Abstract
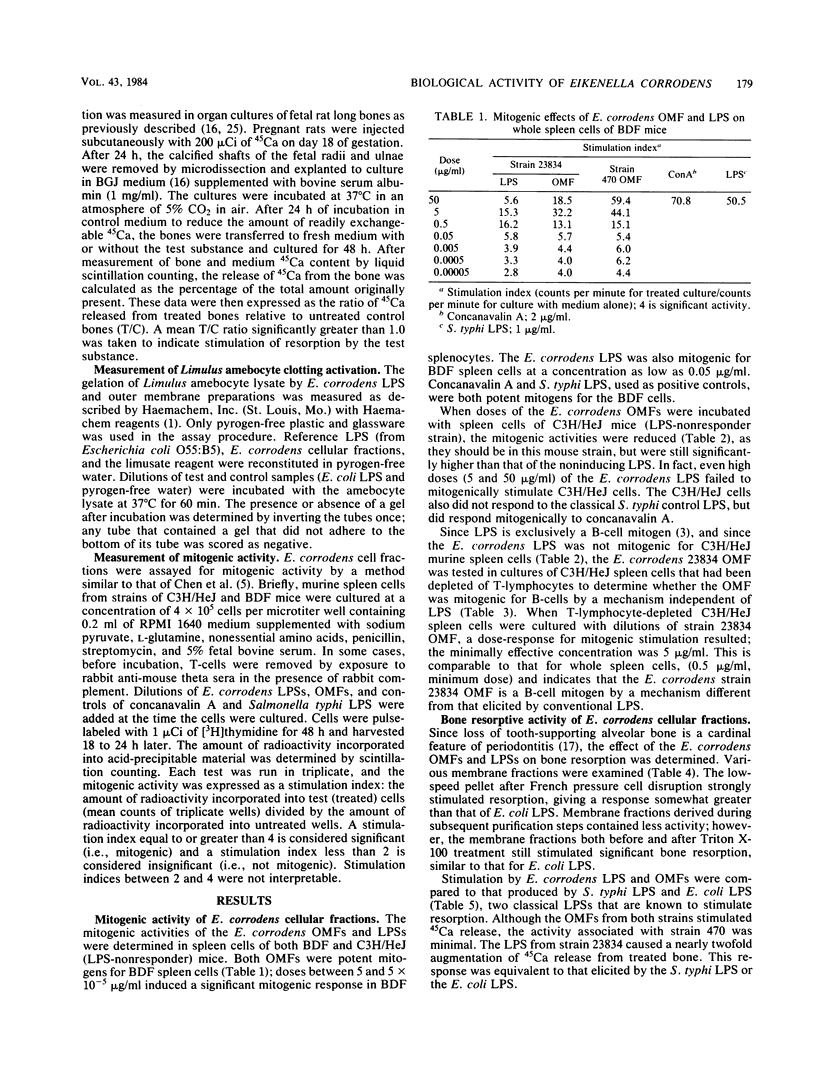
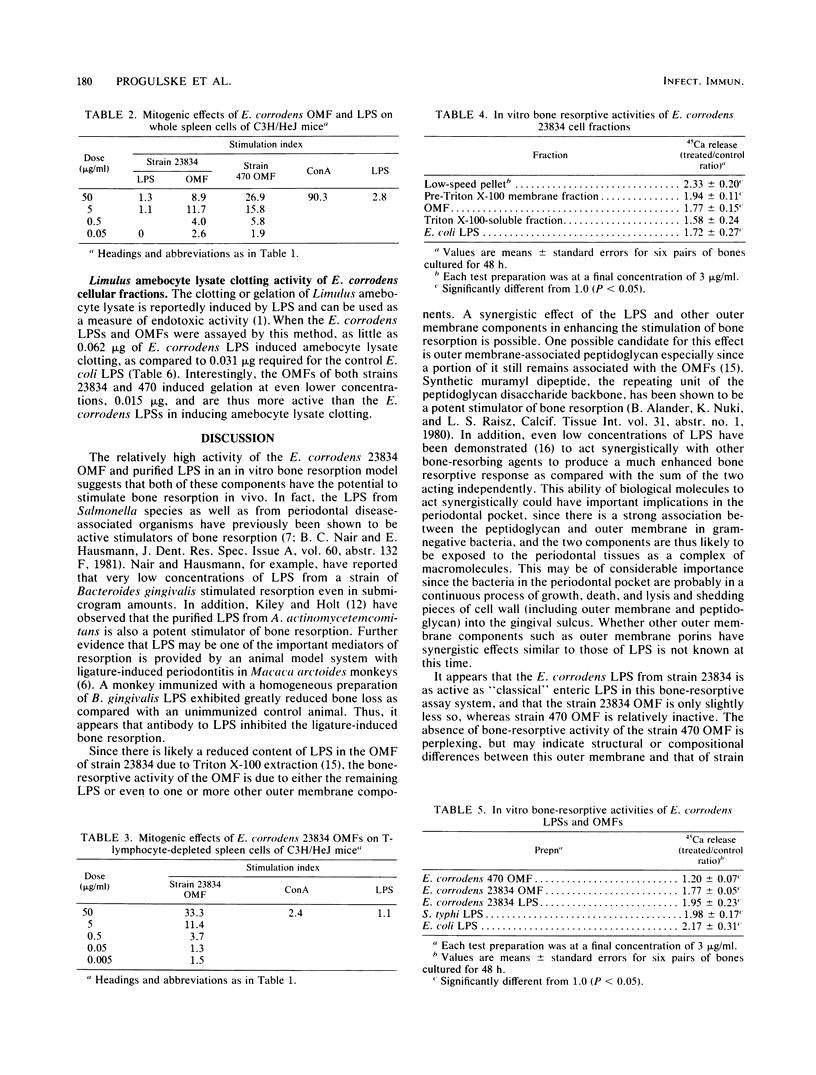
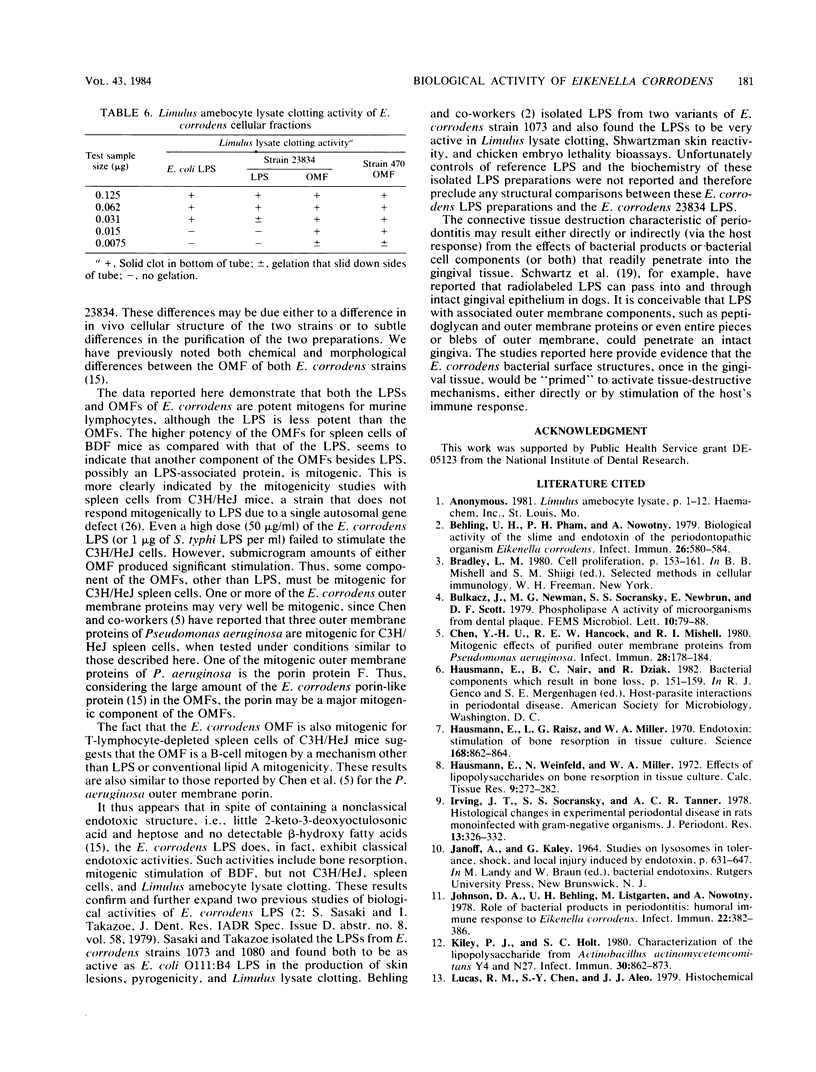
Highly purified preparations of the outer membrane and lipopolysaccharide (LPS) of Eikenella corrodens strain ATCC 23834 and the outer membrane fraction (OMF) of strain 470 were tested in in vitro biological assays. The OMFs of both strains were found to be mitogenic for BDF and C3H/HeJ murine splenocytes. The E. corrodens LPS was mitogenic for BDF spleen cells; however, doses of LPS as high as 50 micrograms/ml failed to stimulate C3H/HeJ cells. When incubated with T-lymphocyte-depleted C3H/HeJ splenocytes, the strain 23834 OMF demonstrated significant mitogenic activity, indicating that the OMF is a B-cell mitogen by a mechanism other than that elicited by conventional LPS. The E. corrodens 23834 OMF and LPS were stimulators of bone resorption when tested in organ cultures of fetal rat long bones. In contrast, the strain 470 OMF was only weakly stimulatory. Both OMFs and LPSs demonstrated "endotoxic" activity, since as little as 0.062 micrograms of E. corrodens LPS and 0.015 micrograms of the OMFs induced gelation in the Limulus amebocyte clotting assay. Thus, despite having a "nonclassical" LPS biochemistry, the E. corrodens LPS elicits classical endotoxic activities. These results also indicate that the surface structures of E. corrodens have significant biological activities as measured in vitro. The expression of such activities in vivo may play an important role in the pathogenesis of periodontitis as well as other E. corrodens infections.
