975 Nov;8(4):477–490. doi: 10.1099/00222615-8-4-477. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Murphy J. R., Skiver J., McBride G. Isolation and partial characterization of a corynebacteriophage beta, tox operator constitutive-like mutant lysogen of Corynebacterium diphtheriae. J Virol. 1976 Apr;18(1):235–244. doi: 10.1128/jvi.18.1.235-244.1976. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Neilands J. B. Microbial iron compounds. Annu Rev Biochem. 1981;50:715–731. doi: 10.1146/annurev.bi.50.070181.003435. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Pappenheimer A. M., Jr Diphtheria toxin. Annu Rev Biochem. 1977;46:69–94. doi: 10.1146/annurev.bi.46.070177.000441. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Payne S. M. Synthesis and utilization of siderophores by Shigella flexneri. J Bacteriol. 1980 Sep;143(3):1420–1424. doi: 10.1128/jb.143.3.1420-1424.1980. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Peters W. J., Warren R. A. The accumulation of phenolic acids and coproporphyrin by iron-deficient cultures of Bacillus subtilis. Can J Microbiol. 1970 Dec;16(12):1179–1185. doi: 10.1139/m70-200. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rimington C. Spectral-absorption coefficients of some porphyrins in the Soret-band region. Biochem J. 1960 Jun;75(3):620–623. doi: 10.1042/bj0750620. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rogers H. J. Iron-Binding Catechols and Virulence in Escherichia coli. Infect Immun. 1973 Mar;7(3):445–456. doi: 10.1128/iai.7.3.445-456.1973. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Russell L. M., Holmes R. K. Initial characterization of the ferric iron transport system of Corynebacterium diphtheriae. J Bacteriol. 1983 Sep;155(3):1439–1442. doi: 10.1128/jb.155.3.1439-1442.1983. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Weinberg E. D. Iron and infection. Microbiol Rev. 1978 Mar;42(1):45–66. doi: 10.1128/mr.42.1.45-66.1978. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Welkos S. L., Holmes R. K. Characterization of a screening test for diphtherial toxin antigen produced by individual plaques of corynebacteriophages. J Clin Microbiol. 1979 Jun;9(6):693–698. doi: 10.1128/jcm.9.6.693-698.1979. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Welkos S. L., Holmes R. K. Regulation of toxinogenesis in Corynebacterium diphtheriae. I. Mutations in bacteriophage beta that alter the effects of iron on toxin production. J Virol. 1981 Mar;37(3):936–945. doi: 10.1128/jvi.37.3.936-945.1981. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- YONEDA M., PAPPENHEIMER A. M., Jr Some effects of iron deficiency on the extracellular products released by toxigenic and nontoxigenic strains of Corynebacterium diphtheriae. J Bacteriol. 1957 Aug;74(2):256–264. doi: 10.1128/jb.74.2.256-264.1957. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]