Abstract
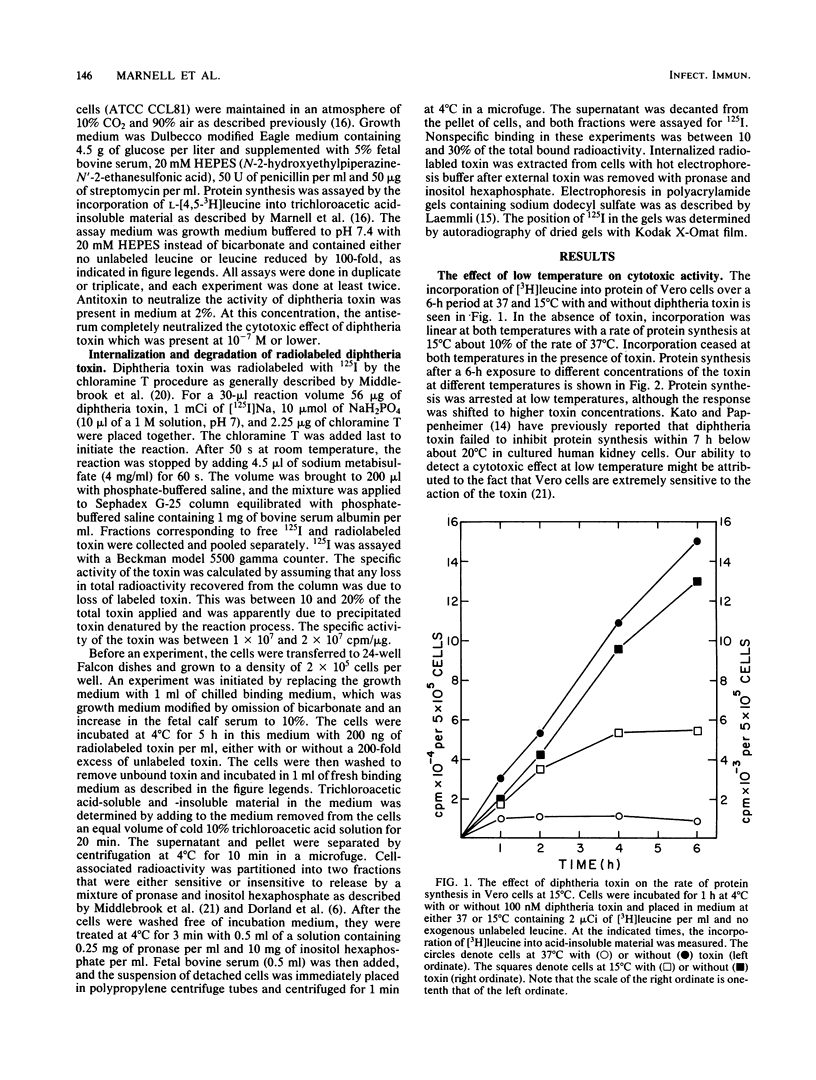
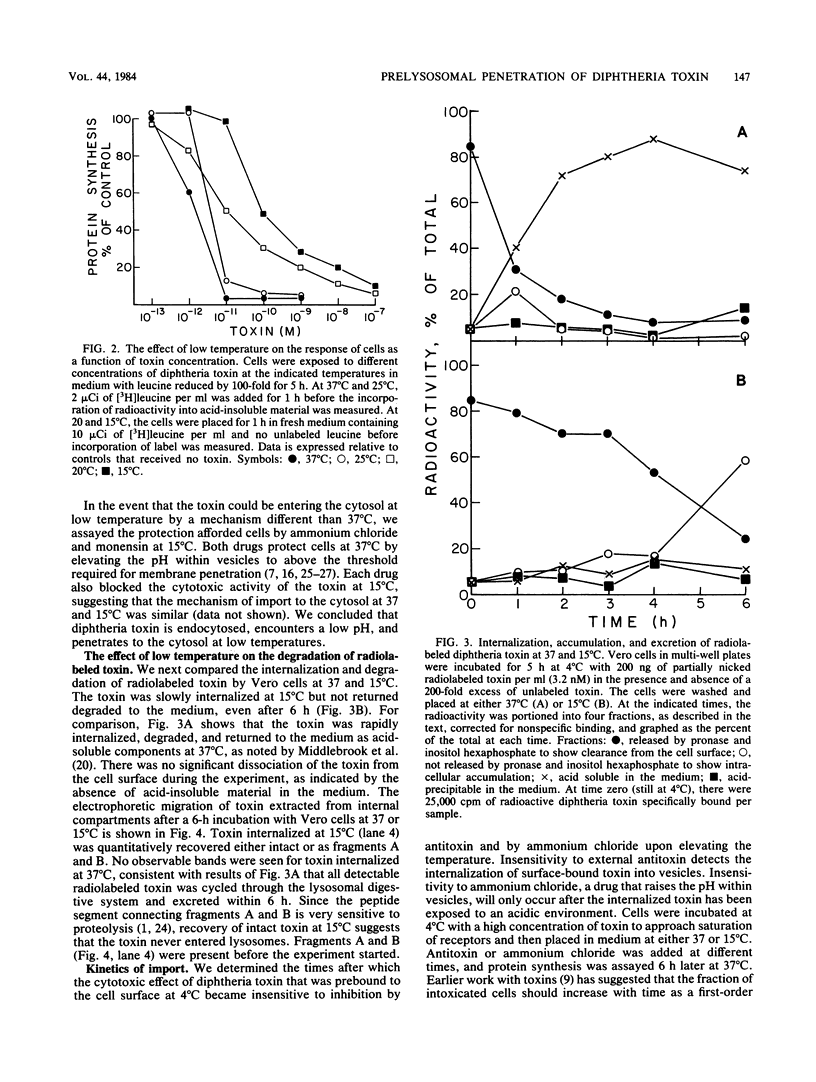
To kill mammalian cells, diphtheria toxin must be endocytosed and encounter a low pH within intracellular vesicles. The low pH initiates penetration of the catalytically active A fragment of the toxin through a membrane and into the cytosol where the A fragment arrests protein synthesis. To investigate whether penetration occurred through a prelysosomal or a lysosomal membrane, we studied the effect of low temperature on the entry of the toxin into the cytosolic and lysosomal compartments. The toxin arrested protein synthesis at 15 degrees C, indicating entry into the cytosol; however, access to lysosomes was apparently blocked at 15 degrees C, suggesting that the toxin had encountered a low pH before reaching lysosomes and had penetrated a prelysosomal membrane. To further investigate the possibility of prelysosomal acidification, we measured the time required for the toxin to encounter a low pH after endocytosis. Acidification occurred within 3 to 4 min after the toxin was internalized into vesicles. This interval is consistent with prelysosomal acidification since the entry of endocytosed ligands into secondary lysosomes usually takes more than 3 to 4 min.
Full text
PDF



Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Collier R. J. Diphtheria toxin: mode of action and structure. Bacteriol Rev. 1975 Mar;39(1):54–85. doi: 10.1128/br.39.1.54-85.1975. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Collier R. J., Kandel J. Structure and activity of diphtheria toxin. I. Thiol-dependent dissociation of a fraction of toxin into enzymically active and inactive fragments. J Biol Chem. 1971 Mar 10;246(5):1496–1503. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Didsbury J. R., Moehring J. M., Moehring T. J. Binding and uptake of diphtheria toxin by toxin-resistant Chinese hamster ovary and mouse cells. Mol Cell Biol. 1983 Jul;3(7):1283–1294. doi: 10.1128/mcb.3.7.1283. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Donovan J. J., Simon M. I., Draper R. K., Montal M. Diphtheria toxin forms transmembrane channels in planar lipid bilayers. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1981 Jan;78(1):172–176. doi: 10.1073/pnas.78.1.172. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Donovan J. J., Simon M. I., Montal M. Insertion of diphtheria toxin into and across membranes: role of phosphoinositide asymmetry. Nature. 1982 Aug 12;298(5875):669–672. doi: 10.1038/298669a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Dorland R. B., Middlebrook J. L., Leppla S. H. Receptor-mediated internalization and degradation of diphtheria toxin by monkey kidney cells. J Biol Chem. 1979 Nov 25;254(22):11337–11342. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Draper R. K., Simon M. I. The entry of diphtheria toxin into the mammalian cell cytoplasm: evidence for lysosomal involvement. J Cell Biol. 1980 Dec;87(3 Pt 1):849–854. doi: 10.1083/jcb.87.3.849. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Dunn W. A., Hubbard A. L., Aronson N. N., Jr Low temperature selectively inhibits fusion between pinocytic vesicles and lysosomes during heterophagy of 125I-asialofetuin by the perfused rat liver. J Biol Chem. 1980 Jun 25;255(12):5971–5978. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Eiklid K., Olsnes S., Pihl A. Entry of lethal doses of abrin, ricin and modeccin into the cytosol of HeLa cells. Exp Cell Res. 1980 Apr;126(2):321–326. doi: 10.1016/0014-4827(80)90270-0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Galloway C. J., Dean G. E., Marsh M., Rudnick G., Mellman I. Acidification of macrophage and fibroblast endocytic vesicles in vitro. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1983 Jun;80(11):3334–3338. doi: 10.1073/pnas.80.11.3334. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Helenius A., Kartenbeck J., Simons K., Fries E. On the entry of Semliki forest virus into BHK-21 cells. J Cell Biol. 1980 Feb;84(2):404–420. doi: 10.1083/jcb.84.2.404. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- KATO I., PAPPENHEIMER A. M., Jr An early effect of diphtheria toxin on the metabolism of mammalian cells growing in culture. J Exp Med. 1960 Aug 1;112:329–349. doi: 10.1084/jem.112.2.329. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kagan B. L., Finkelstein A., Colombini M. Diphtheria toxin fragment forms large pores in phospholipid bilayer membranes. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1981 Aug;78(8):4950–4954. doi: 10.1073/pnas.78.8.4950. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Laemmli U. K. Cleavage of structural proteins during the assembly of the head of bacteriophage T4. Nature. 1970 Aug 15;227(5259):680–685. doi: 10.1038/227680a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Marnell M. H., Stookey M., Draper R. K. Monensin blocks the transport of diphtheria toxin to the cell cytoplasm. J Cell Biol. 1982 Apr;93(1):57–62. doi: 10.1083/jcb.93.1.57. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Marsh M., Bolzau E., Helenius A. Penetration of Semliki Forest virus from acidic prelysosomal vacuoles. Cell. 1983 Mar;32(3):931–940. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(83)90078-8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Maxfield F. R. Weak bases and ionophores rapidly and reversibly raise the pH of endocytic vesicles in cultured mouse fibroblasts. J Cell Biol. 1982 Nov;95(2 Pt 1):676–681. doi: 10.1083/jcb.95.2.676. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Merion M., Schlesinger P., Brooks R. M., Moehring J. M., Moehring T. J., Sly W. S. Defective acidification of endosomes in Chinese hamster ovary cell mutants "cross-resistant" to toxins and viruses. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1983 Sep;80(17):5315–5319. doi: 10.1073/pnas.80.17.5315. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Middlebrook J. L., Dorland R. B., Leppla S. H. Association of diphtheria toxin with Vero cells. Demonstration of a receptor. J Biol Chem. 1978 Oct 25;253(20):7325–7330. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Middlebrook J. L., Dorland R. B., Leppla S. H. Effects of lectins on the interaction of diphtheria toxin with mammalian cells. Exp Cell Res. 1979 Jun;121(1):95–101. doi: 10.1016/0014-4827(79)90448-8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Moynihan M. R., Pappenheimer A. M., Jr Kinetics of adenosinediphosphoribosylation of elongation factor 2 in cells exposed to diphtheria toxin. Infect Immun. 1981 May;32(2):575–582. doi: 10.1128/iai.32.2.575-582.1981. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ohkuma S., Poole B. Fluorescence probe measurement of the intralysosomal pH in living cells and the perturbation of pH by various agents. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1978 Jul;75(7):3327–3331. doi: 10.1073/pnas.75.7.3327. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Pappenheimer A. M., Jr Diphtheria toxin. Annu Rev Biochem. 1977;46:69–94. doi: 10.1146/annurev.bi.46.070177.000441. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- STRAUSS N., HENDEE E. D. The effect of diphtheria toxin on the metabolism of HeLa cells. J Exp Med. 1959 Feb 1;109(2):145–163. doi: 10.1084/jem.109.2.145. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sandvig K., Olsnes S. Diphtheria toxin entry into cells is facilitated by low pH. J Cell Biol. 1980 Dec;87(3 Pt 1):828–832. doi: 10.1083/jcb.87.3.828. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sandvig K., Olsnes S. Entry of the toxic proteins abrin, modeccin, ricin, and diphtheria toxin into cells. II. Effect of pH, metabolic inhibitors, and ionophores and evidence for toxin penetration from endocytotic vesicles. J Biol Chem. 1982 Jul 10;257(13):7504–7513. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sandvig K., Olsnes S. Rapid entry of nicked diphtheria toxin into cells at low pH. Characterization of the entry process and effects of low pH on the toxin molecule. J Biol Chem. 1981 Sep 10;256(17):9068–9076. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Steinman R. M., Mellman I. S., Muller W. A., Cohn Z. A. Endocytosis and the recycling of plasma membrane. J Cell Biol. 1983 Jan;96(1):1–27. doi: 10.1083/jcb.96.1.1. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Tycko B., Maxfield F. R. Rapid acidification of endocytic vesicles containing alpha 2-macroglobulin. Cell. 1982 Mar;28(3):643–651. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(82)90219-7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- van Renswoude J., Bridges K. R., Harford J. B., Klausner R. D. Receptor-mediated endocytosis of transferrin and the uptake of fe in K562 cells: identification of a nonlysosomal acidic compartment. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1982 Oct;79(20):6186–6190. doi: 10.1073/pnas.79.20.6186. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]


