Abstract
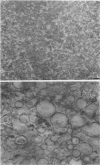
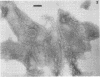
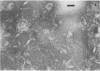
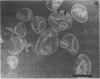
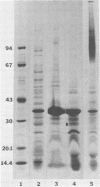
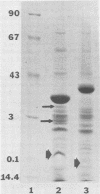
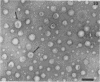
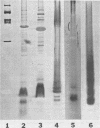
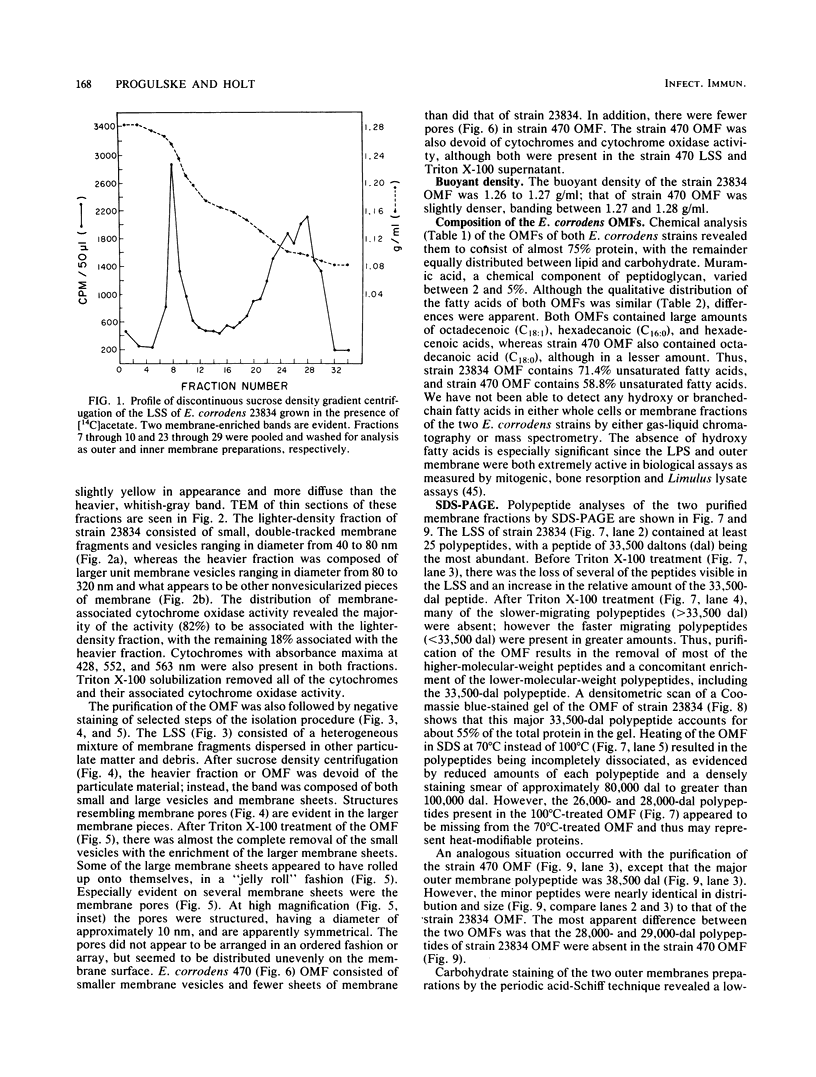
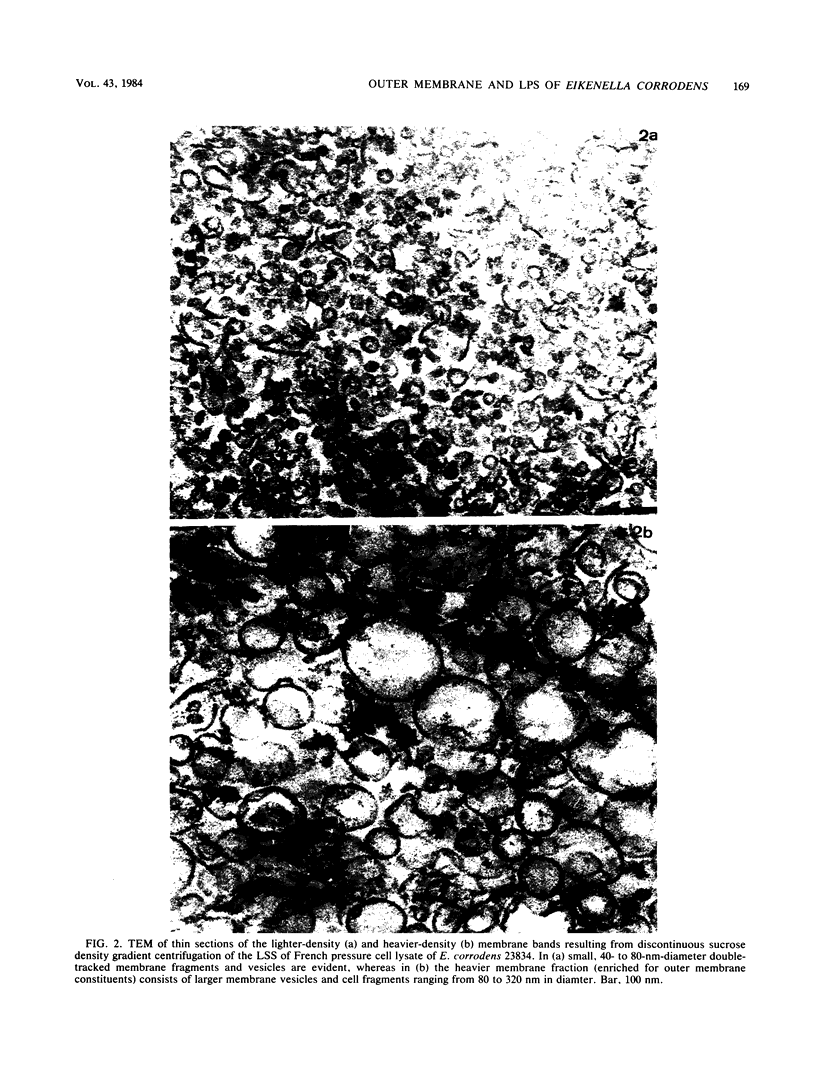
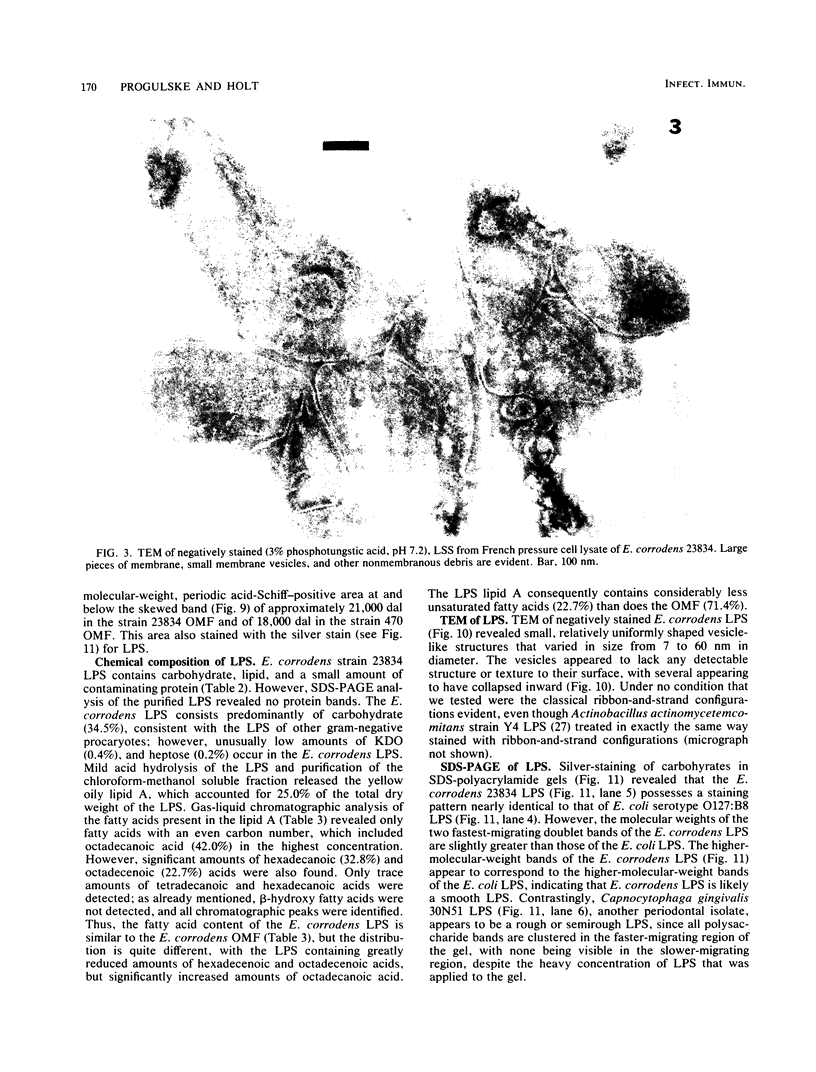
