Abstract
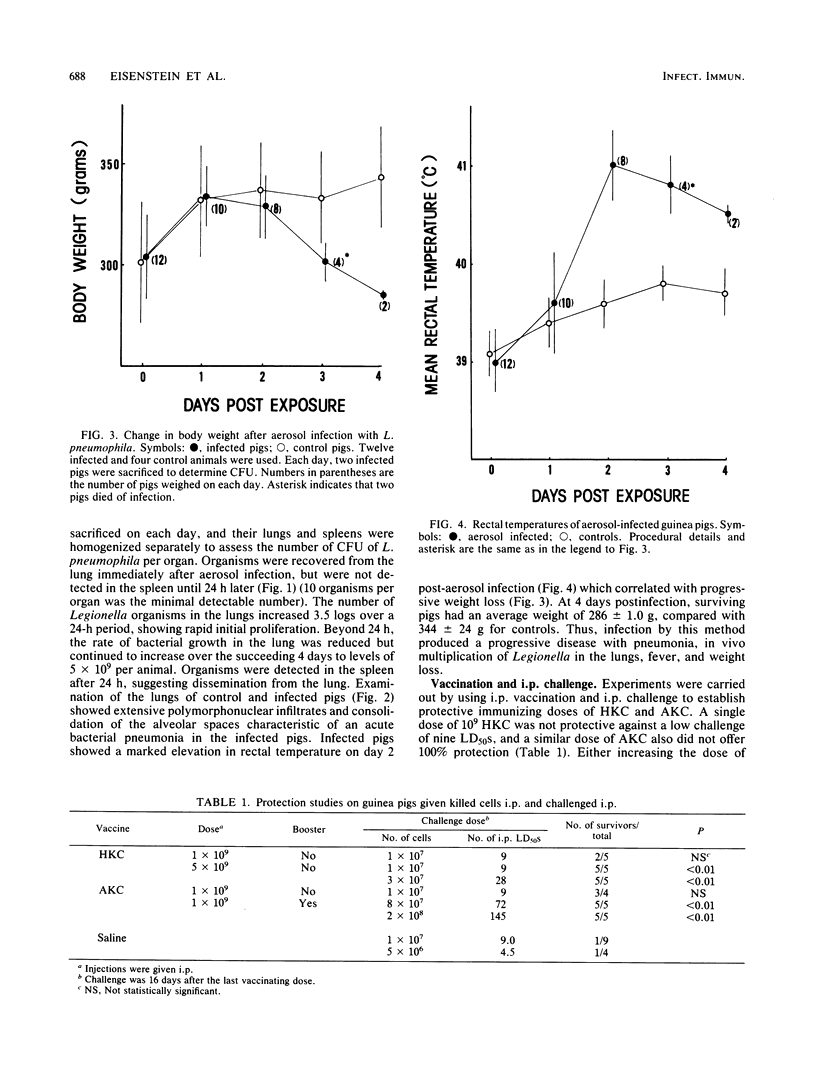
An aerosol model of Legionella infection has been established in guinea pigs. Infected animals showed growth of Legionella in their lungs, dissemination of organisms to the spleen, development of pneumonia and fever, and weight loss. Vaccination studies using heat-killed or acetone-killed cells were carried out, and guinea pigs were challenged intraperitoneally or by using the aerosol model of infection. Both vaccines were shown to give moderately high levels of protection against intraperitoneal challenge (28 to 145 50% lethal doses). Protection was found to be dose dependent and correlated with antibody levels as measured by enzyme-linked immunosorbent assay to an outer membrane antigen and by indirect immunofluorescence to heat-killed cells. In contrast, the same vaccination regimens that protected against intraperitoneal challenge failed to protect guinea pigs against aerosol challenge with comparable doses of Legionella, despite the presence of serum antibody. The results are discussed in terms of the possible requirements for immunity to aerosolized Legionella, including secretory immunoglobulin or cell-mediated immunity.
Full text
PDF



Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Berendt R. F., Young H. W., Allen R. G., Knutsen G. L. Dose-response of guinea pigs experimentally infected with aerosols of Legionella pneumophila. J Infect Dis. 1980 Feb;141(2):186–192. doi: 10.1093/infdis/141.2.186. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bissett M. L., Lee J. O., Lindquist D. S. New serogroup of Legionella pneumophila, serogroup 8. J Clin Microbiol. 1983 May;17(5):887–891. doi: 10.1128/jcm.17.5.887-891.1983. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Brenner D. J., Steigerwalt A. G., McDade J. E. Classification of the Legionnaires' disease bacterium: Legionella pneumophila, genus novum, species nova, of the family Legionellaceae, familia nova. Ann Intern Med. 1979 Apr;90(4):656–658. doi: 10.7326/0003-4819-90-4-656. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Broome C. V., Fraser D. W. Epidemiologic aspects of legionellosis. Epidemiol Rev. 1979;1:1–16. doi: 10.1093/oxfordjournals.epirev.a036204. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Chandler F. W., McDade J. E., Hicklin M. D., Blackmon J. A., Thomason B. M., Ewing E. P., Jr Pathologic findings in guinea pigs inoculated intraperitoneally with the Legionnaires' disease bacterium. Ann Intern Med. 1979 Apr;90(4):671–675. doi: 10.7326/0003-4819-90-4-671. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Collins F. M. Cellular antimicrobial immunity. CRC Crit Rev Microbiol. 1978;7(1):27–91. doi: 10.3109/10408417909101177. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Daisy J. A., Benson C. E., McKitrick J., Friedman H. M. Intracellular replication of Legionella pneumophila. J Infect Dis. 1981 Mar;143(3):460–464. doi: 10.1093/infdis/143.3.460. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Eisenstein T. K., De Cueninck B. J., Resavy D., Shockman G. D., Carey R. B., Swenson R. M. Quantitative determination in human sera of vaccine-induced antibody to type-specific polysaccharides of group B streptococci using an enzyme-linked immunosorbent assay. J Infect Dis. 1983 May;147(5):847–856. doi: 10.1093/infdis/147.5.847. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Elliott J. A., Johnson W., Helms C. M. Ultrastructural localization and protective activity of a high-molecular-weight antigen isolated from Legionella pneumophila. Infect Immun. 1981 Feb;31(2):822–824. doi: 10.1128/iai.31.2.822-824.1981. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Flesher A. R., Jennings H. J., Lugowski C., Kasper D. L. Isolation of a serogroup 1-specific antigen from Legionella pneumophila. J Infect Dis. 1982 Feb;145(2):224–233. doi: 10.1093/infdis/145.2.224. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Friedman R. L., Iglewski B. H., Miller R. D. Identification of a cytotoxin produced by Legionella pneumophila. Infect Immun. 1980 Jul;29(1):271–274. doi: 10.1128/iai.29.1.271-274.1980. