Abstract
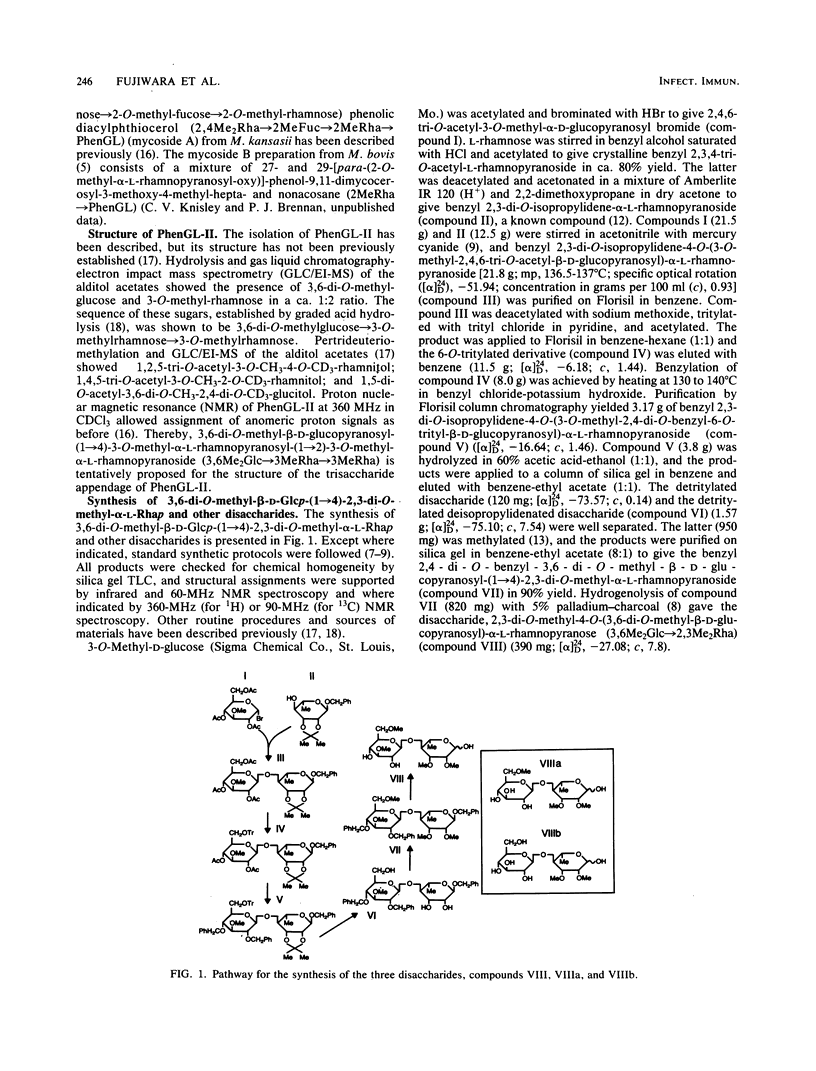
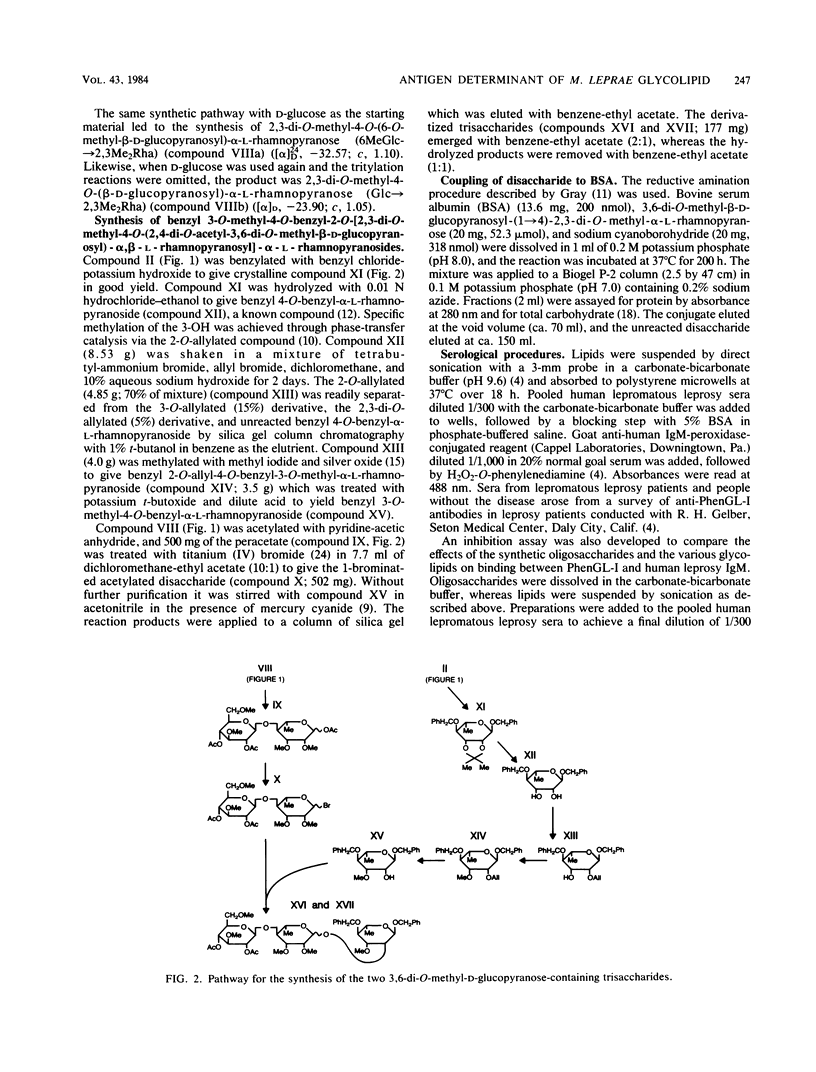
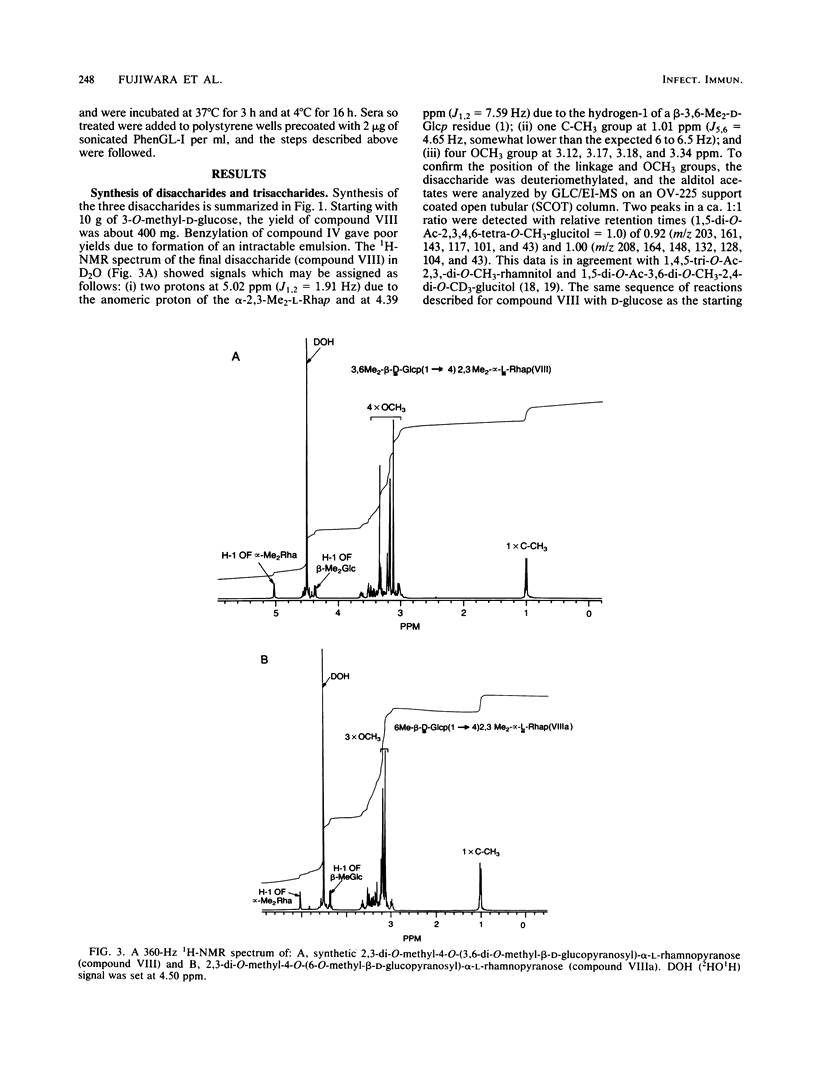
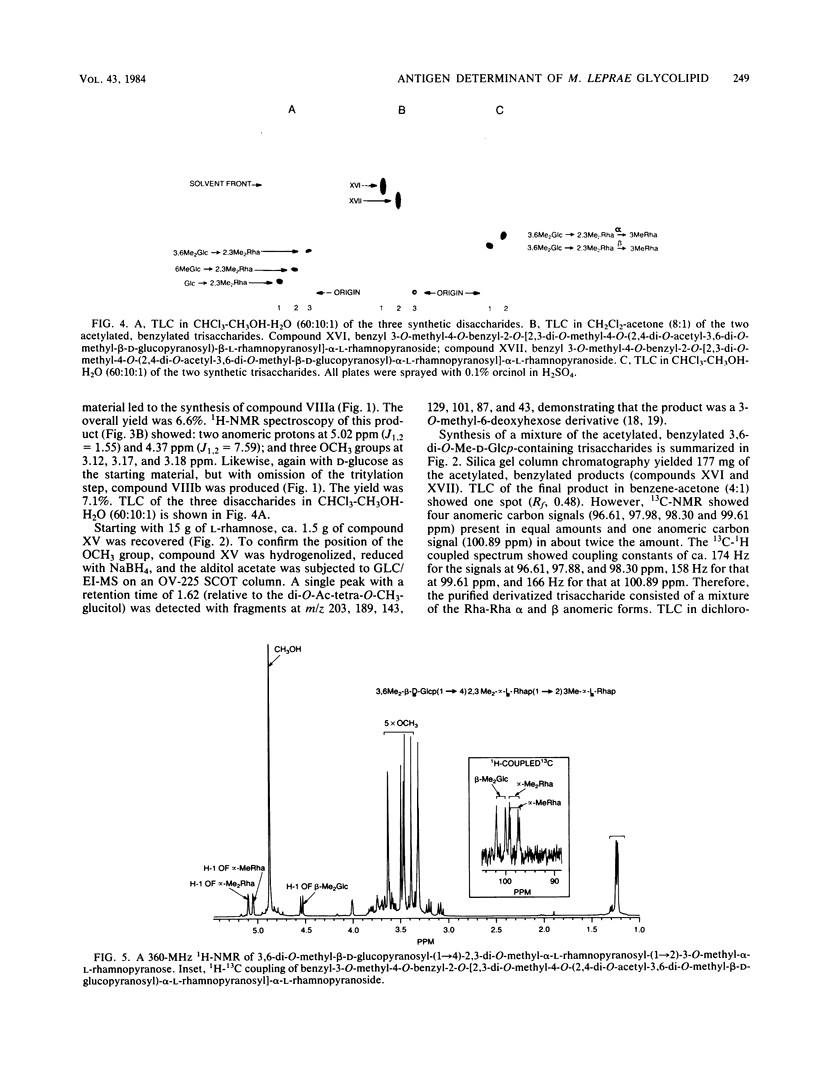
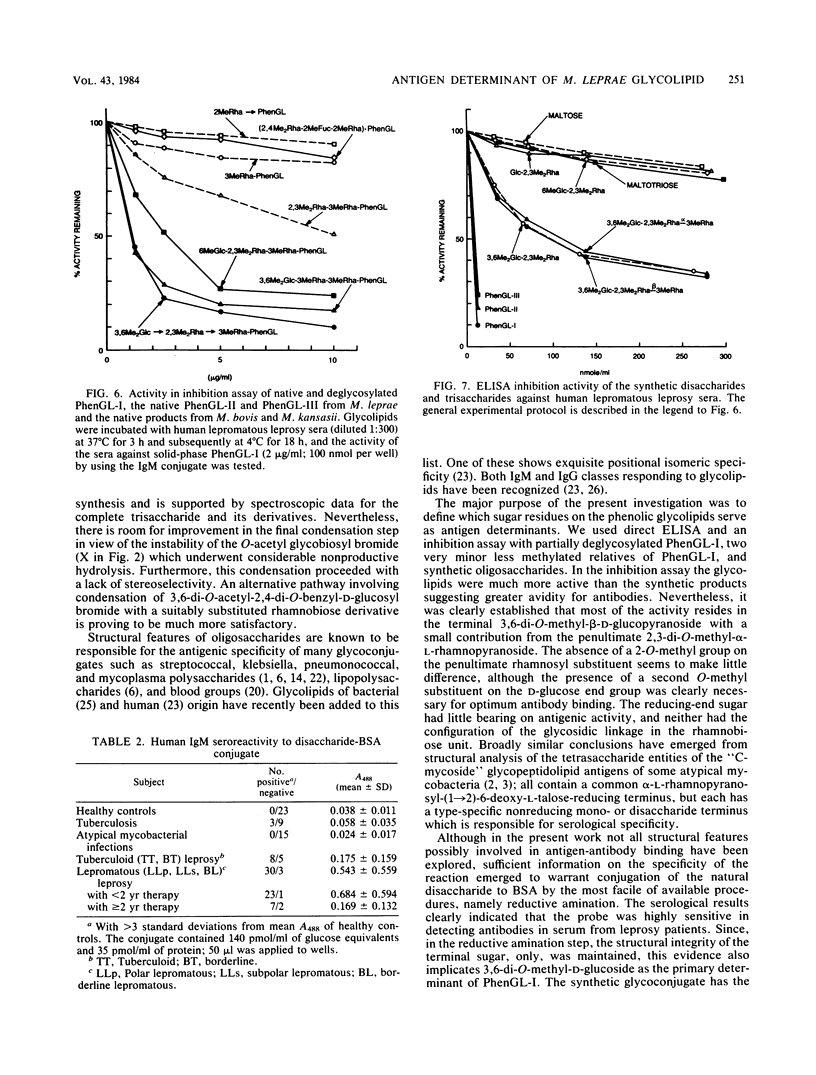
We examined the structural requirements within the species-specific 3,6-di-O-methyl-beta-D-glucopyranosyl-(1 leads to 4)-2,3-di-O-methyl- alpha-L-rhamnopyranosyl-(1 leads to 2)-3-O-methyl-alpha-L-rhamnopyranose unit of the phenolic glycolipid I antigen of Mycobacterium leprae for binding to anti-glycolipid immunoglobulin M