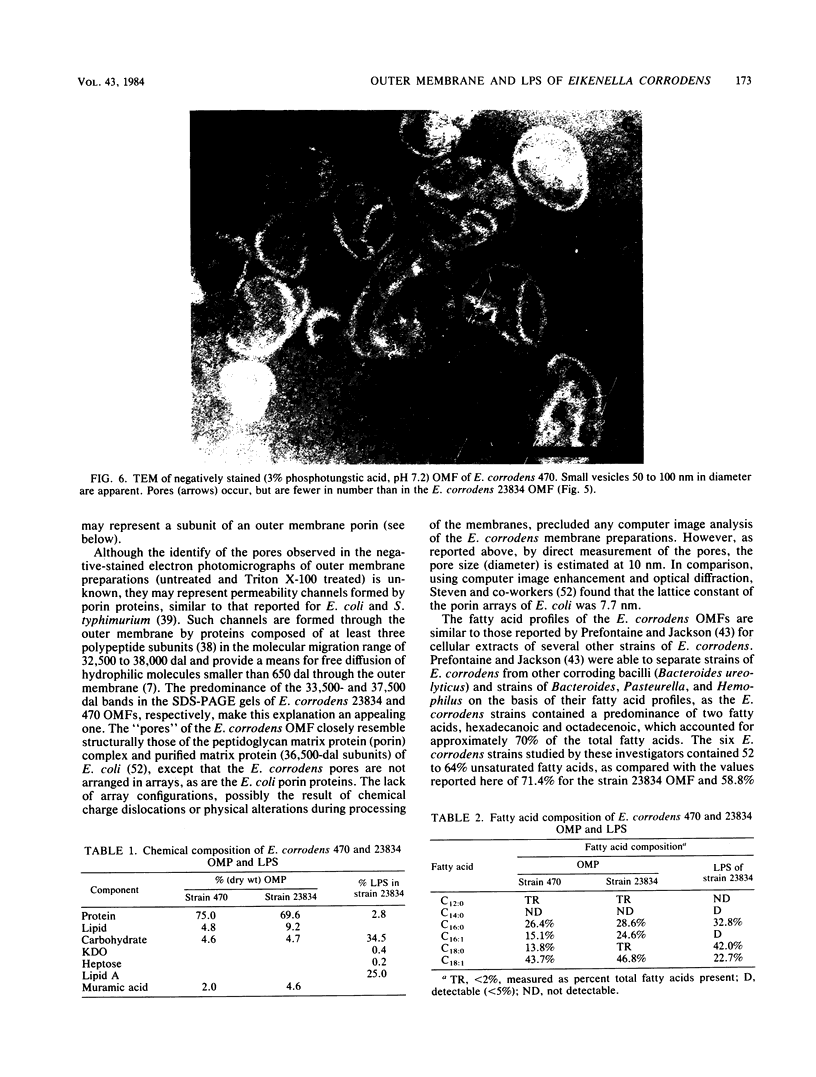
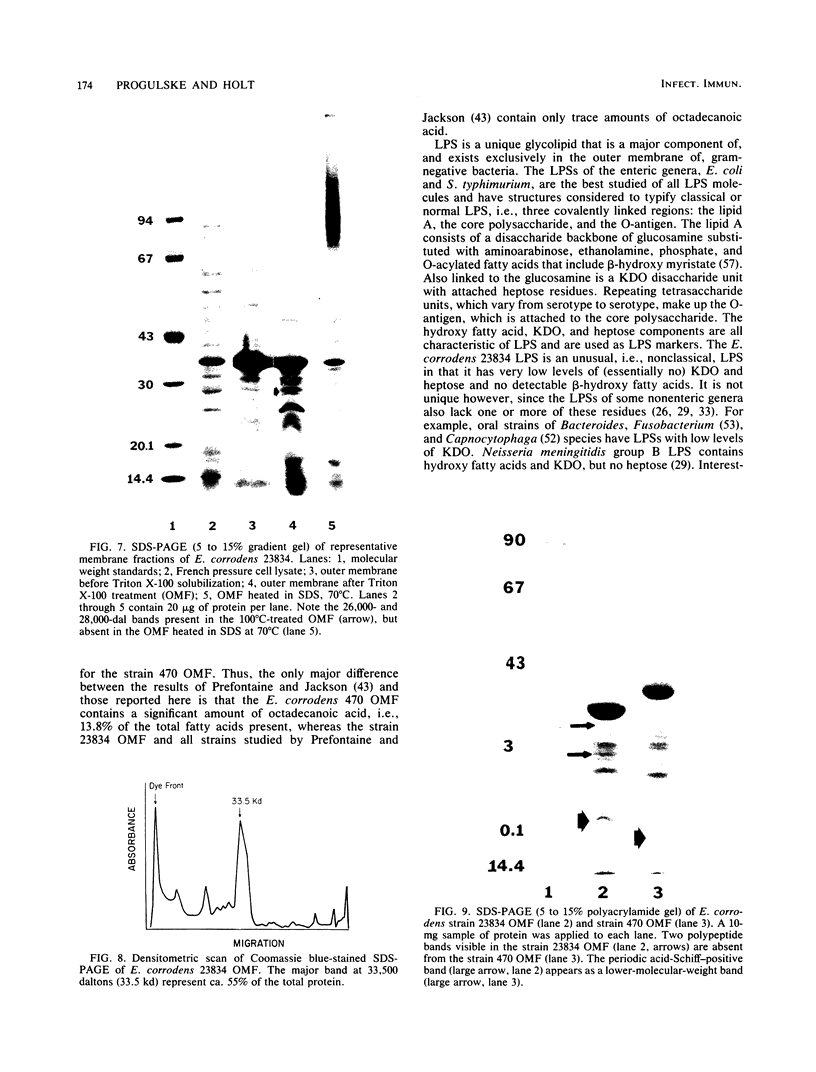
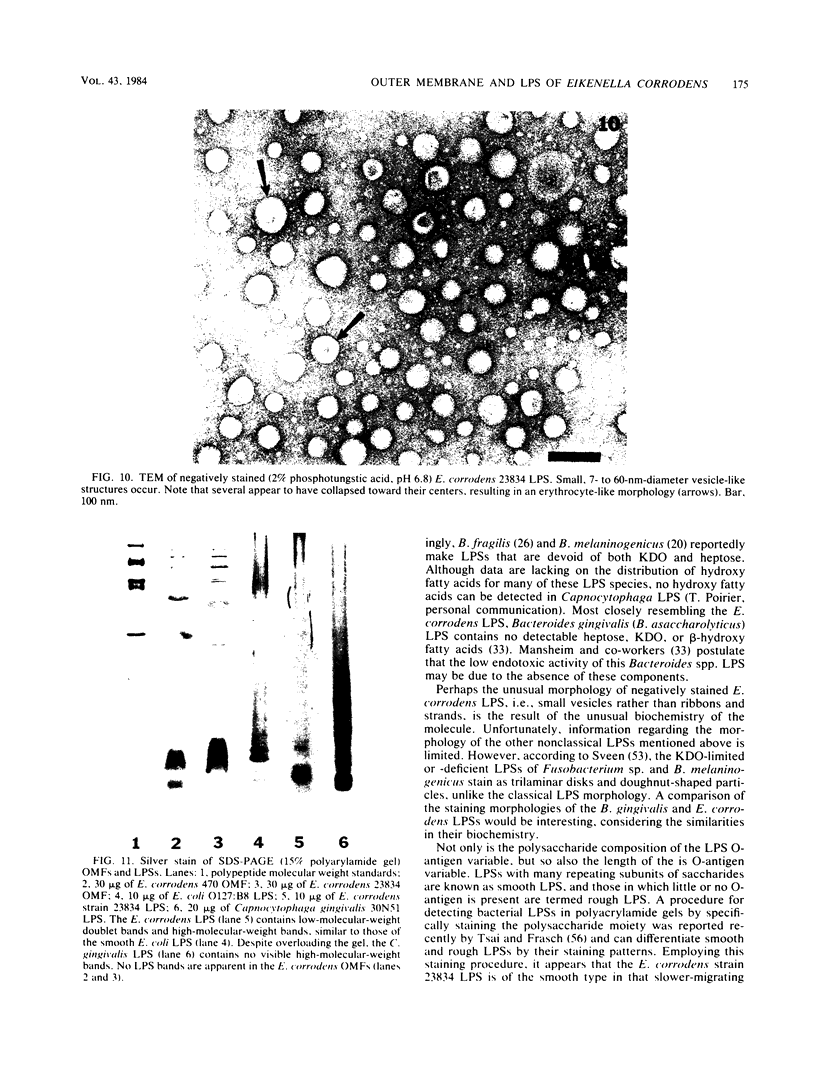
The chemical composition of the outer membrane fractions (OMFs) of Eikenella corrodens strains 23834 and 470 as well as the strain 23834 lipopolysaccharide (LPS) was determined. The OMFs were obtained by Triton X-100 treatment of the heavier membrane fraction from sucrose density centrifugation of the total membrane