Abstract
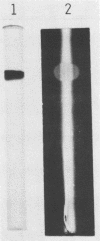
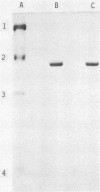
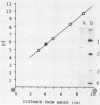
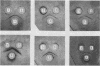
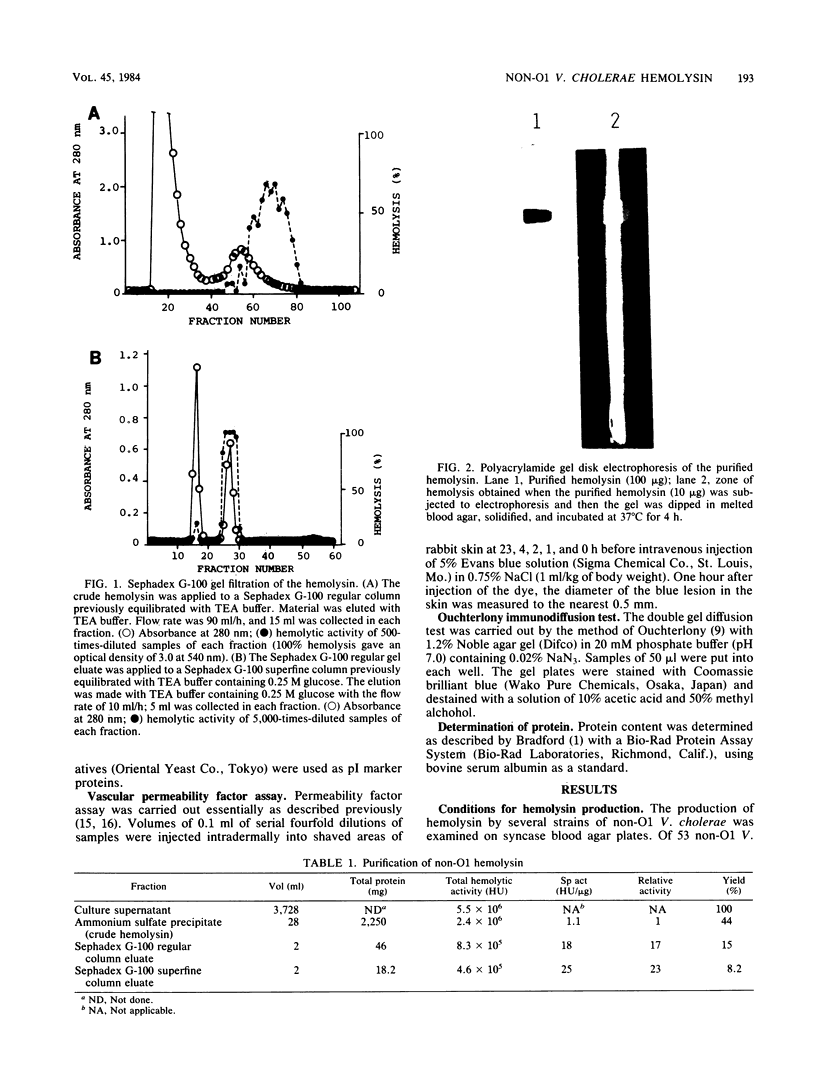
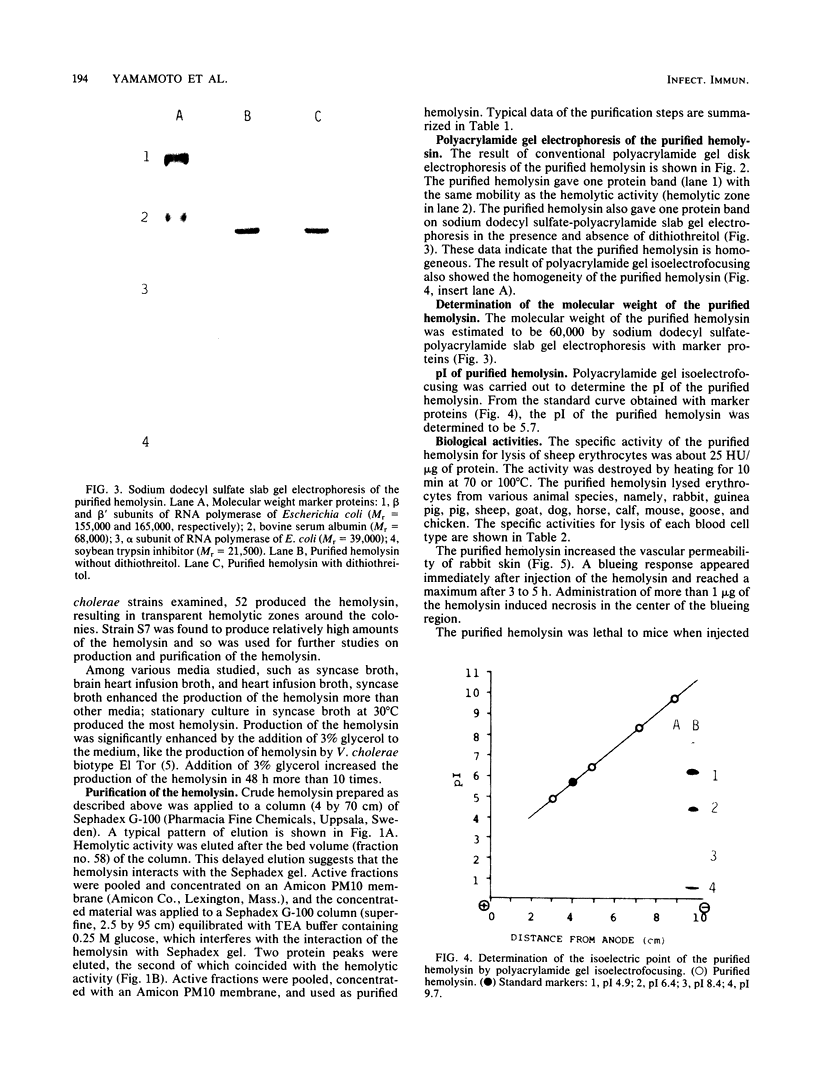
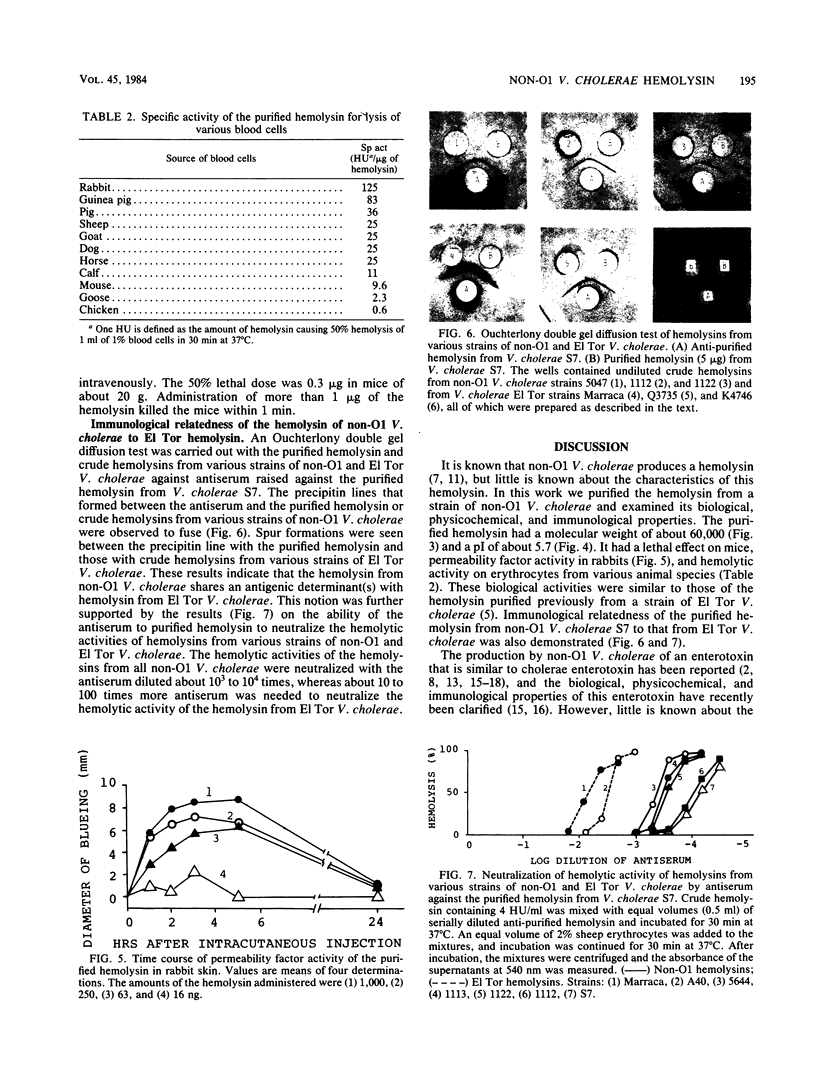
Hemolysin of a non-O1 Vibrio cholerae strain was purified and characterized. The purified hemolysin gave a single protein band on conventional and sodium dodecyl sulfate-gel electrophoresis. Its molecular weight was estimated as 60,000 by sodium dodecyl sulfate-polyacrylamide slab gel electrophoresis. It had a pI of 5.7. The purified hemolysin caused increased vascular permeability of rabbit skin and rapid death of mice on intravenous injection and also lysed erythrocytes of various animal species. An Ouchterlony double gel diffusion test using antiserum against the purified hemolysin indicated that the hemolysin from non-O1 V. cholerae was immunologically related, but not identical, to the hemolysin from El Tor V. cholerae. Antiserum against the purified hemolysin neutralized the hemolytic activity of the hemolysins from not only non-O1 but also El Tor V. cholerae.