from human leprosy sera. We used chemically defined, partially deglycosylated fragments of phenolic glycolipid I, two other minor M. leprae-specific phenolic glycolipids (those containing 6-O-methyl-beta-D-glucopyranosyl-(1 leads to 4)-2,3-di-O-methyl-alpha- L-rhamnopyranosyl-(1 leads to 2)-3-O-methyl-alpha-L-rhamnopyranose and 3,6-di-O-methyl-beta-D-glucopyranosyl-(1 leads to 4)-3-O-methyl-alpha- L-rhamnopyranosyl-(1 leads to 2)-3-O-methyl-alpha-rhamnopyranose units), and phenolic glycolipids from other mycobacteria. Additionally, the trisaccharide of phenolic glycolipid I, the 3,6-di-O-methyl-beta-D-glucopyranosyl-(1 leads to 4)-2, 3-di-O-methyl-alpha-L-rhamnopyranose, the 6-O-methyl-beta-D-glucopyranosyl-(1 leads to 4)-2,3-di-O-methyl-alpha- L-rhamnopyranose, and the beta-D-glucopyranosyl-(1 leads to 4)-2,3-di-O-methyl-alpha- L-rhamnopyranose disaccharides were synthesized and characterized, and their activities were examined. Only the phenolic glycolipids containing 3,6-di-O-methyl-beta-D-glucopyranosyl at the nonreducing terminus were efficient in binding the anti-glycolipid immunoglobulin M, and the 3,6-di-O-methyl-beta-D-glucopyranosyl-containing di- and trisaccharides were the most effective in inhibiting this binding. Thus, the 3,6-di-O-methyl-beta-D-glucopyranosyl substituent was recognized as the primary antigen determinant in phenolic glycolipid I. With this information, bovine serum albumin containing reductively aminated 3,6-di-O-methyl-beta-D-glucopyranosyl-(1 leads to 4)-2,3-di-O-methyl- L-rhamnose was prepared and shown to be highly active in the serodiagnosis of leprosy.