fraction. The resulting OMFs of strains 23834 and 470, free of cytoplasmic membrane components, were found to contain 69.6 and 75.0% (wt/wt) protein, 4.8 and 9.2% lipid, 4.6 and 4.7% carbohydrate, and 2.0 and 4.6% muramic acid, respectively. By sodium dodecyl sulfate-polyacrylamide gel electrophoresis both OMFs contained one major peptide determined to be 33,500 daltons for the strain 23834 OMF, and 37,500 daltons for the strain 470 OMF. Analysis of the OMF fatty acids revealed hexadecanoic, hexadecenoic, octadecenoic, and lesser amounts of octadecanoic acids. Transmission electron microscopic examination of the OMFs revealed typical large sheets of membrane. Structures (10 nm in diameter) resembling pores were also evident. The E. corrodens LPS was found to be composed of 34.5% (wt/wt) carbohydrate and 25.0% lipid A. Only minute amounts of 2-keto-3-deoxyoctonate and heptose could be detected. Fatty acid analysis revealed primarily octadecanoic and hexadecanoic acids, with lesser amounts of octadecenoic acid. No hydroxy fatty acids were detected. Sodium dodecyl sulfate-polyacrylamide gel electrophoresis analysis showed the E. corrodens LPS to resemble other smooth-type LPSs. Transmission electron microscopic examination revealed a vesicle-like morphology. The E. corrodens LPS appears not to be a "classical," i.e., enteric, type of LPS.
