Abstract
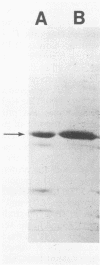
The outer membrane protein F (porin) from the PAO1 strain of Pseudomonas aeruginosa was purified by two different methods. One procedure involved separation by column chromatography of proteins extracted from isolated outer membranes, whereas the other involved extraction from gels after slab polyacrylamide gel electrophoresis of proteins extracted from cell envelopes. Both procedures yielded protein F preparations which successfully immunized mice from subsequent challenge with the PAO1 strain. The protein F preparations contained small quantities of lipopolysaccharide (LPS). This level of LPS contamination protected immunized mice from challenge with the homologous LPS serotype strain. However, immunization of mice with protein F preparations from the PAO1 strain also afforded protection against challenge with two different LPS serotype strains. This protective ability was lost when the protein F preparation was treated with papain before use as a vaccine. These observations support the conclusion that protein F has protective ability, which is not due to LPS contamination, when given as a vaccine. After immunization with the protein F preparation, mice showed an increase in antibody titer to the purified protein F preparation by enzyme-linked immunosorbent assay. Mice were protected passively by administration of rabbit antisera raised to the protein F preparation. These results indicate that the protein F preparation elicits a specific humoral antibody response in immunized animals. Our results suggest that purified protein F has potential as an effective vaccine for P. aeruginosa.
Full text
PDF




Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Adamus G., Mulczyk M., Witkowska D., Romanowska E. Protection against keratoconjunctivitis shigellosa induced by immunization with outer membrane proteins of Shigella spp. Infect Immun. 1980 Nov;30(2):321–324. doi: 10.1128/iai.30.2.321-324.1980. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Buchanan T. M., Pearce W. A., Schoolnik G. K., Arko R. J. Protection against infection with Neisseria gonorrhoeae by immunization with outer membrane protein complex and purified pili. J Infect Dis. 1977 Aug;136 (Suppl):S132–S137. doi: 10.1093/infdis/136.supplement.s132. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Cox C. D. Passage of Pseudomonas aeruginosa in compromised mice. Infect Immun. 1979 Oct;26(1):118–124. doi: 10.1128/iai.26.1.118-124.1979. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Dankert J., Hofstra H. Antibodies against outer membrane proteins in rabbit antisera prepared against Escherichia coli O26 K60. J Gen Microbiol. 1978 Feb;104(2):311–320. doi: 10.1099/00221287-104-2-311. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Dröge W., Lehmann V., Lüderitz O., Westphal O. Structural investigations on the 2-keto-3-deoxyoctonate region of lipopolysaccharides. Eur J Biochem. 1970 May 1;14(1):175–184. doi: 10.1111/j.1432-1033.1970.tb00276.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Fernandes P. B., Kim C., Cundy K. R., Haung N. N. Antibodies to cell envelope proteins of Pseudomonas aeruginosa in cystic fibrosis patients. Infect Immun. 1981 Aug;33(2):527–532. doi: 10.1128/iai.33.2.527-532.1981. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gilleland H. E., Jr, Lyle R. D. Chemical alterations in cell envelopes of polymyxin-resistant Pseudomonas aeruginosa isolates. J Bacteriol. 1979 Jun;138(3):839–845. doi: 10.1128/jb.138.3.839-845.1979. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gilleland H. E., Jr, Murray R. G. Ultrastructural study of polymyxin-resistant isolates of Pseudomonas aeruginosa. J Bacteriol. 1976 Jan;125(1):267–281. doi: 10.1128/jb.125.1.267-281.1976. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gulig P. A., McCracken G. H., Jr, Frisch C. F., Johnston K. H., Hansen E. J. Antibody response of infants to cell surface-exposed outer membrane proteins of Haemophilus influenzae type b after systemic Haemophilus disease. Infect Immun. 1982 Jul;37(1):82–88. doi: 10.1128/iai.37.1.82-88.1982. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hansen E. J., Frisch C. F., McDade R. L., Jr, Johnston K. H. Identification of immunogenic outer membrane proteins of Haemophilus influenzae type b in the infant rat model system. Infect Immun. 1981 Jun;32(3):1084–1092. doi: 10.1128/iai.32.3.1084-1092.1981. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hofstra H., Dankert J. Preparation and quantitative determination of antibodies against major outer mambranes proteins of Escherichia coli O26 K60. J Gen Microbiol. 