Abstract
The ability of Streptococcus pneumoniae to degrade human secretory immunoglobulin A (S-IgA), IgG, and IgM was tested in 102 strains by use of the thin-layer enzyme assay cultivation technique. The strains were isolated from patients with acute phases of otitis media, meningitis, and pneumonia as well as from symptomless carriers. An ability to degrade S-IgA, IgG, and IgM was revealed in 50, 84, and 96 strains, respectively. An IgG- and IgM-degrading ability of S. pneumoniae has not previously been reported. A concurrent degradation of the three immunoglobulins was revealed in 38 strains; degradation of two of them was revealed in 54 strains, and degradation of only one of them was revealed in 9 strains. One strain failed to degrade any of the immunoglobulins. Correlations were not found between the ability of the S. pneumoniae strains to degrade S-IgA, IgG, or IgM and the serotype affiliation or between the ability to degrade IgG or IgM and the origin of strains. However, the ability to degrade S-IgA was evident more often in strains isolated from symptomless carriers and from bronchial secretions of patients with acute pneumonia than it was in strains from patients with acute meningitis or acute otitis media or from the blood of patients with acute pneumonia. These latter findings may indicate a biological significance of S-IgA-degrading ability in bacterial colonization of mucosal surfaces.
Full text
PDF



Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Delacroix D. L., Dive C., Rambaud J. C., Vaerman J. P. IgA subclasses in various secretions and in serum. Immunology. 1982 Oct;47(2):383–385. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Elwing H., Nygren H. Diffusion in gel-enzyme linked immunosorbent assay (DIG-ELISA): a simple method for quantitation of class-specific antibodies. J Immunol Methods. 1979;31(1-2):101–107. doi: 10.1016/0022-1759(79)90290-4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Fabricius L., Dahlén G., Holm S. E., Möller A. J. Influence of combinations of oral bacteria on periapical tissues of monkeys. Scand J Dent Res. 1982 Jun;90(3):200–206. doi: 10.1111/j.1600-0722.1982.tb00728.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Henrichsen J., Berntsson E., Kaijser B. Comparison of counterimmunoelectrophoresis and the capsular reaction test for typing of pneumococci. J Clin Microbiol. 1980 Jun;11(6):589–592. doi: 10.1128/jcm.11.6.589-592.1980. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kaijser B. Pneumococcal infections and the possible need for a vaccine. Scand J Infect Dis. 1979;11(3):179–184. doi: 10.3109/inf.1979.11.issue-3.01. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kilian M. Degradation of immunoglobulins A2, A2, and G by suspected principal periodontal pathogens. Infect Immun. 1981 Dec;34(3):757–765. doi: 10.1128/iai.34.3.757-765.1981. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kilian M., Holmgren K. Ecology and nature of immunoglobulin A1 protease-producing streptococci in the human oral cavity and pharynx. Infect Immun. 1981 Mar;31(3):868–873. doi: 10.1128/iai.31.3.868-873.1981. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kilian M., Mestecky J., Kulhavy R., Tomana M., Butler W. T. IgA1 proteases from Haemophilus influenzae, Streptococcus pneumoniae, Neisseria meningitidis, and Streptococcus sanguis: comparative immunochemical studies. J Immunol. 1980 Jun;124(6):2596–2600. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kilian M., Mestecky J., Schrohenloher R. E. Pathogenic species of the genus Haemophilus and Streptococcus pneumoniae produce immunoglobulin A1 protease. Infect Immun. 1979 Oct;26(1):143–149. doi: 10.1128/iai.26.1.143-149.1979. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Koide N., Muramatsu T. Endo-beta-N-acetylglucosaminidase acting on carbohydrate moieties of glycoproteins. Purification and properties of the enzyme from Diplococcus pneumoniae. J Biol Chem. 1974 Aug 10;249(15):4897–4904. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kornfeld S. J., Plaut A. G. Secretory immunity and the bacterial IgA proteases. Rev Infect Dis. 1981 May-Jun;3(3):521–534. doi: 10.1093/clinids/3.3.521. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Labib R. S., Calvanico N. J., Tomasi T. B., Jr Studies on extracellular proteases of Streptococcus sanguis. Purification and characterization of a human IgA1 specific protease. Biochim Biophys Acta. 1978 Oct 12;526(2):547–559. doi: 10.1016/0005-2744(78)90145-6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Male C. J. Immunoglobulin A1 protease production by Haemophilus influenzae and Streptococcus pneumoniae. Infect Immun. 1979 Oct;26(1):254–261. doi: 10.1128/iai.26.1.254-261.1979. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mancini G., Carbonara A. O., Heremans J. F. Immunochemical quantitation of antigens by single radial immunodiffusion. Immunochemistry. 1965 Sep;2(3):235–254. doi: 10.1016/0019-2791(65)90004-2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mulks M. H., Kornfeld S. J., Plaut A. G. Specific proteolysis of human IgA by Streptococcus pneumoniae and Haemophilus influenzae. J Infect Dis. 1980 Apr;141(4):450–456. doi: 10.1093/infdis/141.4.450. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mulks M. H., Plaut A. G. IgA protease production as a characteristic distinguishing pathogenic from harmless neisseriaceae. N Engl J Med. 1978 Nov 2;299(18):973–976. doi: 10.1056/NEJM197811022991802. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Nygren H., Hansson H. A., Lange S. Studies on the conjugation of horseradish peroxidase to immunoglobulin G via glutaraldehyde. Med Biol. 1979 Jun;57(3):187–191. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Plaut A. G., Gilbert J. V., Artenstein M. S., Capra J. D. Neisseria gonorrhoeae and neisseria meningitidis: extracellular enzyme cleaves human immunoglobulin A. Science. 1975 Dec 12;190(4219):1103–1105. doi: 10.1126/science.810892. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Plaut A. G. Microbial IgA proteases. N Engl J Med. 1978 Jun 29;298(26):1459–1463. doi: 10.1056/NEJM197806292982608. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Stenberg M., Nygren H. A receptor-ligand reaction studied by a novel analytical tool--the Isoscope ellipsometer. Anal Biochem. 1982 Nov 15;127(1):183–192. doi: 10.1016/0003-2697(82)90163-4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- TRURNIT H. J. Studies on enzyme systems at a solid-liquid interface. II. The kinetics of adsorption and reaction. Arch Biochem Biophys. 1954 Jul;51(1):176–199. doi: 10.1016/0003-9861(54)90466-x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wikström M. B., Dahlén G., Linde A. Fibrinogenolytic and fibrinolytic activity in oral microorganisms. J Clin Microbiol. 1983 May;17(5):759–767. doi: 10.1128/jcm.17.5.759-767.1983. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
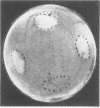
- Wikström M. B. Detection of microbial proteolytic activity by a cultivation plate assay in which different proteins adsorbed to a hydrophobic surface are used as substrates. Appl Environ Microbiol. 1983 Feb;45(2):393–400. doi: 10.1128/aem.45.2.393-400.1983. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]