Full text
PDF





Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- BLIGH E. G., DYER W. J. A rapid method of total lipid extraction and purification. Can J Biochem Physiol. 1959 Aug;37(8):911–917. doi: 10.1139/o59-099. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Behling U. H., Pham P. H., Nowotny A. Biological activity of the slime and endotoxin of the periodontopathic organism Eikenella corrodens. Infect Immun. 1979 Nov;26(2):580–584. doi: 10.1128/iai.26.2.580-584.1979. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Brooks G. F., O'Donoghue J. M., Rissing J. P., Soapes K., Smith J. W. Eikenella corrodens, a recently recognized pathogen: infections in medical-surgical patients and in association with methylphenidate abuse. Medicine (Baltimore) 1974 Sep;53(5):325–342. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Cheetham P. S. Removal of triton X-100 from aqueous solution using amberlite XAD-2. Anal Biochem. 1979 Jan 15;92(2):447–452. doi: 10.1016/0003-2697(79)90683-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Darveau R. P., Charnetzky W. T., Hurlbert R. E. Outer membrane protein composition of Yersinia pestis at different growth stages and incubation temperatures. J Bacteriol. 1980 Aug;143(2):942–949. doi: 10.1128/jb.143.2.942-949.1980. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Decad G. M., Nikaido H. Outer membrane of gram-negative bacteria. XII. Molecular-sieving function of cell wall. J Bacteriol. 1976 Oct;128(1):325–336. doi: 10.1128/jb.128.1.325-336.1976. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Devoe I. W., Golchrist J. E. Localization of tetramethylphenylenediamine-oxidase in the outer cell wall layer of Neisseria meningitidis. J Bacteriol. 1976 Oct;128(1):144–148. doi: 10.1128/jb.128.1.144-148.1976. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- DiRienzo J. M., Nakamura K., Inouye M. The outer membrane proteins of Gram-negative bacteria: biosynthesis, assembly, and functions. Annu Rev Biochem. 1978;47:481–532. doi: 10.1146/annurev.bi.47.070178.002405. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Fairbanks G., Steck T. L., Wallach D. F. Electrophoretic analysis of the major polypeptides of the human erythrocyte membrane. Biochemistry. 1971 Jun 22;10(13):2606–2617. doi: 10.1021/bi00789a030. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Glassman A. B., Simpson J. S. Eikenella corrodens: a clinical problem. J Am Dent Assoc. 1975 Dec;91(6):1237–1241. doi: 10.14219/jada.archive.1975.0540. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Goodman A. D. Eikenella corrodens isolated in oral infections of dental origin. Oral Surg Oral Med Oral Pathol. 1977 Jul;44(1):128–134. doi: 10.1016/0030-4220(77)90254-7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hadzija O. A simple method for the quantitative determination of muramic acid. Anal Biochem. 1974 Aug;60(2):512–517. doi: 10.1016/0003-2697(74)90261-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hancock R. E., Carey A. M. Outer membrane of Pseudomonas aeruginosa: heat- 2-mercaptoethanol-modifiable proteins. J Bacteriol. 1979 Dec;140(3):902–910. doi: 10.1128/jb.140.3.902-910.1979. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hancock R. E., Nikaido H. Outer membranes of gram-negative bacteria. XIX. Isolation from Pseudomonas aeruginosa PAO1 and use in reconstitution and definition of the permeability barrier. J Bacteriol. 1978 Oct;136(1):381–390. doi: 10.1128/jb.136.1.381-390.1978. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Heckels J. E. The surface of Neisseria gonorrhoeae: isolation of the major components of the outer membrane. J Gen Microbiol. 1977 Apr;99(2):333–341. doi: 10.1099/00221287-99-2-333. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Henriksen S. D. Corroding bacteria from the respiratory tract. 2. Bacteroides corrodens. Acta Pathol Microbiol Scand. 1969;75(1):91–96. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hofstad T. Chemical characteristics of Bacteroides melaninogenicus endotoxin. Arch Oral Biol. 1968 Sep;13(9):1149–1155. doi: 10.1016/0003-9969(68)90067-8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Jones J. L., Romig D. A. Eikenella corrodens: a pathogen in head and neck infections. Oral Surg Oral Med Oral Pathol. 