Full text
PDF


Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Al-Samarrai T. H., Smith P. F., Lynn R. J. Identification of the major antigenic determinants on lipoglycans from Acholeplasma granularum and Acholeplasma axanthum. Infect Immun. 1983 May;40(2):629–632. doi: 10.1128/iai.40.2.629-632.1983. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Brennan P. J., Aspinall G. O., Shin J. E. Structure of the specific oligosaccharides from the glycopeptidolipid antigens of serovars in the Mycobacterium avium-Mycobacterium intracellulare-Mycobacterium scrofulaceum complex. J Biol Chem. 1981 Jul 10;256(13):6817–6822. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Brennan P. J., Mayer H., Aspinall G. O., Nam Shin J. E. Structures of the glycopeptidolipid antigens from serovars in the Mycobacterium avium/Mycobacterium intracellulare/Mycobacterium scrofulaceum serocomplex. Eur J Biochem. 1981 Mar 16;115(1):7–15. doi: 10.1111/j.1432-1033.1981.tb06190.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Brett S. J., Draper P., Payne S. N., Rees R. J. Serological activity of a characteristic phenolic glycolipid from Mycobacterium leprae in sera from patients with leprosy and tuberculosis. Clin Exp Immunol. 1983 May;52(2):271–279. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Chan W. W., Schutt H., Brand K. Active subunits of transaldolase bound to sepharose. Eur J Biochem. 1973 Dec 17;40(2):533–541. doi: 10.1111/j.1432-1033.1973.tb03224.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Cho S. N., Yanagihara D. L., Hunter S. W., Gelber R. H., Brennan P. J. Serological specificity of phenolic glycolipid I from Mycobacterium leprae and use in serodiagnosis of leprosy. Infect Immun. 1983 Sep;41(3):1077–1083. doi: 10.1128/iai.41.3.1077-1083.1983. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- DEMARTEAU-GINSBURG H., LEDERER E. SUR LA STRUCTURE CHIMIQUE DU MYCOSIDE B. Biochim Biophys Acta. 1963 Aug 27;70:442–451. doi: 10.1016/0006-3002(63)90774-1. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gray G. R. Antibodies to carbohydrates: preparation of antigens by coupling carbohydrates to proteins by reductive amination with cyanoborohydride. Methods Enzymol. 1978;50:155–160. doi: 10.1016/0076-6879(78)50014-1. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- HAKOMORI S. A RAPID PERMETHYLATION OF GLYCOLIPID, AND POLYSACCHARIDE CATALYZED BY METHYLSULFINYL CARBANION IN DIMETHYL SULFOXIDE. J Biochem. 1964 Feb;55:205–208. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Heidelberger M., Dudman W. F., Nimmich W. Immunochemical relationships of certain capsular polysaccharides of Klebsiella, pneumococci and Rhizobia. J Immunol. 1970 Jun;104(6):1321–1328. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hunter S. W., Brennan P. J. A novel phenolic glycolipid from Mycobacterium leprae possibly involved in immunogenicity and pathogenicity. J Bacteriol. 1981 Sep;147(3):728–735. doi: 10.1128/jb.147.3.728-735.1981. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hunter S. W., Brennan P. J. Further specific extracellular phenolic glycolipid antigens and a related diacylphthiocerol from Mycobacterium leprae. J Biol Chem. 1983 Jun 25;258(12):7556–7562. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hunter S. W., Fujiwara T., Brennan P. J. Structure and antigenicity of the major specific glycolipid antigen of Mycobacterium leprae. J Biol Chem. 1982 Dec 25;257(24):15072–15078. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- MCCARTY M. Variation in the group-specific carbohydrate of group A streptococci. II. Studies on the chemical basis for serological specificity of the carbohydrates. J Exp Med. 1956 Nov 1;104(5):629–643. doi: 10.1084/jem.104.5.629. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Maugh T. H., 2nd Leprosy vaccine trials to begin soon. Science. 1982 Feb 26;215(4536):1083–1086. doi: 10.1126/science.7063841. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Nudelman E., Kannagi R., Hakomori S., Parsons M., Lipinski M., Wiels J., Fellous M., Tursz T. A glycolipid antigen associated with Burkitt lymphoma defined by a monoclonal antibody. Science. 1983 Apr 29;220(4596):509–511. doi: 10.1126/science.6836295. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Paulsen H., Bünsch A. Synthesis of the pentasaccharide chain of the Forssman antigen. Angew Chem Int Ed Engl. 1980;19(11):902–903. doi: 10.1002/anie.198009021. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sugiyama T., Smith P. F., Langworthy T. A., Mayberry W. R. Immunological analysis of glycolipids and lipopolysaccharides derived from various mycoplasmas. Infect Immun. 1974 Dec;10(6):1273–1279. doi: 10.1128/iai.10.6.1273-1279.1974. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Young W. W., Jr, Hakomori S. I. Therapy of mouse lymphoma with monoclonal antibodies to glycolipid: selection of low antigenic variants in vivo. Science. 1981 Jan 30;211(4481):487–489. doi: 10.1126/science.7455688. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]



