Abstract
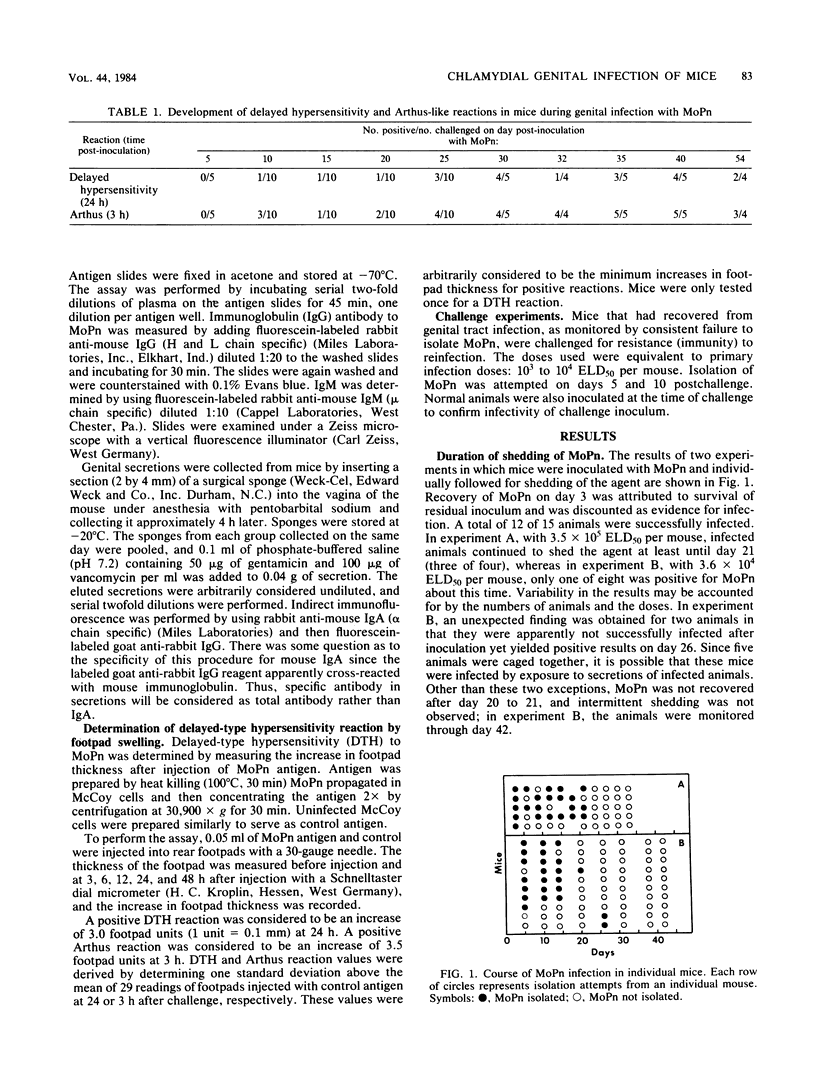
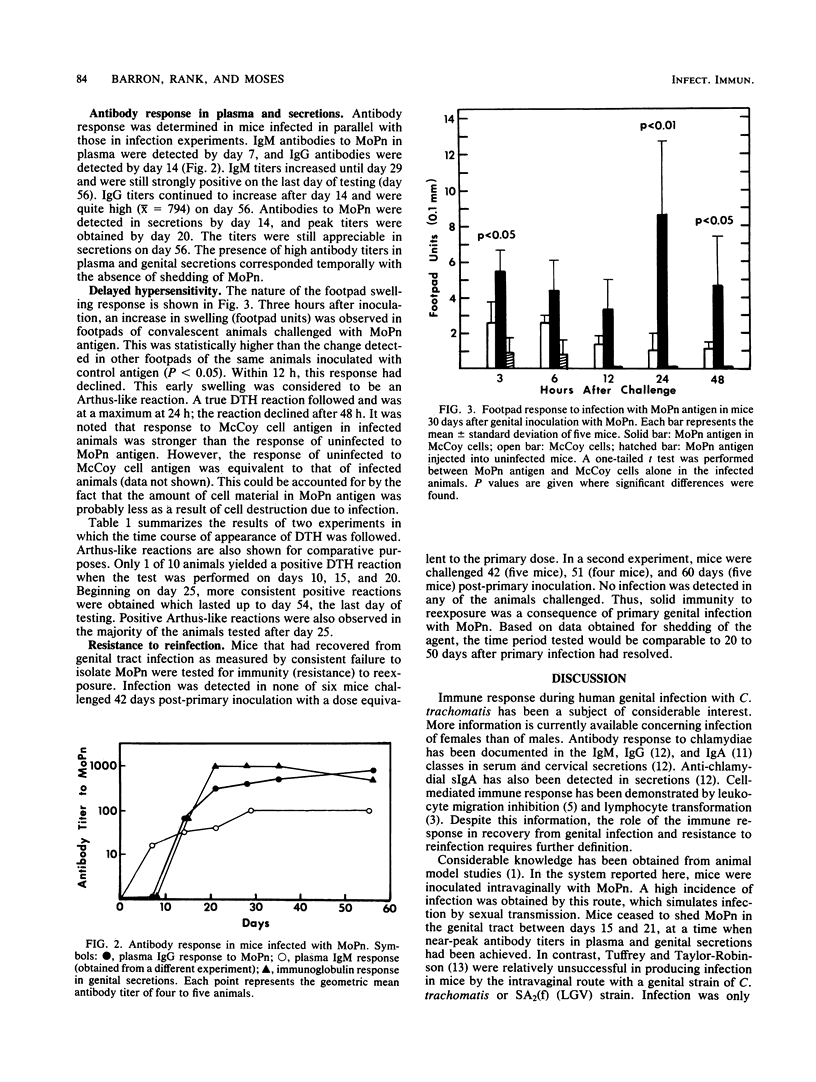
Female Swiss-Webster mice were inoculated intravaginally with mouse pneumonitis agent (MoPn), a Chlamydia trachomatis biovar. Inoculation with 3.5 X 10(5) egg lethal doses per mouse resulted in shedding of the agent from the genital tract for as long as 21 days. Immunoglobulin M antibodies to MoPn were detected in plasma by day 7 post-inoculation, and immunoglobulin G antibodies were detected by day 14. Antibodies were detected in genital secretions by day 20, and titers in plasma and secretions were still considerable on day 56. Delayed-type hypersensitivity tests, determined by footpad swelling, were not positive in appreciable numbers of animals until after day 25. Delayed-type hypersensitivity reactions were maximal 24 h after testing and were preceded by an Arthus-like reaction, which appeared within 3 h and declined by 12 h. Convalescent animals were rechallenged by intravaginal inoculation and were found to be solidly immune.
Full text
PDF

Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Barron A. L., White H. J., Rank R. G., Soloff B. L., Moses E. B. A new animal model for the study of Chlamydia trachomatis genital infections: infection of mice with the agent of mouse pneumonitis. J Infect Dis. 1981 Jan;143(1):63–66. doi: 10.1093/infdis/143.1.63. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Brunham R. C., Martin D. H., Kuo C. C., Wang S. P., Stevens C. E., Hubbard T., Holmes K. K. Cellular immune response during uncomplicated genital infection with Chlamydia trachomatis in humans. Infect Immun. 1981 Oct;34(1):98–104. doi: 10.1128/iai.34.1.98-104.1981. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Evans R. T., Taylor-Robinson D. Comparison of various McCoy cell treatment procedures used for detection of Chlamydia trachomatis. J Clin Microbiol. 1979 Aug;10(2):198–201. doi: 10.1128/jcm.10.2.198-201.1979. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hanna L., Kerlan R., Senyk G., Stites D. P., Juster R. P., Jawetz E. Immune responses to chlamydial antigens in humans. Med Microbiol Immunol. 1982;171(1):1–10. doi: 10.1007/BF02122702. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Harrison H. R., Lee S. M., Lucas D. O. Chlamydia trachomatis pneumonitis in the C57BL/KsJ mouse: pathologic and immunologic features. J Lab Clin Med. 1982 Dec;100(6):953–962. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kramer M. J., Cleeland R., Grunberg E. Activity of oral amoxicillin, ampicillin, and oxytetracycline against infection with chlamydia trachomatis in mice. J Infect Dis. 1979 Jun;139(6):717–719. doi: 10.1093/infdis/139.6.717. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kuo C., Chen W. J. A mouse model of Chlamydia trachomatis pneumonitis. J Infect Dis. 1980 Feb;141(2):198–202. doi: 10.1093/infdis/141.2.198. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Richmond S. J., Milne J. D., Hilton A. L., Caul E. O. Antibodies to Chlamydia trachomatis in cervicovaginal secretions: relation to serum antibodies and current chlamydial infection. Sex Transm Dis. 1980 Jan-Mar;7(1):11–15. doi: 10.1097/00007435-198001000-00003. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Schachter J., Cles L., Ray R., Hines P. A. Failure of serology in diagnosing chlamydial infections of the female genital tract. J Clin Microbiol. 1979 Nov;10(5):647–649. doi: 10.1128/jcm.10.5.647-649.1979. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Williams D. M., Schachter J., Drutz D. J., Sumaya C. V. Pneumonia due to Chlamydia trachomatis in the immunocompromised (nude) mouse. J Infect Dis. 1981 Feb;143(2):238–241. doi: 10.1093/infdis/143.2.238. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Williams D. M., Schachter J., Grubbs B., Sumaya C. V. The role of antibody in host defense against the agent of mouse pneumonitis. J Infect Dis. 1982 Feb;145(2):200–205. doi: 10.1093/infdis/145.2.200. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]