1979 Dec;48(6):501–505. doi: 10.1016/0030-4220(79)90292-5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kamio Y., Takahashi H. Outer membrane proteins and cell surface structure of Selenomonas ruminantium. J Bacteriol. 1980 Feb;141(2):899–907. doi: 10.1128/jb.141.2.899-907.1980. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kaplan J. M., McCracken G. H., Jr, Nelson J. D. Infections in children caused by the HB group of bacteria. J Pediatr. 1973 Mar;82(3):398–403. doi: 10.1016/s0022-3476(73)80112-x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Karkhanis Y. D., Zeltner J. Y., Jackson J. J., Carlo D. J. A new and improved microassay to determine 2-keto-3-deoxyoctonate in lipopolysaccharide of Gram-negative bacteria. Anal Biochem. 1978 Apr;85(2):595–601. doi: 10.1016/0003-2697(78)90260-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kasper D. L. Chemical and biological characterization of the lipopolysaccharide of Bacteroides fragilis subspecies fragilis. J Infect Dis. 1976 Jul;134(1):59–66. doi: 10.1093/infdis/134.1.59. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kiley P., Holt S. C. Characterization of the lipopolysaccharide from Actinobacillus actinomycetemcomitans Y4 and N27. Infect Immun. 1980 Dec;30(3):862–873. doi: 10.1128/iai.30.3.862-873.1980. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Laemmli U. K. Cleavage of structural proteins during the assembly of the head of bacteriophage T4. Nature. 1970 Aug 15;227(5259):680–685. doi: 10.1038/227680a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Limjuco G. A., Karkhanis Y. D., Zeltner J. Y., Maigetter R. Z., King J. J., Carlo D. J. Studies on the chemical composition of lipopolysaccharide from Neisseria meningitidis group B. J Gen Microbiol. 1978 Feb;104(2):187–191. doi: 10.1099/00221287-104-2-187. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Loeb M. R., Zachary A. L., Smith D. H. Isolation and partial characterization of outer and inner membranes from encapsulated Haemophilus influenzae type b. J Bacteriol. 1981 Jan;145(1):596–604. doi: 10.1128/jb.145.1.596-604.1981. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lugtenberg B., Bronstein H., van Selm N., Peters R. Peptidoglycan-associated outer membrane proteins in gammegatine bacteria. Biochim Biophys Acta. 1977 Mar 17;465(3):571–578. doi: 10.1016/0005-2736(77)90274-7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lugtenberg B., Van Alphen L. Molecular architecture and functioning of the outer membrane of Escherichia coli and other gram-negative bacteria. Biochim Biophys Acta. 1983 Mar 21;737(1):51–115. doi: 10.1016/0304-4157(83)90014-x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mansheim B. J., Onderdonk A. B., Kasper D. L. Immunochemical and biologic studies of the lipopolysaccharide of Bacteroides melaninogenicus subspecies asaccharolyticus. J Immunol. 1978 Jan;120(1):72–78. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Marsden H. B., Hyde W. A. Isolation of Bacteroides corrodens from infections in children. J Clin Pathol. 1971 Mar;24(2):117–119. doi: 10.1136/jcp.24.2.117. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Matsushita K., Adachi O., Shinagawa E., Ameyama M. Isolation and characterization of outer and inner membranes from Pseudomonas aeruginosa and effect of EDTA on the membranes. J Biochem. 1978 Jan;83(1):171–181. doi: 10.1093/oxfordjournals.jbchem.a131888. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Miura T., Mizushima S. Separation by density gradient centrifugation of two types of membranes from spheroplast membrane of Escherichia coli K12. Biochim Biophys Acta. 1968 Jan 3;150(1):159–161. doi: 10.1016/0005-2736(68)90020-5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mizuno T., Kageyama M. Separation and characterization of the outer membrane of Pseudomonas aeruginosa. J Biochem. 1978 Jul;84(1):179–191. doi: 10.1093/oxfordjournals.jbchem.a132106. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Nakae T., Nikaido H. Outer membrane as a diffusion barrier in Salmonella typhimurium. Penetration of oligo- and polysaccharides into isolated outer membrane vesicles and cells with degraded peptidoglycan layer. J Biol Chem. 1975 Sep 25;250(18):7359–7365. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Newman M. G., Socransky S. S., Savitt E. D., Propas D. A., Crawford A. Studies of the microbiology of periodontosis. J Periodontol. 