Full text
PDF

Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Behling U. H., Pham P. H., Nowotny A. Biological activity of the slime and endotoxin of the periodontopathic organism Eikenella corrodens. Infect Immun. 1979 Nov;26(2):580–584. doi: 10.1128/iai.26.2.580-584.1979. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Chen Y. H., Hancock R. E., Mishell R. I. Mitogenic effects of purified outer membrane proteins from Pseudomonas aeruginosa. Infect Immun. 1980 Apr;28(1):178–184. doi: 10.1128/iai.28.1.178-184.1980. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hausmann E., Raisz L. G., Miller W. A. Endotoxin: stimulation of bone resorption in tissue culture. Science. 1970 May 15;168(3933):862–864. doi: 10.1126/science.168.3933.862. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hausmann E., Weinfeld N., Miller W. A. Effects of lipopolysaccharides on bone resorption in tissue culture. Calcif Tissue Res. 1972;9(4):272–282. doi: 10.1007/BF02061967. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Irving J. T., Socransky S. S., Tanner A. C. Histological changes in experimental periodontal disease in rats monoinfected with gram-negative organisms. J Periodontal Res. 1978 Jul;13(4):326–332. doi: 10.1111/j.1600-0765.1978.tb00187.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Johnson D. A., Behling U. H., Listgarten M., Nowotny A. Role of bacterial products in periodontitis: humoral immune response to Eikenella corrodens. Infect Immun. 1978 Nov;22(2):382–386. doi: 10.1128/iai.22.2.382-386.1978. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kiley P., Holt S. C. Characterization of the lipopolysaccharide from Actinobacillus actinomycetemcomitans Y4 and N27. Infect Immun. 1980 Dec;30(3):862–873. doi: 10.1128/iai.30.3.862-873.1980. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Page R. C., Schroeder H. E. Pathogenesis of inflammatory periodontal disease. A summary of current work. Lab Invest. 1976 Mar;34(3):235–249. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Progulske A., Holt S. C. Isolation and characterization of the outer membrane and lipopolysaccharide from Eikenella corrodens. Infect Immun. 1984 Jan;43(1):166–177. doi: 10.1128/iai.43.1.166-177.1984. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Raisz L. G., Nuki K., Alander C. B., Craig R. G. Interactions between bacterial endotoxin and other stimulators of bone resorption in organ culture. J Periodontal Res. 1981 Jan;16(1):1–7. doi: 10.1111/j.1600-0765.1981.tb00943.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Robertson P. B., Lantz M., Marucha P. T., Kornman K. S., Trummel C. L., Holt S. C. Collagenolytic activity associated with Bacteroides species and Actinobacillus actinomycetemcomitans. J Periodontal Res. 1982 May;17(3):275–283. doi: 10.1111/j.1600-0765.1982.tb01154.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Schwartz J., Stinson F. L., Parker R. B. The passage of tritiated bacterial endotoxin across intact gingival crevicular epithelium. J Periodontol. 1972 May;43(5):270–276. doi: 10.1902/jop.1972.43.5.270. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Socransky S. S. Microbiology of periodontal disease -- present status and future considerations. J Periodontol. 1977 Sep;48(9):497–504. doi: 10.1902/jop.1977.48.9.497. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Taichman N. S., Wilton J. M. Leukotoxicity of an extract from Actinobacillus actinomycetemcomitans for human gingival polymorphonuclear leukocytes. Inflammation. 1981 Mar;5(1):1–12. doi: 10.1007/BF00910774. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Tanner A. C., Haffer C., Bratthall G. T., Visconti R. A., Socransky S. S. A study of the bacteria associated with advancing periodontitis in man. J Clin Periodontol. 1979 Oct;6(5):278–307. doi: 10.1111/j.1600-051x.1979.tb01931.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Trummel C. L., Mundy G. R., Raisz L. G. Release of osteoclast activating factor by normal human peripheral blood leukocytes. J Lab Clin Med. 1975 Jun;85(6):1001–1007. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Watson J., Riblet R. Genetic control of responses to bacterial lipopolysaccharides in mice. I. Evidence for a single gene that influences mitogenic and immunogenic respones to lipopolysaccharides. J Exp Med. 1974 Nov 1;140(5):1147–1161. doi: 10.1084/jem.140.5.1147. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]