1980 Apr;117(2):437–447. doi: 10.1099/00221287-117-2-437. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Holby N., Olling S. Pseudomonas aeruginosa infection in cystic fibrosis. Bactericidal effect of serum from normal individuals and patients with cystic fibrosis on P. aeruginosa strains from patients with cystic fibrosis or other diseases. Acta Pathol Microbiol Scand C. 1977 Apr;85(2):107–114. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Homma J. Y., Ghoda A., Goto S., Jo K., Kato I., Kodama H., Kosakai N., Kono M., Shionoya H., Terada Y. Proposal of an international standard for the infraspecific serologic classification of Pseudomonas aeruginosa. Jpn J Exp Med. 1979 Feb;49(1):89–94. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kabir S. Composition and immunochemical properties of outer membrane proteins of Vibrio cholerae. J Bacteriol. 1980 Oct;144(1):382–389. doi: 10.1128/jb.144.1.382-389.1980. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Karch H., Nixdorff K. Antibody-producing cell responses to an isolated outer membrane protein and to complexes of this antigen with lipopolysaccharide or with vesicles of phospholipids from Proteus mirabilis. Infect Immun. 1981 Mar;31(3):862–867. doi: 10.1128/iai.31.3.862-867.1981. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kuusi N., Nurminen M., Saxen H., Valtonen M., Mäkelä P. H. Immunization with major outer membrane proteins in experimental salmonellosis of mice. Infect Immun. 1979 Sep;25(3):857–862. doi: 10.1128/iai.25.3.857-862.1979. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kuusi N., Nurminen M., Saxén H., Mäkelä P. H. Immunization with major outer membrane protein (porin) preparations in experimental murine salmonellosis: effect of lipopolysaccharide. Infect Immun. 1981 Nov;34(2):328–332. doi: 10.1128/iai.34.2.328-332.1981. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Loeb M. R., Smith D. H. Human antibody response to individual outer membrane proteins of Haemophilus influenzae type b. Infect Immun. 1982 Sep;37(3):1032–1036. doi: 10.1128/iai.37.3.1032-1036.1982. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Markwell M. A., Haas S. M., Bieber L. L., Tolbert N. E. A modification of the Lowry procedure to simplify protein determination in membrane and lipoprotein samples. Anal Biochem. 1978 Jun 15;87(1):206–210. doi: 10.1016/0003-2697(78)90586-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Meister A., Tate S. S., Griffith O. W. Gamma-glutamyl transpeptidase. Methods Enzymol. 1981;77:237–253. doi: 10.1016/s0076-6879(81)77032-0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mutharia L. M., Nicas T. I., Hancock R. E. Outer membrane proteins of Pseudomonas aeruginosa serotype strains. J Infect Dis. 1982 Dec;146(6):770–779. doi: 10.1093/infdis/146.6.770. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Nathan P., Holder I. A., MacMillan B. G. Burn wounds: microbiology, local host defenses, and current therapy. CRC Crit Rev Clin Lab Sci. 1973 Jul;4(1):61–100. doi: 10.3109/10408367309151684. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Pier G. B., Sidberry H. F., Sadoff J. C. Protective immunity induced in mice by immunization with high-molecular-weight polysaccharide from Pseudomonas aeruginosa. Infect Immun. 1978 Dec;22(3):919–925. doi: 10.1128/iai.22.3.919-925.1978. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Robertson S. M., Frisch C. F., Gulig P. A., Kettman J. R., Johnston K. H., Hansen E. J. Monoclonal antibodies directed against a cell surface-exposed outer membrane protein of Haemophilus influenzae type b. Infect Immun. 1982 Apr;36(1):80–88. doi: 10.1128/iai.36.1.80-88.1982. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Whitecar J. P., Jr, Luna M., Bodey G. P. Pseudomonas bacteremia in patients with malignant diseases. Am J Med Sci. 1970 Oct;60(4):216–223. doi: 10.1097/00000441-197010000-00003. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Yoshimura F., Zalman L. S., Nikaido H. Purification and properties of Pseudomonas aeruginosa porin. J Biol Chem. 1983 Feb 25;258(4):2308–2314. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Zollinger W. D., Mandrell R. E., Altieri P., Berman S., Lowenthal J., Artenstein M. S. Safety and immunogenicity of a Neisseria meningitidis type 2 protein vaccine in animals and humans. J Infect Dis. 1978 Jun;137(6):728–739. doi: 10.1093/infdis/137.6.728. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]