1976 Jul;47(7):373–379. doi: 10.1902/jop.1976.47.7.373. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Orndorff P. E., Dworkin M. Separation and properties of the cytoplasmic and outer membranes of vegetative cells of Myxococcus xanthus. J Bacteriol. 1980 Feb;141(2):914–927. doi: 10.1128/jb.141.2.914-927.1980. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Osborn M. J., Gander J. E., Parisi E., Carson J. Mechanism of assembly of the outer membrane of Salmonella typhimurium. Isolation and characterization of cytoplasmic and outer membrane. J Biol Chem. 1972 Jun 25;247(12):3962–3972. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Progulske A., Holt S. C. Transmission-scanning electron microscopic observations of selected Eikenella corrodens strains. J Bacteriol. 1980 Aug;143(2):1003–1018. doi: 10.1128/jb.143.2.1003-1018.1980. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Progulske A., Mishell R., Trummel C., Holt S. C. Biological activities of Eikenella corrodens outer membrane and lipopolysaccharide. Infect Immun. 1984 Jan;43(1):178–182. doi: 10.1128/iai.43.1.178-182.1984. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Schnaitman C. A. Comparison of the envelope protein compositions of several gram-negative bacteria. J Bacteriol. 1970 Dec;104(3):1404–1405. doi: 10.1128/jb.104.3.1404-1405.1970. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Schnaitman C. A. Protein composition of the cell wall and cytoplasmic membrane of Escherichia coli. J Bacteriol. 1970 Nov;104(2):890–901. doi: 10.1128/jb.104.2.890-901.1970. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Schnaitman C. A. Solubilization of the cytoplasmic membrane of Escherichia coli by Triton X-100. J Bacteriol. 1971 Oct;108(1):545–552. doi: 10.1128/jb.108.1.545-552.1971. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Smith H. Microbial surfaces in relation to pathogenicity. Bacteriol Rev. 1977 Jun;41(2):475–500. doi: 10.1128/br.41.2.475-500.1977. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Socransky S. S. Microbiology of periodontal disease -- present status and future considerations. J Periodontol. 1977 Sep;48(9):497–504. doi: 10.1902/jop.1977.48.9.497. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Stern K., Nersasian R. R., O'Keefe P., Plisner K., Doku H. C. Eikenella osteomyelitis of the mandible associated with anemia of chronic disease. J Oral Surg. 1978 Apr;36(4):285–289. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Steven A. C., Heggeler B., Müller R., Kistler J., Rosenbusch J. P. Ultrastructure of a periodic protein layer in the outer membrane of Escherichia coli. J Cell Biol. 1977 Feb;72(2):292–301. doi: 10.1083/jcb.72.2.292. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Stevens R. H., Sela M. N., McArthur W. P., Nowotny A., Hammond B. F. Biological and chemical characterization of endotoxin from Capnocytophaga sputigena. Infect Immun. 1980 Jan;27(1):246–254. doi: 10.1128/iai.27.1.246-254.1980. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sveen K. The capacity of lipopolysaccharides from bacteroides, fusobacterium and veillonella to produce skin inflammation and the local and generalized Shwartzman reaction in rabbits. J Periodontal Res. 1977 Sep;12(5):340–350. doi: 10.1111/j.1600-0765.1977.tb01525.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Tanner A. C., Haffer C., Bratthall G. T., Visconti R. A., Socransky S. S. A study of the bacteria associated with advancing periodontitis in man. J Clin Periodontol. 1979 Oct;6(5):278–307. doi: 10.1111/j.1600-051x.1979.tb01931.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Tsai C. M., Frasch C. E. A sensitive silver stain for detecting lipopolysaccharides in polyacrylamide gels. Anal Biochem. 1982 Jan 1;119(1):115–119. doi: 10.1016/0003-2697(82)90673-x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Westphal O. Bacterial endotoxins. The second Carl Prausnitz Memorial Lecture. Int Arch Allergy Appl Immunol. 1975;49(1-2):1–43. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wright B. G., Rebers P. A. Procedure for determining heptose and hexose in lipopolysaccharides. Modification of the cysteine-sulfuric acid method. Anal Biochem. 1972 Oct;49(2):307–319. doi: 10.1016/0003-2697(72)90433-2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]