Full text
PDF

Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Bradford M. M. A rapid and sensitive method for the quantitation of microgram quantities of protein utilizing the principle of protein-dye binding. Anal Biochem. 1976 May 7;72:248–254. doi: 10.1006/abio.1976.9999. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Craig J. P., Yamamoto K., Takeda Y., Miwatani T. Production of cholera-like enterotoxin by a Vibrio cholerae non-O1 strain isolated from the environment. Infect Immun. 1981 Oct;34(1):90–97. doi: 10.1128/iai.34.1.90-97.1981. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- DAVIS B. J. DISC ELECTROPHORESIS. II. METHOD AND APPLICATION TO HUMAN SERUM PROTEINS. Ann N Y Acad Sci. 1964 Dec 28;121:404–427. doi: 10.1111/j.1749-6632.1964.tb14213.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Finkelstein R. A., Atthasampunna P., Chulasamaya M., Charunmethee P. Pathogenesis of experimental cholera: biologic ativities of purified procholeragen A. J Immunol. 1966 Mar;96(3):440–449. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Honda T., Finkelstein R. A. Purification and characterization of a hemolysin produced by Vibrio cholerae biotype El Tor: another toxic substance produced by cholera vibrios. Infect Immun. 1979 Dec;26(3):1020–1027. doi: 10.1128/iai.26.3.1020-1027.1979. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Laemmli U. K. Cleavage of structural proteins during the assembly of the head of bacteriophage T4. Nature. 1970 Aug 15;227(5259):680–685. doi: 10.1038/227680a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- McIntyre O. R., Feeley J. C. Characteristics of non-cholera Vibrios isolated from cases of human diarrhoea. Bull World Health Organ. 1965;32(5):627–632. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Oashi M., Shimada T., Fukumi H. In vitro production of enterotoxin and hemorrhagic principle by Vibrio cholerae, NAG. Jpn J Med Sci Biol. 1972 Jun;25(3):179–194. doi: 10.7883/yoken1952.25.179. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sakazaki R., Tamura K., Murase M. Determination of the hemolytic activity of Vibrio cholerae. Jpn J Med Sci Biol. 1971 Apr;24(2):83–91. doi: 10.7883/yoken1952.24.83. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sanyal S. C., Alam K., Neogi P. K., Huq M. I., Al-Mahmud K. A. A new cholera toxin. Lancet. 1983 Jun 11;1(8337):1337–1337. doi: 10.1016/s0140-6736(83)92449-2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Yamamoto K., Takeda Y., Miwatani T., Craig J. P. Evidence that a non-O1 Vibrio cholerae produces enterotoxin that is similar but not identical to cholera enterotoxin. Infect Immun. 1983 Sep;41(3):896–901. doi: 10.1128/iai.41.3.896-901.1983. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Yamamoto K., Takeda Y., Miwatani T., Craig J. P. Purification and some properties of a non-o1 Vibrio cholerae enterotoxin that is identical to cholera enterotoxin. Infect Immun. 1983 Mar;39(3):1128–1135. doi: 10.1128/iai.39.3.1128-1135.1983. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Zinnaka Y., Carpenter C. C., Jr An enterotoxin produced by noncholera vibrios. Johns Hopkins Med J. 1972 Dec;131(6):403–411. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]