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Fulginiti V. A., Eller J. J., Sieber O. F., Joyner J. W., Minamitani M., Meiklejohn G. Respiratory virus immunization. I. A field trial of two inactivated respiratory virus vaccines; an aqueous trivalent parainfluenza virus vaccine and an alum-precipitated respiratory syncytial virus vaccine. Am J Epidemiol. 1969 Apr;89(4):435–448. doi: 10.1093/oxfordjournals.aje.a120956. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Horwitz M. A., Silverstein S. C. Legionnaires' disease bacterium (Legionella pneumophila) multiples intracellularly in human monocytes. J Clin Invest. 1980 Sep;66(3):441–450. doi: 10.1172/JCI109874. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kapikian A. Z., Mitchell R. H., Chanock R. M., Shvedoff R. A., Stewart C. E. An epidemiologic study of altered clinical reactivity to respiratory syncytial (RS) virus infection in children previously vaccinated with an inactivated RS virus vaccine. Am J Epidemiol. 1969 Apr;89(4):405–421. doi: 10.1093/oxfordjournals.aje.a120954. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Katz S. M., Hashemi S. Electron microscopic examination of the inflammatory response to Legionella pneumophila in guinea pigs. Lab Invest. 1982 Jan;46(1):24–32. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kishimoto R. A., White J. D., Shirey F. G., McGann V. G., Berendt R. F., Larson E. W., Hedlund K. W. In vitro responses of guinea pig peritoneal macrophages to Legionella pneumophila. Infect Immun. 1981 Mar;31(3):1209–1213. doi: 10.1128/iai.31.3.1209-1213.1981. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- LANDY M. Enhancement of the immunogenicity of typhoid vaccine by retention of the V1 antigen. Am J Hyg. 1953 Sep;58(2):148–164. doi: 10.1093/oxfordjournals.aje.a119596. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- MIDDLEBROOK G. An apparatus for airborne infection of mice. Proc Soc Exp Biol Med. 1952 May;80(1):105–110. doi: 10.3181/00379727-80-19538. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mackaness G. B. Resistance to intracellular infection. J Infect Dis. 1971 Apr;123(4):439–445. doi: 10.1093/infdis/123.4.439. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- McDade J. E., Shepard C. C., Fraser D. W., Tsai T. R., Redus M. A., Dowdle W. R. Legionnaires' disease: isolation of a bacterium and demonstration of its role in other respiratory disease. N Engl J Med. 1977 Dec 1;297(22):1197–1203. doi: 10.1056/NEJM197712012972202. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Orrison L. H., Cherry W. B., Tyndall R. L., Fliermans C. B., Gough S. B., Lambert M. A., McDougal L. K., Bibb W. F., Brenner D. J. Legionella oakridgensis: unusual new species isolated from cooling tower water. Appl Environ Microbiol. 1983 Feb;45(2):536–545. doi: 10.1128/aem.45.2.536-545.1983. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rinaldo C. R., Jr, Pasculle A. W., Myerowitz R. L., Gress F. M., Dowling J. N. Growth of the Pittsburgh pneumonia agent in animal cell cultures. Infect Immun. 1981 Sep;33(3):939–943. doi: 10.1128/iai.33.3.939-943.1981. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Winn W. C., Jr, Davis G. S., Gump D. W., Craighead J. E., Beaty H. N. Legionnaires' pneumonia after intratracheal inoculation of guinea pigs and rats. Lab Invest. 1982 Dec;47(6):568–578. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Winn W. C., Jr, Myerowitz R. L. The pathology of the Legionella pneumonias. A review of 74 cases and the literature. Hum Pathol. 1981 May;12(5):401–422. doi: 10.1016/s0046-8177(81)80021-4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wong K. H., Schalla W. O., Arko R. J., Bullard J. C., Feeley J. C. Immunochemical, serologic, and immunologic properties of major antigens isolated from the Legionnaires' disease bacterium. Observations bearing on the feasibility of a vaccine. Ann Intern Med. 1979 Apr;90(4):634–638. doi: 10.7326/0003-4819-90-4-634. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wong M. C., Ewing E. P., Jr, Callaway C. S., Peacock W. L., Jr Intracellular multiplication of Legionella pneumophila in cultured human embryonic lung fibroblasts. Infect Immun. 1980 Jun;28(3):1014–1018. doi: 10.1128/iai.28.3.1014-1018.1980. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]